
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The structural formulas involved in the sequence of given reactions for the formation of adipic acid or hexamethylene diamine are to be written, with given molecular formula of each compound and IR data of some compound.
Concept introduction:
A
Nylon is a polymer that consists of adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine as monomer units.
Nylon
The formation of Nylon
The addition of hydrogen to double or triple bond is a hydrogenation reaction.
Hydrogenation of
Infrared spectroscopy is a simple, instrumental technique, which helps to determine the presence of various functional groups.
It depends on the interactions of atoms or molecules with the electromagnetic radiation.
The molecules that have dipole moment are IR active and the molecules that do not have dipole moment are IR inactive.
Cyclohexanol shows IR peak at
Cyclic ketone shows IR peak at
Answer to Problem 1PP
Solution:
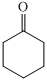
(a) The structures involved in the sequence are as follows:
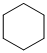 ,
, 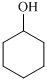 ,
, 
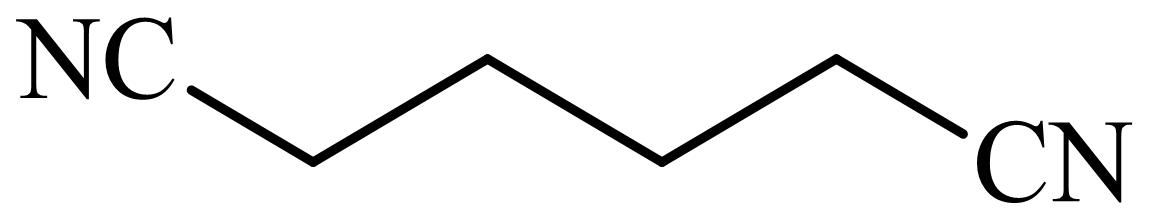
(b) The structures involved in the sequence are as follows:
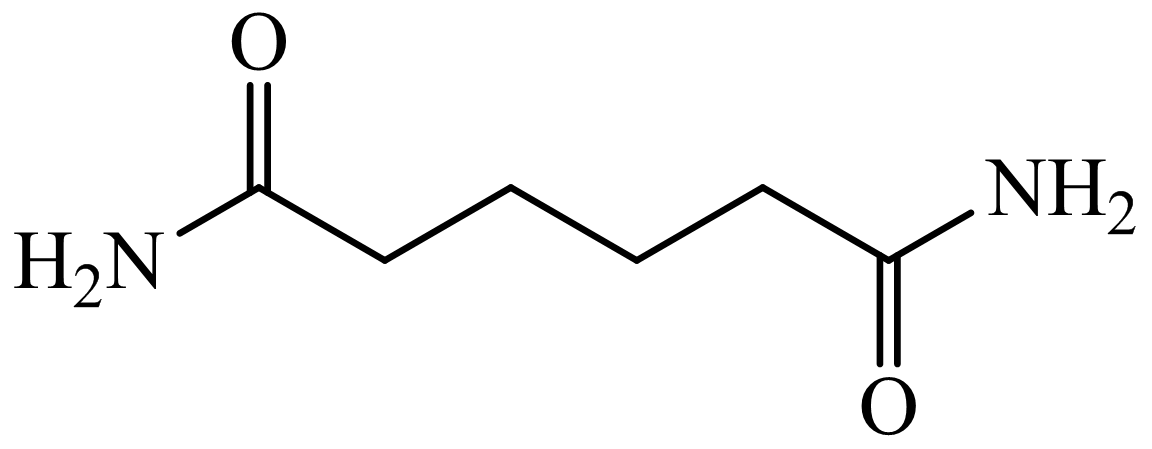 ,
, 
(c) The structures involved in the sequence are as follows:
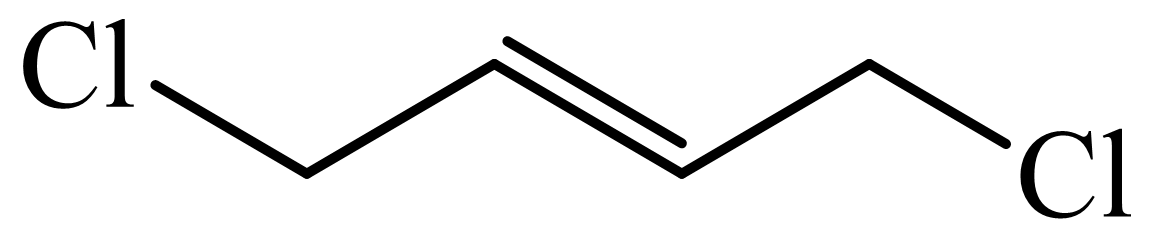 ,
, 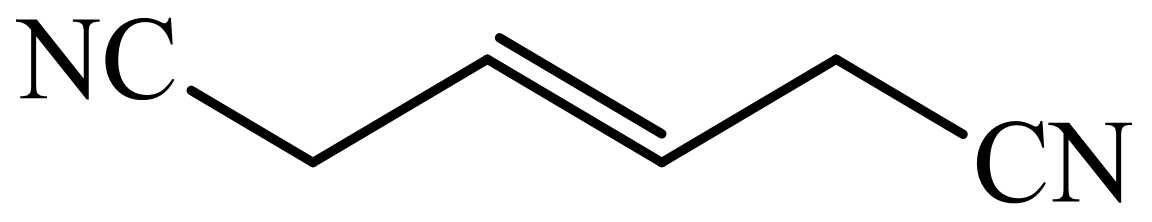 ,
,
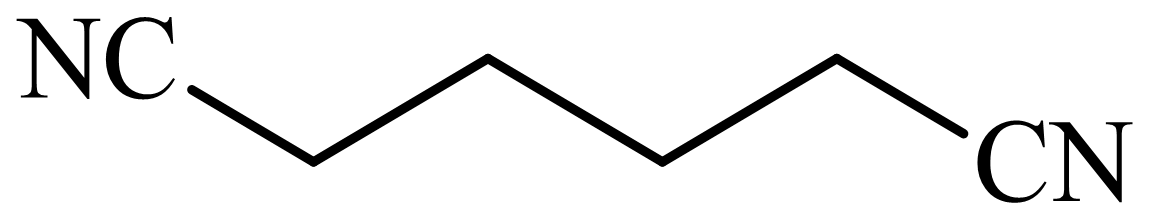
(d) The structures involved in the sequence are as follows:
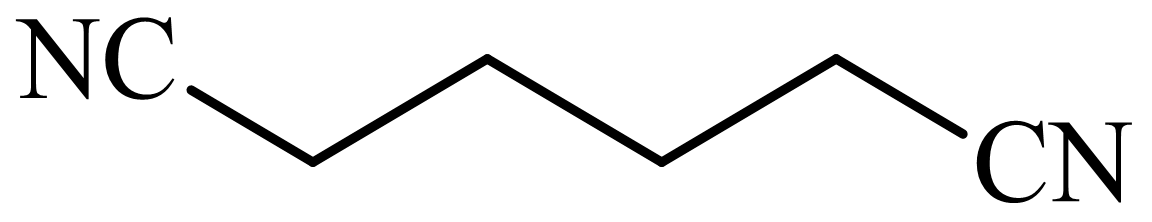
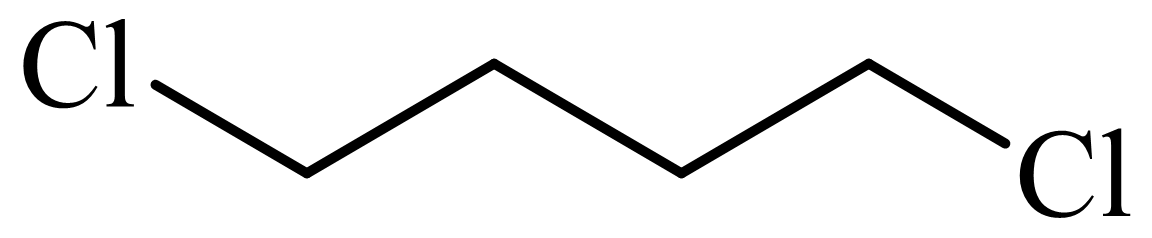 ,
, 
Explanation of Solution
a)
For the formation of adipic acid, first, benzene undergoes hydrogenation reaction to form cyclohexane, which then undergoes oxidation in the presence of catalyst to give cyclohexanol ( I.R. peak at
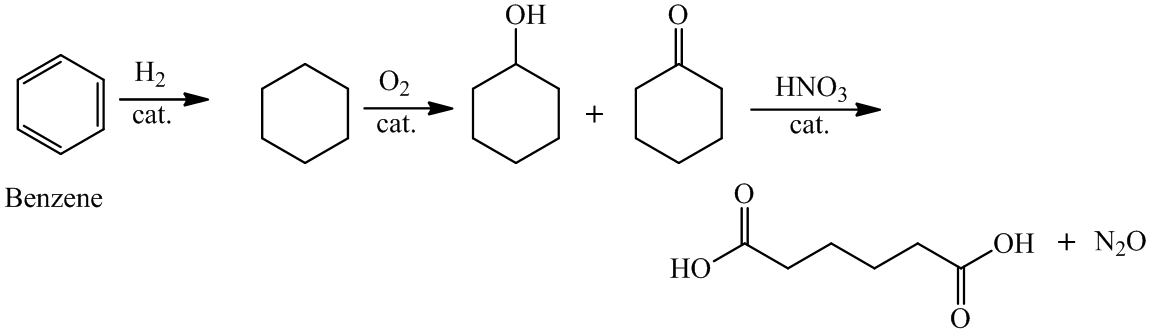
Hence, adipic acid is formed in this sequence of reactions.
b)
Here, adipic acid reacts with two molecules of ammonia to form ammonium salt of adipic acid. Then, on heating, this salt loses two molecules of water to form
The whole sequence can be written as
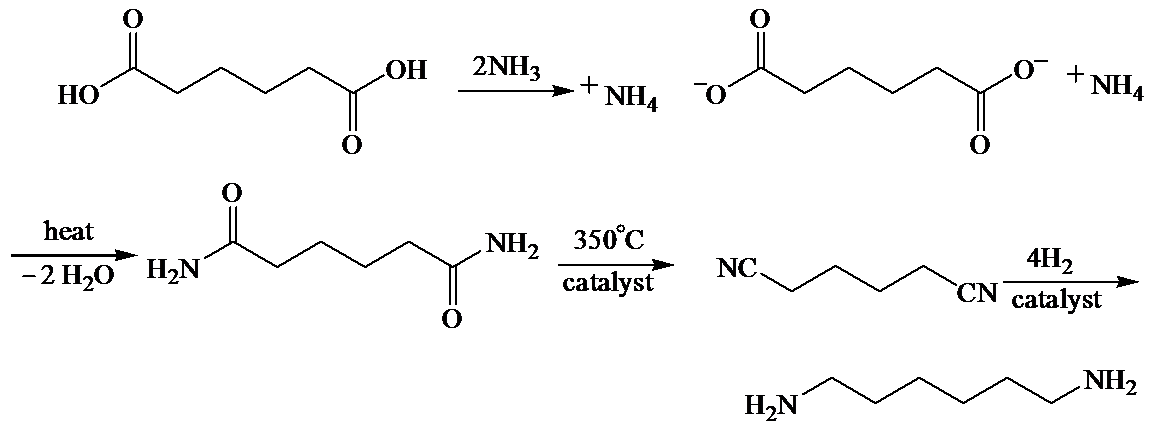
Hence, hexamethylene diamine is formed in this sequence of reactions.
c)
Here,
The whole sequence can be written as
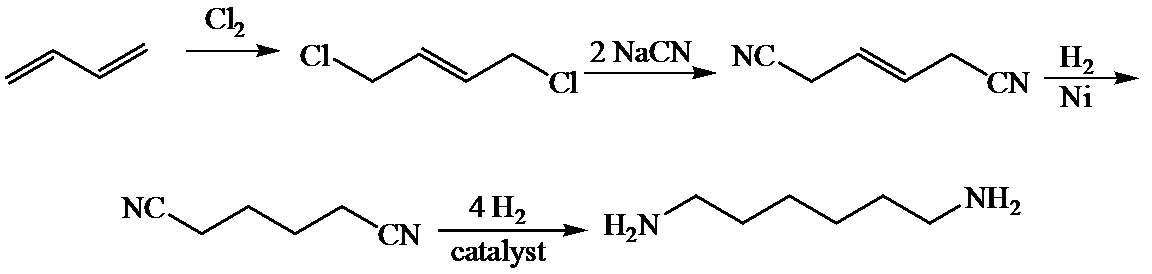
Hence, hexamethylene diamine is formed in this sequence of reactions.
d)
Here, tetrahydrofuran undergoes chlorination in the presence of hydrochloric acid resulting in the formation of
The whole sequence can be written as
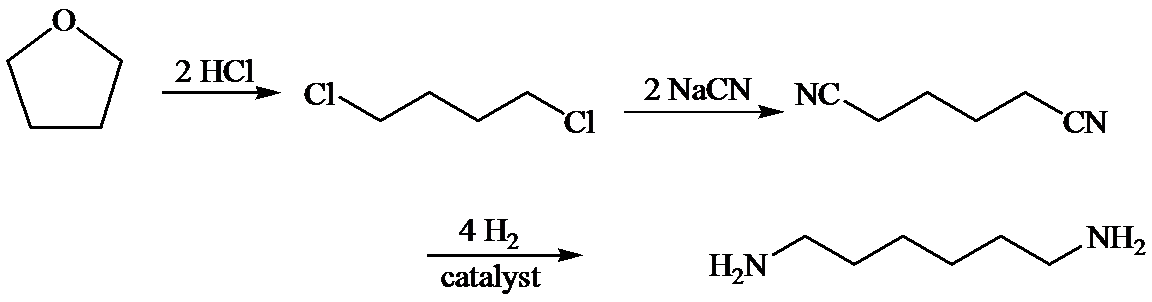
Hence, hexamethylene diamine is formed in this sequence of reactions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter E Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- (a 4 shows scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of extruded actions of packing bed for two capillary columns of different diameters, al 750 (bottom image) and b) 30-μm-i.d. Both columns are packed with the same stationary phase, spherical particles with 1-um diameter. A) When the columns were prepared, the figure shows that the column with the larger diameter has more packing irregularities. Explain this observation. B) Predict what affect this should have on band broadening and discuss your prediction using the van Deemter terms. C) Does this figure support your explanations in application question 33? Explain why or why not and make any changes in your answers in light of this figure. Figure 4 SEM images of sections of packed columns for a) 750 and b) 30-um-i.d. capillary columns.³arrow_forwardfcrip = ↓ bandwidth Il temp 32. What impact (increase, decrease, or no change) does each of the following conditions have on the individual components of the van Deemter equation and consequently, band broadening? Increase temperature Longer column Using a gas mobile phase instead of liquid Smaller particle stationary phase Multiple Paths Diffusion Mass Transferarrow_forward34. Figure 3 shows Van Deemter plots for a solute molecule using different column inner diameters (i.d.). A) Predict whether decreasing the column inner diameters increase or decrease bandwidth. B) Predict which van Deemter equation coefficient (A, B, or C) has the greatest effect on increasing or decreasing bandwidth as a function of i.d. and justify your answer. Figure 3 Van Deemter plots for hydroquinone using different column inner diameters (i.d. in μm). The data was obtained from liquid chromatography experiments using fused-silica capillary columns packed with 1.0-μm particles. 35 20 H(um) 큰 20 15 90 0+ 1500 100 75 550 01 02 594 05 μ(cm/sec) 30 15 10arrow_forward
- elow are experimentally determined van Deemter plots of column efficiency, H, vs. flow rate. H is a quantitative measurement of band broadening. The left plot is for a liquid chromatography application and the night is for gas chromatography. Compare and contrast these two plots in terms of the three band broadening mechanisms presented in this activity. How are they similar? How do they differ? Justify your answers.? 0.4 H (mm) 0.2 0.1- 0.3- 0 0.5 H (mm) 8.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0- 3.0 T +++ 1.0 1.5 0 2.0 4.0 Flow Rate, u (cm/s) 6.0 8.0 Flow Rate, u (cm/s)arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: + H ZH NaBH3CN H+ n. ? Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant R in this organic reaction? + R H3O+ + • Draw the structure of R in the drawing area below. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds if it's necessary to draw one particular enantiomer. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- What would be the best choices for the missing reagents 1 and 3 in this synthesis? 1 1. PPh3 2. n-BuLi 2 • Draw the missing reagents in the drawing area below. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. • Do not draw the missing reagent 2. If you draw 1 correctly, we'll know what it is. • Note: if one of your reagents needs to contain a halogen, use bromine. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardThe product on the right-hand side of this reaction can be prepared from two organic reactants, under the conditions shown above and below the arrow. Draw 1 and 2 below, in any arrangement you like. 1+2 NaBH₂CN H+ N Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X $arrow_forwardExplain what is the maximum absorbance of in which caffeine absorbs?arrow_forward
- Explain reasons as to why the amount of caffeine extracted from both a singular extraction (5ml Mountain Dew) and a multiple extraction (2 x 5.0ml Mountain Dew) were severely high when compared to coca-cola?arrow_forwardProtecting Groups and Carbonyls 6) The synthesis generates allethrolone that exhibits high insect toxicity but low mammalian toxicity. They are used in pet shampoo, human lice shampoo, and industrial sprays for insects and mosquitos. Propose detailed mechanistic steps to generate the allethrolone label the different types of reagents (Grignard, acid/base protonation, acid/base deprotonation, reduction, oxidation, witting, aldol condensation, Robinson annulation, etc.) III + VI HS HS H+ CH,CH,Li III I II IV CI + P(Ph)3 V ༼ Hint: no strong base added VI S VII IX HO VIII -MgBr HgCl2,HgO HO. isomerization aqeuous solution H,SO, ༽༽༤༽༽ X MeOH Hint: enhances selectivity for reaction at the S X ☑arrow_forwardDraw the complete mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydration of this alkene. esc 田 Explanation Check 1 888 Q A slock Add/Remove step Q F4 F5 F6 A བྲA F7 $ % 5 @ 4 2 3 & 6 87 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Ce W E R T Y U S D LL G H IK DD 요 F8 F9 F10 F1 * ( 8 9 0 O P J K L Z X C V B N M H He commandarrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry In FocusChemistryISBN:9781305084476Author:Tro, Nivaldo J., Neu, Don.Publisher:Cengage Learning


