
Concept explainers
Arrange the compounds of each of the following series in order of increasing acidity:
Interpretation:
The compounds of each of the given series are to be arranged in order of increasing acidity.
Concept introduction:
Acidity depends on the
Resonance structures are the structures in which two or more possible electron structures are drawn. In the resonance structure, the position of the atoms is the same but position of the electrons is different.
Resonance causes delocalization of electron pairs, which increases the stability of the base.
Answer to Problem 1P
Solution:
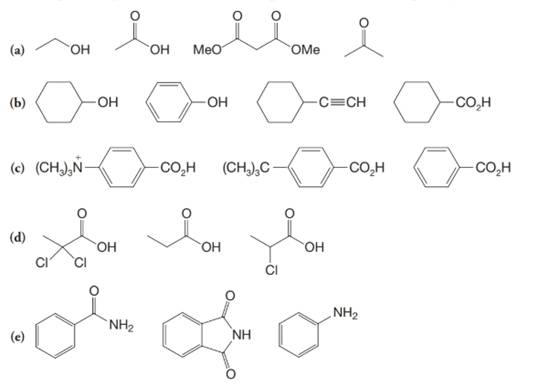
(a)
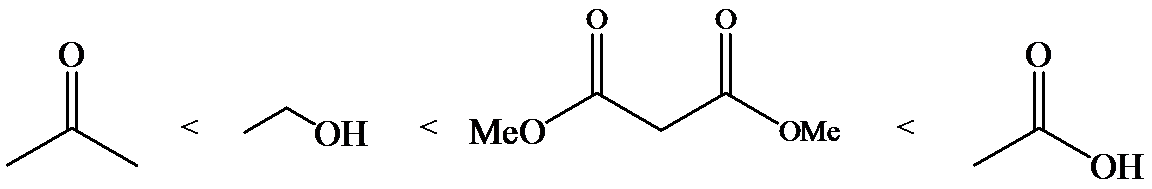
(b)
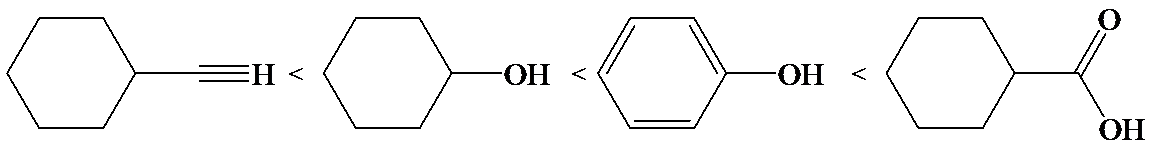
(c)

(d)
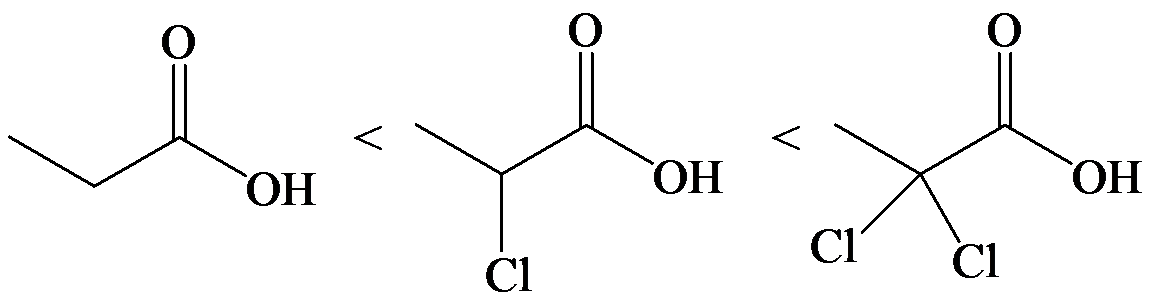
(e)
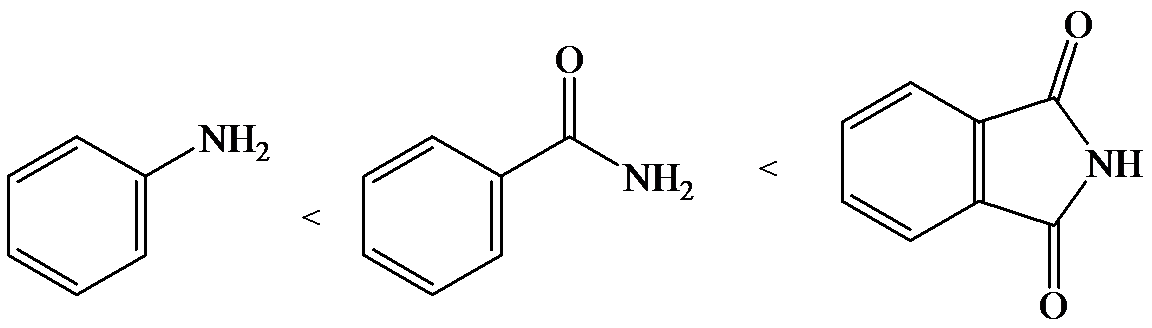
Explanation of Solution
a)
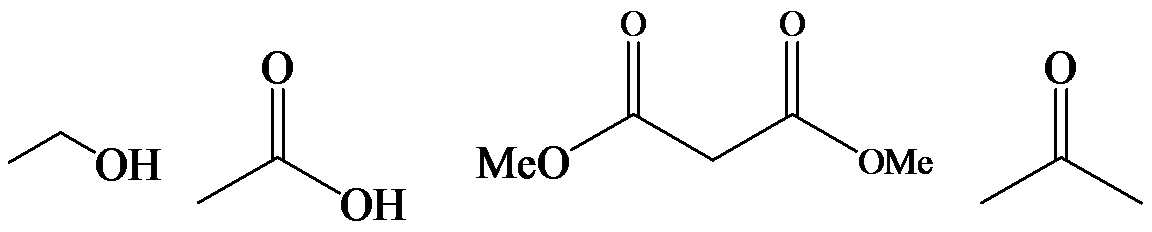
