1 When A is invertible, MATLAB finds A by factoring LU (where L may be permuted lower triangular), inverting L and U, and then computing U¹L1. Use this method to compute the inverse of the given matrix A. 2 -6 2 A = - 10 28 - 6 0-2 2 Compute U¹ and L¯1. U-1 L-1 : = " where A = 100 - 5 10 0 1 1 2-6 - 2 O 0 N 4 0 -2
1 When A is invertible, MATLAB finds A by factoring LU (where L may be permuted lower triangular), inverting L and U, and then computing U¹L1. Use this method to compute the inverse of the given matrix A. 2 -6 2 A = - 10 28 - 6 0-2 2 Compute U¹ and L¯1. U-1 L-1 : = " where A = 100 - 5 10 0 1 1 2-6 - 2 O 0 N 4 0 -2
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Erwin Kreyszig
Chapter2: Second-order Linear Odes
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ
Related questions
Question
Hello there, can you help me solve a problem with subparts? Thanks!

Transcribed Image Text:Compute \( A^{-1} \).
\( A^{-1} = \boxed{\phantom{0}} \)
![**LU Factorization and Matrix Inversion Method**
When A is invertible, MATLAB finds \( A^{-1} \) by factoring LU (where L may be permuted lower triangular), inverting L and U, and then computing \( U^{-1} L^{-1} \). Use this method to compute the inverse of the given matrix A.
Matrix \( A \) is given by:
\[
A =
\begin{bmatrix}
2 & -6 & 2 \\
-10 & 28 & -6 \\
0 & -2 & 2
\end{bmatrix}
\]
This is expressed as a product of matrices:
\[
A =
\begin{bmatrix}
1 & 0 & 0 \\
-5 & 1 & 0 \\
0 & 1 & 1
\end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix}
2 & -6 & 2 \\
0 & -2 & 4 \\
0 & 0 & -2
\end{bmatrix}
\]
**Task:**
Compute \( U^{-1} \) and \( L^{-1} \).
- \( U^{-1} = \boxed{} \)
- \( L^{-1} = \boxed{} \)
**Explanation:**
The above matrices demonstrate LU decomposition where:
- L is a lower triangular matrix.
- U is an upper triangular matrix.
To find the inverse of matrix A, calculate the inverses of L and U separately and then multiply \( U^{-1} \) by \( L^{-1} \).](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fe00cebfb-aec4-474d-8979-79a2d105b819%2F80417d50-a2d5-4803-a33a-ea7af81176d1%2Fbblh3fx_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:**LU Factorization and Matrix Inversion Method**
When A is invertible, MATLAB finds \( A^{-1} \) by factoring LU (where L may be permuted lower triangular), inverting L and U, and then computing \( U^{-1} L^{-1} \). Use this method to compute the inverse of the given matrix A.
Matrix \( A \) is given by:
\[
A =
\begin{bmatrix}
2 & -6 & 2 \\
-10 & 28 & -6 \\
0 & -2 & 2
\end{bmatrix}
\]
This is expressed as a product of matrices:
\[
A =
\begin{bmatrix}
1 & 0 & 0 \\
-5 & 1 & 0 \\
0 & 1 & 1
\end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix}
2 & -6 & 2 \\
0 & -2 & 4 \\
0 & 0 & -2
\end{bmatrix}
\]
**Task:**
Compute \( U^{-1} \) and \( L^{-1} \).
- \( U^{-1} = \boxed{} \)
- \( L^{-1} = \boxed{} \)
**Explanation:**
The above matrices demonstrate LU decomposition where:
- L is a lower triangular matrix.
- U is an upper triangular matrix.
To find the inverse of matrix A, calculate the inverses of L and U separately and then multiply \( U^{-1} \) by \( L^{-1} \).
Expert Solution
Step 1: Explanation
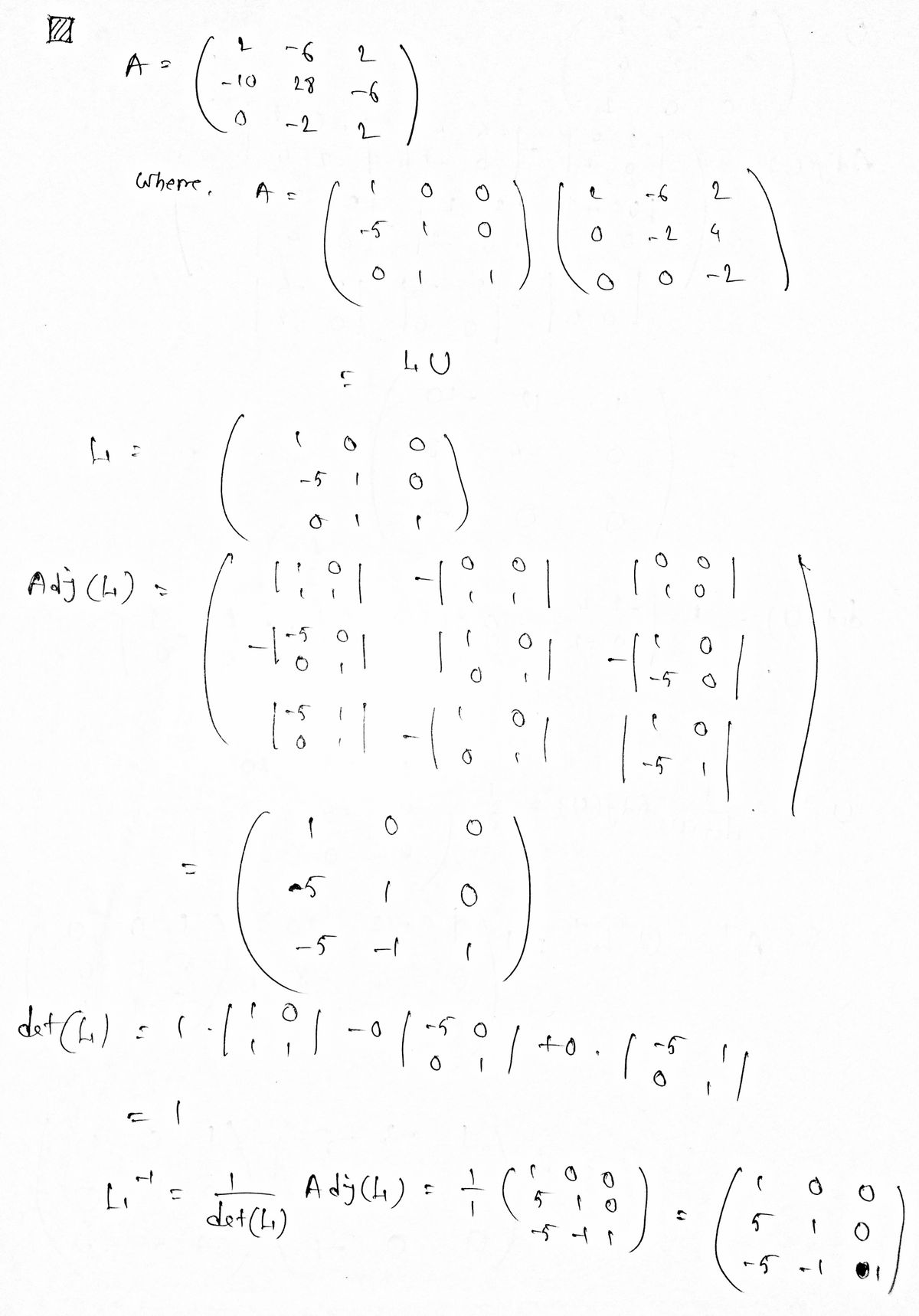
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780470458365
Author:
Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:
Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9780073397924
Author:
Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat…
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781118141809
Author:
Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:
WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:
9781337798310
Author:
Peterson, John.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

