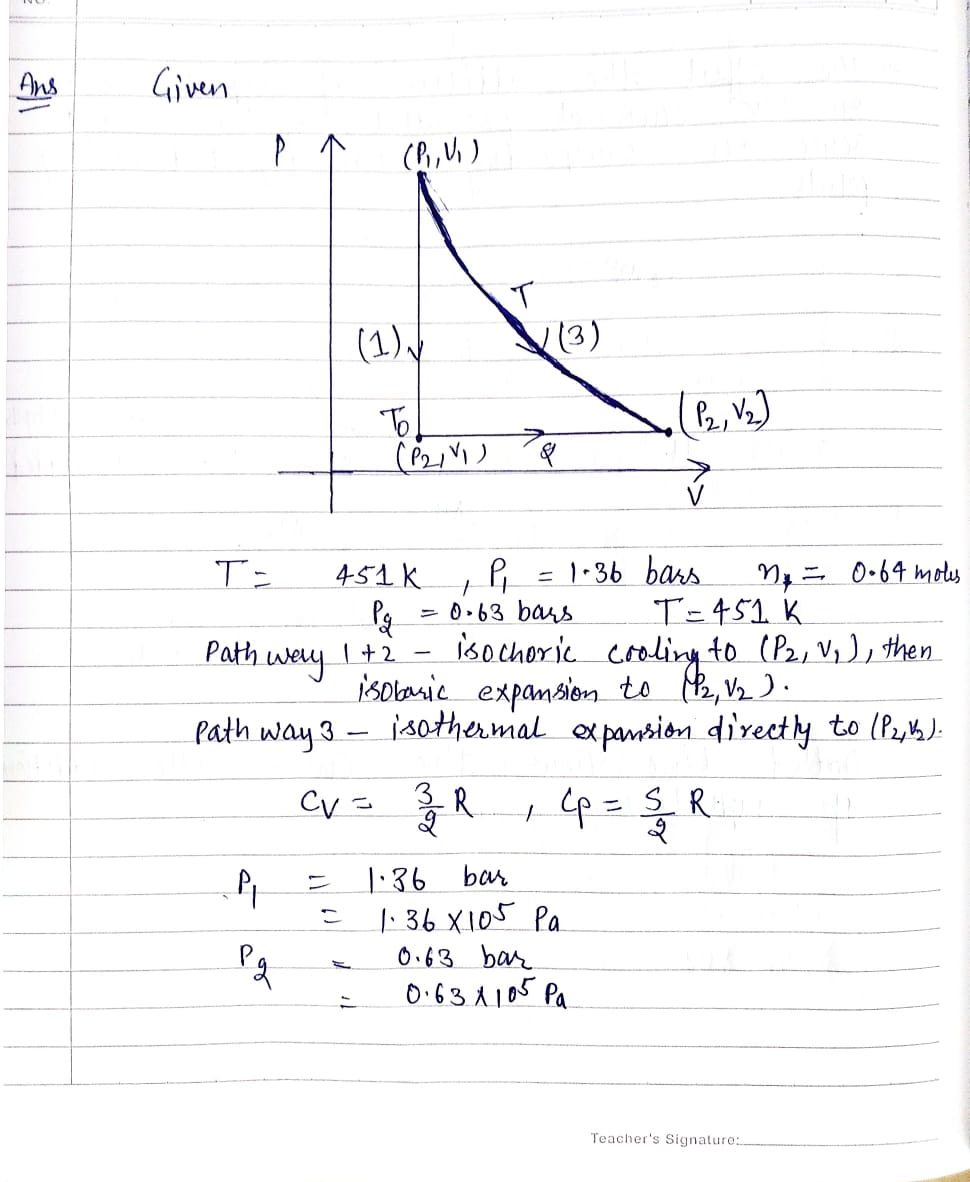
0.64 moles of an ideal gas undergoes a couple of change processes that move the system from (P₁, V₁) to (P2, V₂) as shown on the diagram below. Both points share the same temperature, T = 451 K, and P₁ = 1.36 bars, P₂ = 0.63 bars. The two pathways are defined as Pathway 1 + 2- isochoric cooling to (P2, V₁), then isobaric expansion to (P2, V₂). Pathway 3- isothermal expansion directly to (P2, V₂). 3 For the purposes of this problem, you may assume that C₁ = ³R and Cp = R. 2 P↑ (P₁,V₁) To (P₂, V₁) T (3) (2) (P₂, V₂) V a) Find the volumes V₁ and V₂ and compute AV (in L) for the net process. (b) For each of the three paths drawn, calculate AU, AH, and AS. Report the first two in units of kJ, and the last in units of J/K. (c) Since Gibbs energy is a state function, AG is the same for both pathways. Evaluate it for the net process and report it in units of kJ. Note: The temperature at the point (P2, V₁) is different from that of the isotherm, and has been labeled To. You may need to define this temperature in your calculations. Also, for part (c) the absolute entropy content at that same point can be assumed to be 200 J/K.
Thermochemistry
Thermochemistry can be considered as a branch of thermodynamics that deals with the connections between warmth, work, and various types of energy, formed because of different synthetic and actual cycles. Thermochemistry describes the energy changes that occur as a result of reactions or chemical changes in a substance.
Exergonic Reaction
The term exergonic is derived from the Greek word in which ‘ergon’ means work and exergonic means ‘work outside’. Exergonic reactions releases work energy. Exergonic reactions are different from exothermic reactions, the one that releases only heat energy during the course of the reaction. So, exothermic reaction is one type of exergonic reaction. Exergonic reaction releases work energy in different forms like heat, light or sound. For example, a glow stick releases light making that an exergonic reaction and not an exothermic reaction since no heat is released. Even endothermic reactions at very high temperature are exergonic.

Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 6 images









