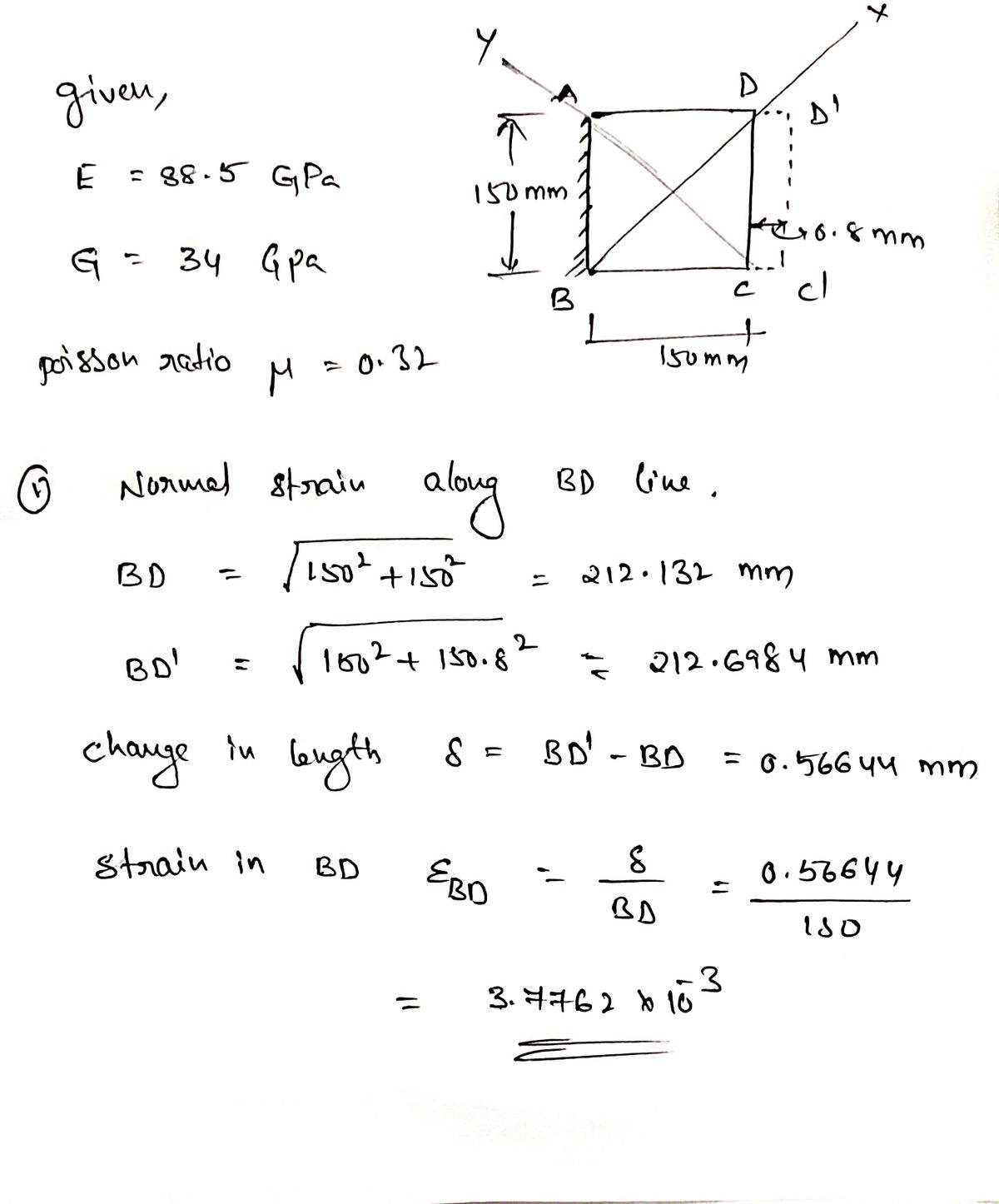
1. The plate below is attached to the vertical surface AB. Its top and bottom surfaces slide smoothly along the horizontal surfaces AD and BC, but are prevented from moving vertically. The plate can move freely in the z- direction (perpendicular to the page). The right side of the plate is uniformly pulled such that it displaces 0.8 mm to the right. The plate is aluminum, which has the following material properties: 150 nim Modulus of Elasticity = 88.5 GPa 150 mum HFo.Bmm Modulus of Rigidity = 34 GPa Poisson Ratio = 0.32
1. The plate below is attached to the vertical surface AB. Its top and bottom surfaces slide smoothly along the horizontal surfaces AD and BC, but are prevented from moving vertically. The plate can move freely in the z- direction (perpendicular to the page). The right side of the plate is uniformly pulled such that it displaces 0.8 mm to the right. The plate is aluminum, which has the following material properties: 150 nim Modulus of Elasticity = 88.5 GPa 150 mum HFo.Bmm Modulus of Rigidity = 34 GPa Poisson Ratio = 0.32
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:1. The plate below is attached to the vertical surface AB. Its
top and bottom surfaces slide smoothly along the
horizontal surfaces AD and BC, but are prevented from
moving vertically. The plate can move freely in the z-
direction (perpendicular to the page). The right side of the
plate is uniformly pulled such that it displaces 0.8 mm to
the right. The plate is aluminum, which has the following
material properties:
150 nim
BERA
Modulus of Elasticity = 88.5 GPa
%3D
150 num
F0.8mm
Modulus of Rigidity 34 GPa
%3D
Poisson Ratio = 0.32

Transcribed Image Text:С.
Determine the normal strain along line BD.
d. Determine the normal stress in the x and y directions. Note that the stain along AC is equal to the
strain along BD. Assume the temperature remains constant. (If you are unable to solve part c, use
normal strain = 0.0025 mm/mm for AC and BD.)
Expert Solution
Step 1
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780073398006
Author:
Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning