(a)
The budget constraint.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Since the income is $4,000 and
Thus, the consumer will consume 80X.
Since the income is $4,000 and price of good Y is $100, the quantity of good Y can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the consumer will consume 40Y.
Now, the budget constraint can be represented as follows:
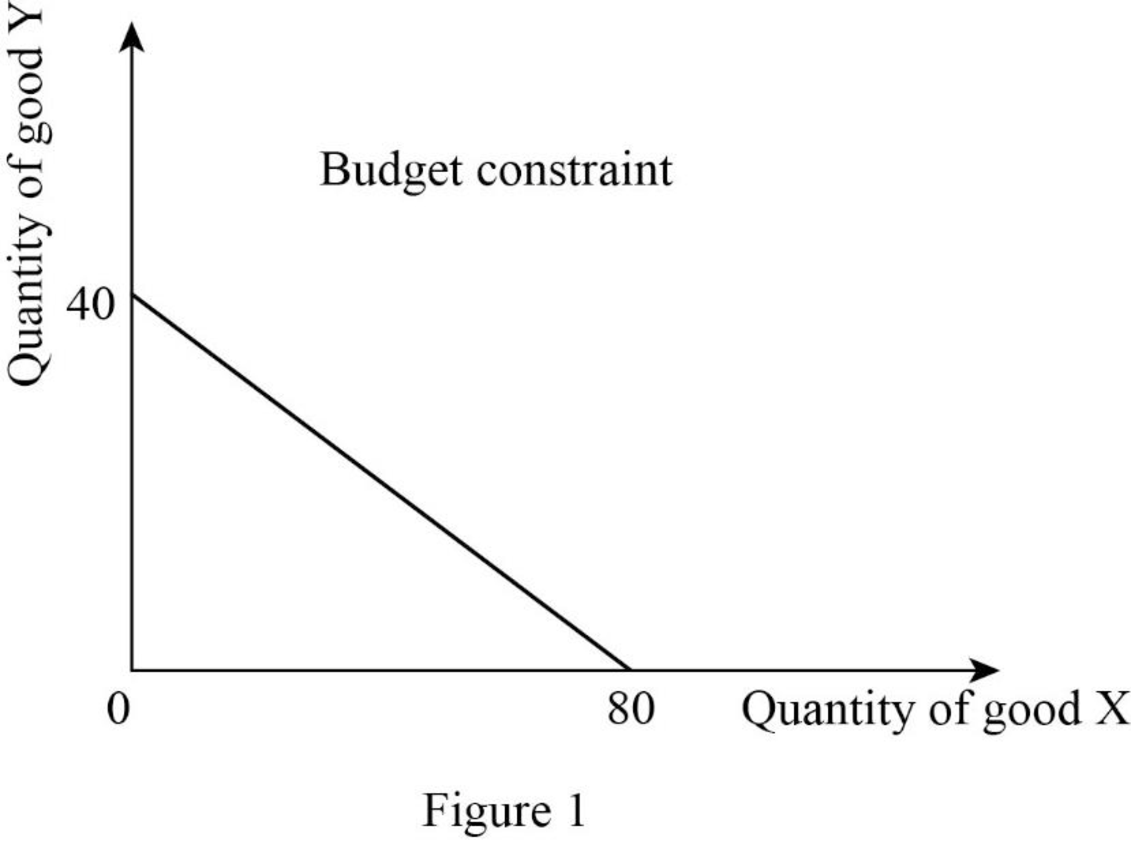
In Figure 1, the vertical axis measures the quantity of good Y and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of good X.
Budget constraints: Budget constraint refers to the possible combination of goods and services that a consumer can purchase at a given price level with the entire income.
(b)
The budget constraint.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Since the income is $3,000 and price of good X is $25, the quantity of good X can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the consumer will consume 120X.
Since the income is $3,000 and price of good Y is $200, the quantity of good Y can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the consumer will consume 15Y.
Now, the budget constraint can be represented as follows:
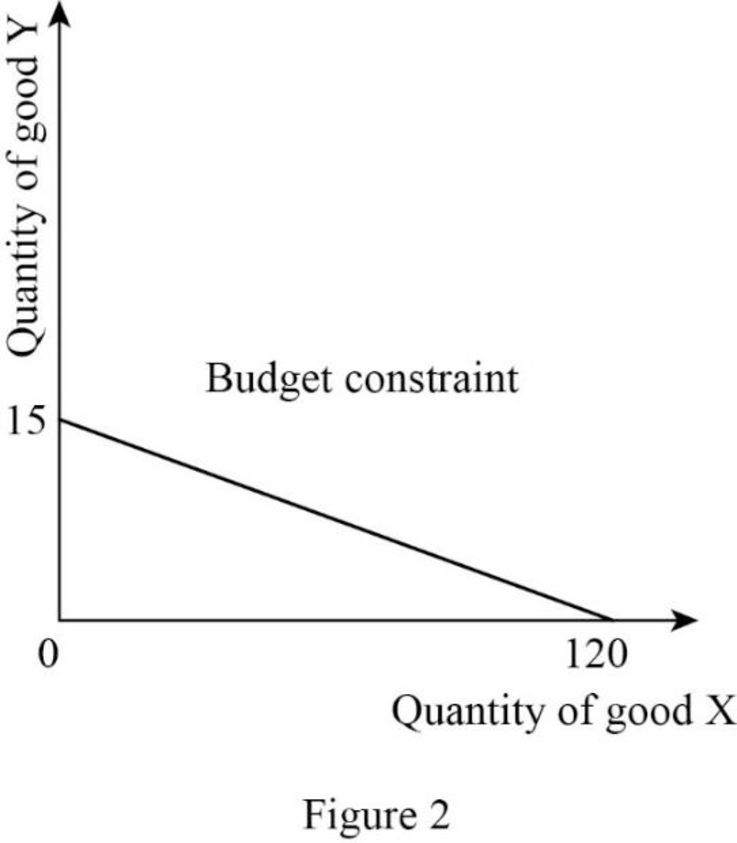
In Figure 2, the vertical axis measures the quantity of good Y and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of good X.
Budget constraints: Budget constraint refers to the possible combination of goods and services that a consumer can purchase at a given price level with the entire income.
(c)
The budget constraint.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Since the income is $2,000 and price of good X is $40, the quantity of good X can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the consumer will consume 50X.
Since the income is $2,000 and price of good Y is $150, the quantity of good Y can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the consumer will consume 13.33Y.
Now, the budget constraint can be represented as follows:
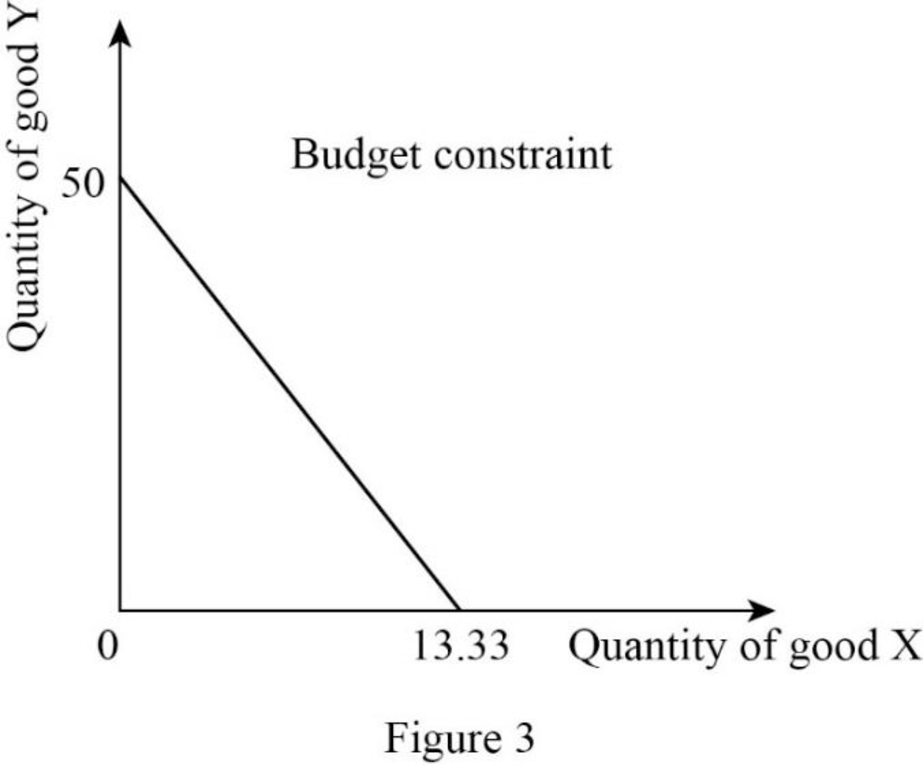
In Figure 3, the vertical axis measures the quantity of good Y and the horizontal axis measures the quantity of good X.
Budget constraints: Budget constraint refers to the possible combination of goods and services that a consumer can purchase at a given price level with the entire income.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter C Solutions
Aplia, 1 Term Printed Access Card For Arnold's Microeconomics, 13th
- Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’reexplaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Write it all in paragraphs: 2. Give an overview of the equation of exchange (EoE) as used by Classical Theory. Now,carefully explain each variable in the EoE. What is meant by the “quantity theory of money”and how is it different from or the same as the equation of exchange?arrow_forwardZbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwh Zbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwh Zbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwhZbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwhZbsbwhjw8272:shbwhahwharrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all:arrow_forward
- Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’reexplaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 4. Draw a Keynesian AD curve in P – Y space and list the shift factors that will shift theKeynesian AD curve upward and to the right. Draw a separate Classical AD curve in P – Yspace and list the shift factors that will shift the Classical AD curve upward and to the right.arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 10. What is the mechanism or process that allows the expenditure multiplier to “work” in theKeynesian Cross Model? Explain and show both mathematically and graphically. What isthe underpinning assumption for the process to transpire?arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 15. How is the Keynesian expenditure multiplier implicit in the Keynesian version of the AD/ASmodel? Explain and show mathematically. (note: this is a tough one)arrow_forward
- Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 13. What would happen to the net exports function in Europe and the US respectively if thedemand for dollars rises worldwide? Explain why.arrow_forward20. Given the mathematical model below, solve for the expenditure multiplier for a) government spending, G; and b) for consumer taxes, T. (medium difficulty) Y=C+I+G C=Co+b(Y-T) 1 = 10 T=To+tY G = Go+gYarrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 11. What exactly is a rectangular hyperbola and what relevance is it to classical economics?arrow_forward
- Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 9. Explain the difference between absolute and comparative advantage in a family setting, i.e.using parents and children. What can we glean from knowing about comparative andabsolute advantages?arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 18. Explain why most economists believe it is absolutely necessary to allow free trade in aneconomy. Why is it harmful (under most circumstances) to have tariffs and trade barriers?arrow_forwardUse the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all: 19. How does the multiplier work in theory? How would you interpret Robert Barro’s empiricalfindings of a multiplier (note, not the MPC) of 0.8? What about Christine Romar’s finding ofa multiplier of 1.5?arrow_forward
 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Economics Today and Tomorrow, Student EditionEconomicsISBN:9780078747663Author:McGraw-HillPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Economics Today and Tomorrow, Student EditionEconomicsISBN:9780078747663Author:McGraw-HillPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co