The α-hydrogen atoms of carbonyl groups are acidic. The acidity arises from the electron withdrawing effect of the carbonyl and resonance stabilization of its conjugate base. The electron donating effect of  groups tends to destabilize anions. In diketone, there is an active methylene, adjacent to two carbonyl groups. This indicates more resonance stabilization. The charge of anion can be delocalized to both oxygen atoms. The hydroxyl proton in carboxylic acid is an α-proton. On comparing the acidity of carboxylic acids and alcohols, alcohol is less acidic than carboxylic acid.
groups tends to destabilize anions. In diketone, there is an active methylene, adjacent to two carbonyl groups. This indicates more resonance stabilization. The charge of anion can be delocalized to both oxygen atoms. The hydroxyl proton in carboxylic acid is an α-proton. On comparing the acidity of carboxylic acids and alcohols, alcohol is less acidic than carboxylic acid.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:
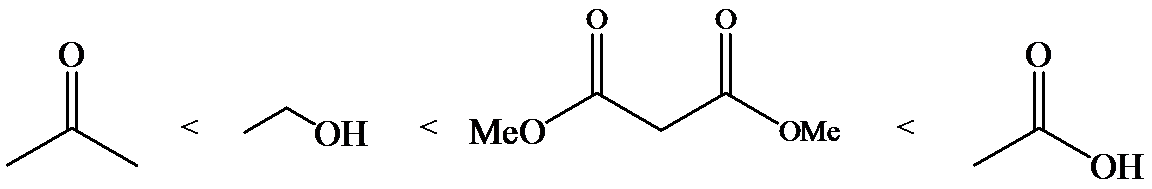
b)
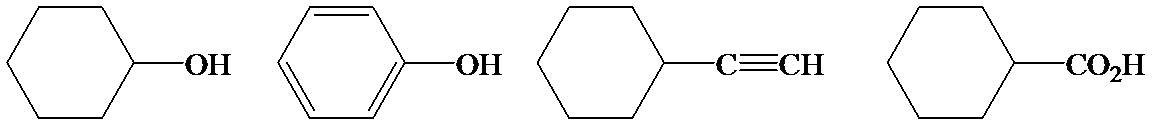
Phenol is more acidic than cyclohexanol because the resonance stabilization in both is different.
In the case of cyclohexane carboxylic acid, negative charge is shared between two different oxygen atoms making it more stabilized than phenoxide. Hence, the removal of proton from cyclohexane carboxylic acid is easier than phenol, making it more acidic than phenol.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:
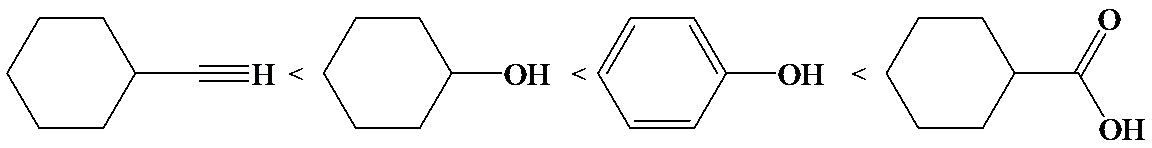
c)
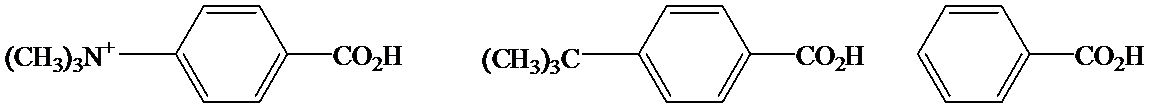
In the case of carboxylic acids, electron substituents increase acidity by inductive electron donation. The electron-donating tert-butyl group destabilizes the conjugate base of benzoic acid, making it less acidic.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:

d)
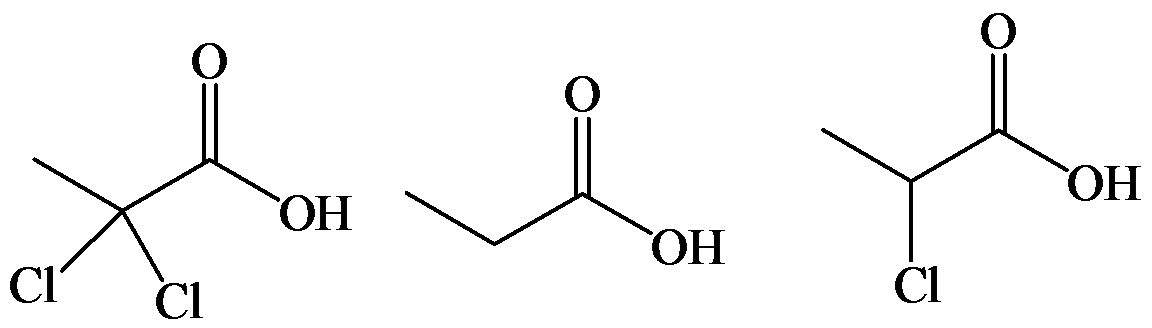
The electron-withdrawing chloro groups increase the acidity of carboxylic acid by increasing the stability of the carboxylate ion. Hence, the carboxylic acid with more chloro groups is more acidic.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:
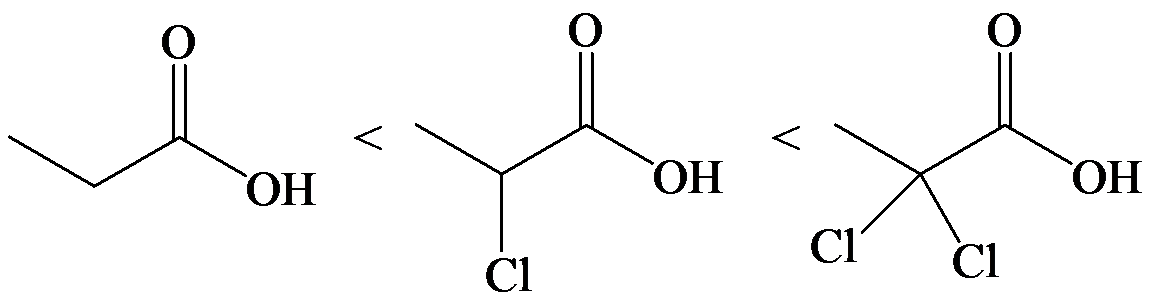
e)

The lone pair electron in aniline is localized on the nitrogen atom, whereas onbenzamide, it is delocalized between oxygen and nitrogen via resonance. Therefore, benzamide is more acidic than aniline.
So, the increasing order of the acidity is as follows:
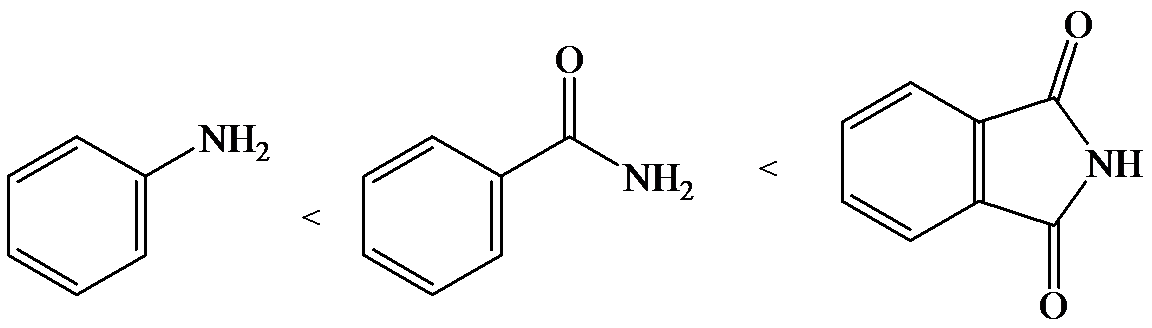
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter SRP Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-ETEXT REG ACCESS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning


