
Concept explainers
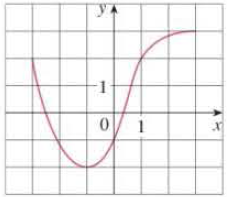
FIGURE FOR PROBLEM 1
1. The graph of a function f is given at the left
- (a) State the value of f(−1)
- (b) Estimate the value of f(2)
- (c) For what values of x is f(x) = 2?
- (d) Estimate the values of x such that f(x) = 0.
- (e) State the domain and range of f.
(a)
To state: The value of
Answer to Problem 1CDT
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Spot the point
To find the value of
Now the intersecting point of the graph of the function and the line
From the figure, it is clear that the value of
Thus, the value of
(b)
To estimate: The value of
Answer to Problem 1CDT
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Spot the point
To find the value of
Now the intersecting point of the graph of the function and the line
From the figure, it is clear that the value of
Thus, the value of
(c)
To find: The value of x such that
Answer to Problem 1CDT
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Spot the point
To find the value of
Now the x-coordinate of the intersecting point of the graph of the function and the line
From the figure, it is clear that the value of
Thus, the value of
(d)
To estimate: The value of x such that
Answer to Problem 1CDT
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Spot the point
To find the value of
Now the x-coordinate of the intersecting point of the graph of the function and the line
From the figure, it is clear that the value of
Thus, the value of
(e)
To state: The domain and range of the function
Explanation of Solution
The set of all possible values of the independent variables in a function is called the domain of the function.
From the figure, it is clear that the function
Thus, the domain of the function
The resulting set of possible values of the dependent variable is called the range.
From the figure, it is clear that the function
Thus, the range of the function
Chapter T Solutions
Bundle: Single Variable Calculus: Concepts And Contexts, Enhanced Edition, 4th + Webassign Printed Access Card For Stewart's Calculus: Concepts And Contexts, Multi-term
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)
Precalculus
Elementary Statistics Using The Ti-83/84 Plus Calculator, Books A La Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- Can you help explain what I did based on partial fractions decomposition?arrow_forwardSuppose that a particle moves along a straight line with velocity v (t) = 62t, where 0 < t <3 (v(t) in meters per second, t in seconds). Find the displacement d (t) at time t and the displacement up to t = 3. d(t) ds = ["v (s) da = { The displacement up to t = 3 is d(3)- meters.arrow_forwardLet f (x) = x², a 3, and b = = 4. Answer exactly. a. Find the average value fave of f between a and b. fave b. Find a point c where f (c) = fave. Enter only one of the possible values for c. c=arrow_forward
- please do Q3arrow_forwardUse the properties of logarithms, given that In(2) = 0.6931 and In(3) = 1.0986, to approximate the logarithm. Use a calculator to confirm your approximations. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) (a) In(0.75) (b) In(24) (c) In(18) 1 (d) In ≈ 2 72arrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral. (Remember the constant of integration.) √tan(8x) tan(8x) sec²(8x) dxarrow_forward
- Find the indefinite integral by making a change of variables. (Remember the constant of integration.) √(x+4) 4)√6-x dxarrow_forwarda -> f(x) = f(x) = [x] show that whether f is continuous function or not(by using theorem) Muslim_mathsarrow_forwardUse Green's Theorem to evaluate F. dr, where F = (√+4y, 2x + √√) and C consists of the arc of the curve y = 4x - x² from (0,0) to (4,0) and the line segment from (4,0) to (0,0).arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





