Reactions of Ethers
Ethers (R-O-R’) are compounds formed by replacing hydrogen atoms of an alcohol (R-OH compound) or a phenol (C6H5OH) by an aryl/ acyl group (functional group after removing single hydrogen from an aromatic ring). In this section, reaction, preparation and behavior of ethers are discussed in the context of organic chemistry.
Epoxides
Epoxides are a special class of cyclic ethers which are an important functional group in organic chemistry and generate reactive centers due to their unusual high reactivity. Due to their high reactivity, epoxides are considered to be toxic and mutagenic.
Williamson Ether Synthesis
An organic reaction in which an organohalide and a deprotonated alcohol forms ether is known as Williamson ether synthesis. Alexander Williamson developed the Williamson ether synthesis in 1850. The formation of ether in this synthesis is an SN2 reaction.
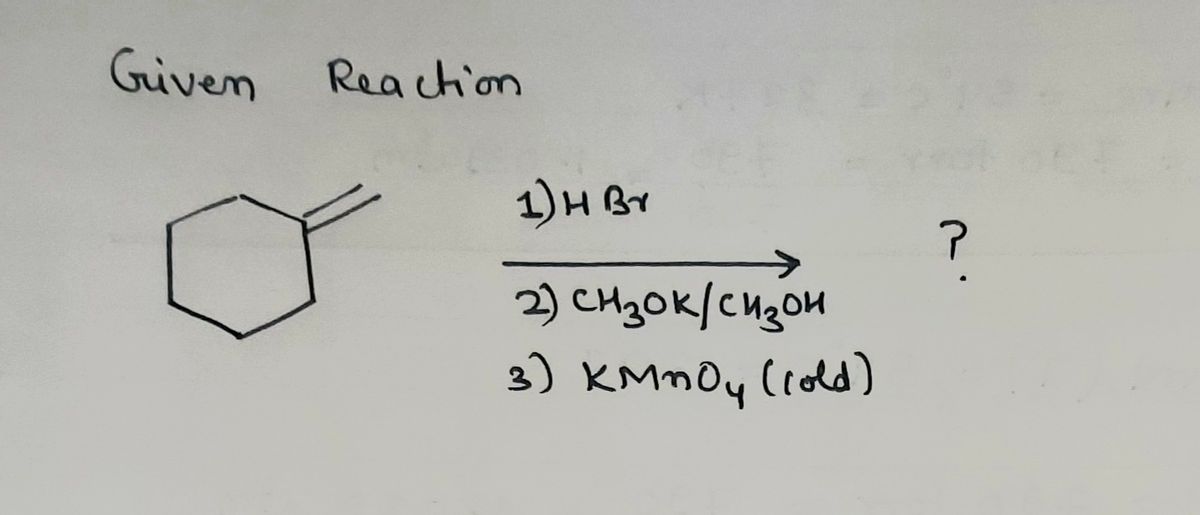
Please find the major products include stereochemistry if relevant. State if there are enantiomers.
Thanks!

Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









