1. Predict the ¹H NMR spectrum for compounds (b)-(f) below. Add in the missing hydrogens ● ● ● Determine the number of ¹H NMR signals in each compound below. Label each type of proton (A, B, etc.) and fill in the tables provided on the following page with a row for each type of proton (signal). Predict the integration (#H's), the chemical shift range (ppm), and calculated chemical shift (ppm), that you would expect for each signal. Determine the splitting pattern for each signal using the n+1 rule, where n is the number of H's on adjacent carbon atoms. O ● · . Sketch the predicted 'H NMR spectrum of each compound and use nmrdb.org to check your work Approximate the central chemical shift of the signal on the x-axis and draw each splitting pattern. Don't worry about incorporating integration (peak size). (a) Br (c) Splitting patterns: singlet, doublet, triplet, quartet, pentet, sextet, heptet, or multiplet. There is no splitting through heteroatoms (O, N, S, etc.) - all OH's are singlets! Br (e) (b) OH (d) -OH
1. Predict the ¹H NMR spectrum for compounds (b)-(f) below. Add in the missing hydrogens ● ● ● Determine the number of ¹H NMR signals in each compound below. Label each type of proton (A, B, etc.) and fill in the tables provided on the following page with a row for each type of proton (signal). Predict the integration (#H's), the chemical shift range (ppm), and calculated chemical shift (ppm), that you would expect for each signal. Determine the splitting pattern for each signal using the n+1 rule, where n is the number of H's on adjacent carbon atoms. O ● · . Sketch the predicted 'H NMR spectrum of each compound and use nmrdb.org to check your work Approximate the central chemical shift of the signal on the x-axis and draw each splitting pattern. Don't worry about incorporating integration (peak size). (a) Br (c) Splitting patterns: singlet, doublet, triplet, quartet, pentet, sextet, heptet, or multiplet. There is no splitting through heteroatoms (O, N, S, etc.) - all OH's are singlets! Br (e) (b) OH (d) -OH
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
please do a, b, and c!

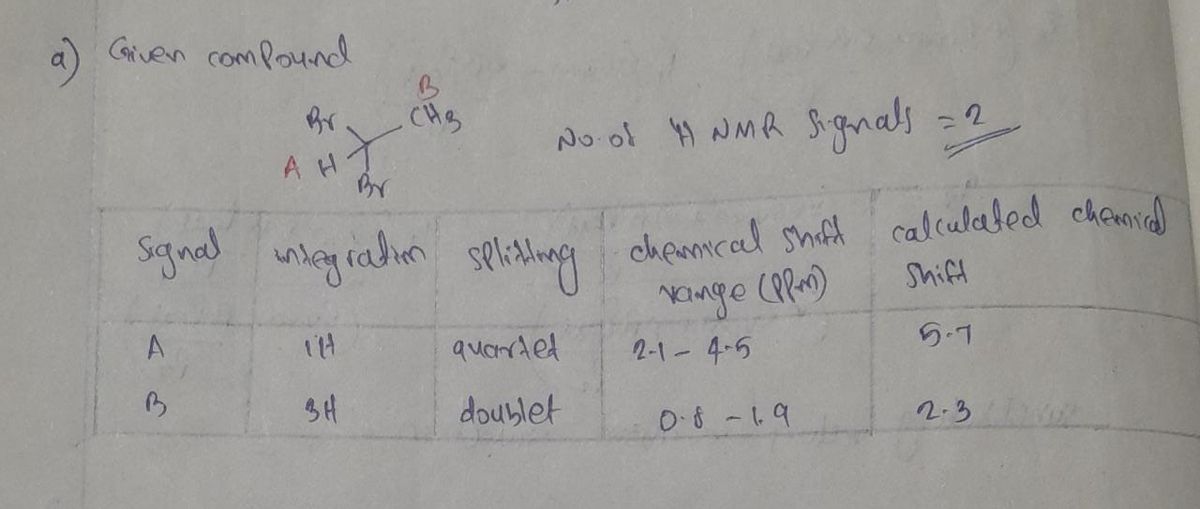
Transcribed Image Text:1. Predict the ¹H NMR spectrum for compounds (b) - (f) below.
Add in the missing hydrogens
Determine the number of ¹H NMR signals in each compound below.
Label each type of proton (A, B, etc.) and fill in the tables provided on the following page with a row for
each type of proton (signal).
Predict the integration (#H's), the chemical shift range (ppm), and calculated chemical shift (ppm),
that you would expect for each signal.
Determine the splitting pattern for each signal using the n+1 rule, where n is the number of H's
on adjacent carbon atoms.
O
Splitting patterns: singlet, doublet, triplet, quartet, pentet, sextet, heptet, or multiplet.
There is no splitting through heteroatoms (O, N, S, etc.) - all OH's are singlets!
Sketch the predicted ¹H NMR spectrum of each compound and use nmrdb.org to check your work
Approximate the central chemical shift of the signal on the x-axis and draw each splitting pattern.
Don't worry about incorporating integration (peak size).
(c)
(a) Br
■
.
Br
(e)
(b)
OH
O
(d)
-OH
Expert Solution
Step 1
 l
l
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY