
1.
Indicate the method used to account for the investment in D common stock and F bonds, and explain.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Available-for-sale (AFS) securities: The category of passive investments which are held as idle funds to serve the future operating and strategic purposes, are referred to as available-for-sale securities. The percentage of passive investments in debt or equity will be less than 20%.
Fair value method: The method of accounting the investments in short-term debt, and short-term and long-term equity securities, with an ownership of less than 20% of the outstanding stock of the investee, is referred to as fair value method.
Method used to account investment in stock of Corporation D: Since the investor company, Company OG purchased 14.74%
Method used to account investment in bonds of Corporation F: Since the bonds are not intended to hold till maturity, they are considered as short-term, and hence, fair value method is used.
2.
a.
Journalize the purchase of investment in available-for-sale securities’ transaction in the years 2014 and 2015.
2.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in
stockholders’ equity accounts. - Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Prepare journal entry for purchase of investment in AFS.
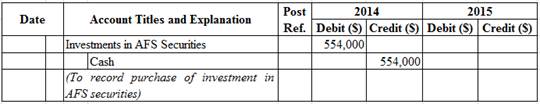
Table (1)
Note: No purchases were made in 2015.
Description:
- Investments in AFS Securities is an asset account. Since stock investments are purchased, asset value increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute cost of investment in AFS securities.
Step 1: Compute cost of investment in stock.
Step 2: Compute cost of investment in AFS securities.
Note: Refer to Equation (1) for value and computation of cost of investment in stock.
b.
Journalize the entry for income reported by investee companies for the years 2014 and 2015.
b.
Explanation of Solution
The income reported by Corporations D and F are not recorded by Company OG because the type of investment is passive, and not of significant influence. So, for the two years 2014 and 2015, Company OG will not record any entry for the net income of the investee.
c.
Journalize the entry for receipt of dividend and interest revenue for the years 2014 and 2015.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry for cash dividend received and interest received.
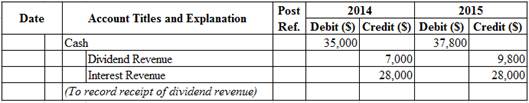
Table (2)
Description:
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Dividend Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
- Interest Revenue is a revenue account. Since revenues increase equity, equity value is increased, and an increase in equity is credited.
Working Notes:
Compute amount of dividend received in 2014.
Compute amount of dividend received in 2015.
d.
Journalize the
d.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry for adjusting the cost of AFS securities to the fair market value, as on December 31, 2014, and 2015.
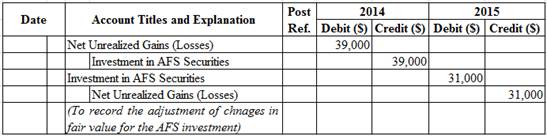
Table (3)
Description:
2014:
- Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) is an adjustment account used to report gain or loss on adjusting cost of investment at fair market value. Since loss has occurred and losses decrease stockholders’ equity value, a decrease in stockholders’ equity value is debited. This loss is reported as component of Other Comprehensive Income (OCI) on the Statement of Comprehensive Income.
- Investments in AFS Securities is an asset account. The account is credited because the market price was decreased, and eventually the asset value decreased.
2015:
- Investments in AFS Securities is an asset account. The account is debited because the market price was increased, and eventually the asset value increased.
- Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) is an adjustment account used to report gain or loss on adjusting cost of investment at fair market value. Since gain has occurred and gains increase stockholders’ equity value, an increase in stockholders’ equity value is credited. This gain is reported as component of Other Comprehensive Income (OCI) on the Statement of Comprehensive Income.
Working Notes:
Determine the unrealized gain or loss on investment on December 31, 2014.
Step 1: Compute the fair value of investment on December 31, 2014.
Step 2: Compute total fair value of investment in AFS securities on December 31, 2014.
Note: Refer to Equation (2) for value and computation of fair value of investment in stock.
Step 3: Compute unrealized gain or loss on investment in AFS securities.
Note: Refer to Equations (1) and (3) for both the values.
Determine the unrealized gain or loss on investment on December 31, 2015.
Step 1: Compute the fair value of investment on December 31, 2015.
Step 2: Compute total fair value of investment in AFS securities on December 31, 2015.
Note: Refer to Equation (2) for value and computation of fair value of investment in stock.
Step 3: Compute unrealized gain or loss on investment in AFS securities.
Note: Refer to Equations (3) and (5) for both the values.
3.
a.
Show the reporting of long-term assets related to AFS investments, on the
3.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Reporting of long-term assets on balance sheet:
| Company OG | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| December 31 | ||
| Assets: | 2014 | 2015 |
| Long-term assets: | ||
| Investment in Available-For-Sale-Securities | 515,000 | 546,000 |
Table (4)
b.
Show the reporting of net unrealized gains (losses) related to AFS investments, on the stockholders’ equity section of Company OG, on December 31, 2014 and 2015.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Reporting of net unrealized gains (losses) on statement of stockholders’ equity:
| Company OG | ||
| Statement of Stockholders’ Equity | ||
| December 31 | ||
| 2014 | 2015 | |
| Stockholders’ Equity: | ||
| Common Stock | XXX | |
| | XXX | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income: | ||
| Net unrealized gains (losses) | (39,000) | (8,000) |
Table (5)
c.
Show the revenue related to AFS investments, reported on the income statement of Company OG, for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2015.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement presentation:
| Company OG | ||
| Income Statement (Partial) | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31 | ||
| Other Revenue: | 2014 | 2015 |
| Interest revenue | $28,000 | $28,000 |
| Dividend revenue | 7,000 | 9,800 |
Table (6)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter E Solutions
Financial Accounting, 8th Edition
- Accurate Answerarrow_forwardCarter Inc. had $3,000 of supplies on hand on January 1. During the year, the company purchased $4,800 of supplies, and on December 31, determined that only $1,200 of supplies were still on hand. The adjusting entry for Carter Inc. on December 31 will include: a. Debit Supplies $4,800 b. Credit Supplies Expense $6,600 c. Debit Supplies Expense $6,600 d. Debit Supplies Expense $2,800arrow_forwardHello tutor please provide this question solution general accountingarrow_forward
- Provide answerarrow_forwardProblem related general Accounting 52arrow_forwardSummit Corporation provided the following financial details: Financial Data: Beginning Total Assets: $600,000 Ending Total Assets: $640,000 • Net Income: $125,000 • Tax Rate: 30% Calculate: Return on Total Assets (ROA)arrow_forward
- Subject general accountingarrow_forwardBig Company purchased Small Company for $1,450,000. Small Company had assets with a fair value of $1,150,000, and liabilities with a fair value of $200,000. Use this information to determine the dollar value of good will.arrow_forwardA $2,000 bond issued in 2018 pays $180 in interest each year. What is the current yield on the bond if it can be purchased for $1,500?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





