Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133915426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9.1, Problem 4P
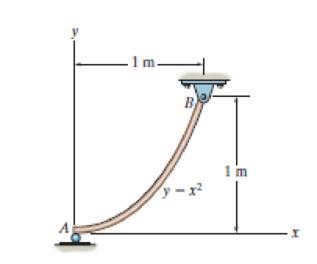
Locate the center of gravity ȳ of the homogeneous rod.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A 10-kg box is pulled along P,Na rough surface by a force P, as shown in thefigure. The pulling force linearly increaseswith time, while the particle is motionless att = 0s untilit reaches a maximum force of100 Nattimet = 4s. If the ground has staticand kinetic friction coefficients of u, = 0.6 andHU, = 0.4 respectively, determine the velocityof the
A
1
0
-
kg box is pulled along P
,
N
a rough surface by a force P
,
as shown in the
figure. The pulling force linearly increases
with time, while the particle is motionless at
t
=
0
s untilit reaches a maximum force of
1
0
0
Nattimet
=
4
s
.
If the ground has static
and kinetic friction coefficients of u
,
=
0
.
6
and
HU
,
=
0
.
4
respectively, determine the velocity
of the particle att
=
4
s
.
Calculate the speed of the driven member with the following conditions:
Diameter of the motor pulley: 4 in Diameter of the driven pulley: 12 in Speed of the motor pulley: 1800 rpm
4. In the figure, shaft A made of AISI 1010 hot-rolled steel, is welded to a fixed
support and is subjected to loading by equal and opposite Forces F via shaft B.
Stress concentration factors K₁ (1.7) and Kts (1.6) are induced by the 3mm fillet.
Notch sensitivities are q₁=0.9 and qts=1. The length of shaft A from the fixed
support to the connection at shaft B is 1m. The load F cycles from 0.5 to 2kN and
a static load P is 100N. For shaft A, find the factor of safety (for infinite life) using
the modified Goodman fatigue failure criterion.
3 mm
fillet
Shaft A
20 mm
25 mm
Shaft B
25 mm
Chapter 9 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
Ch. 9.1 - In each case, use the element shown and specify...Ch. 9.1 - Determine the centroid (x,y) of the shaded area....Ch. 9.1 - Determine the centroid (x,y) of the shaded area....Ch. 9.1 - Determine the centroid of the shaded area. Prob....Ch. 9.1 - Locate the center of mass x of the straight rod if...Ch. 9.1 - Locate the centroid of the homogeneous solid...Ch. 9.1 - Locate the centroid z of the homogeneous solid...Ch. 9.1 - Locate the center of mass of the homogeneous rod...Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 2PCh. 9.1 - Locate the center of gravity x of the homogeneous...
Ch. 9.1 - Locate the center of gravity of the homogeneous...Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 5PCh. 9.1 - Locate the centroid of the area.Ch. 9.1 - Locate the centroid x of the parabolic area. Prob....Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 8PCh. 9.1 - Locate the centroid x of the shaded area. Probs....Ch. 9.1 - Locate the centroid of the shaded area. Probs....Ch. 9.1 - Locate the centroid x of the area. Probs. 9-11/12Ch. 9.1 - Locate the centroid of the area. Probs. 9-11/12Ch. 9.1 - Locate the centroid x of the area. Probs. 9-13/14Ch. 9.1 - Locate the centroid of the area. Probs. 9-13/14Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 15PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 16PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 17PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 18PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 19PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 20PCh. 9.1 - Locate the centroid x of the shaded area. Probs....Ch. 9.1 - Locate the centroid of the shaded area. Probs....Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 23PCh. 9.1 - Locate the centroid of the shaded area. Probs....Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 25PCh. 9.1 - Locate the centroid x of the shaded area. Probs....Ch. 9.1 - Locate the centroid of the shaded area. Probs....Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 28PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 29PCh. 9.1 - Locate the centroid x of the shaded area. Probs....Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 31PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 32PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 33PCh. 9.1 - The steel plate is 0.3 m thick and has a density...Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 35PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 36PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 37PCh. 9.1 - Determine the location r of the centroid C for the...Ch. 9.1 - Locate the center of gravity of the volume. The...Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 40PCh. 9.1 - Locate the centroid z of the frustum of the...Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 42PCh. 9.1 - Locate the centroid of the quarter-cone. Prob....Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 44PCh. 9.1 - Locate the centroid z of the volume. Prob. 9-45Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 46PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 47PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 48PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 49PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 50PCh. 9.2 - Locate the centroid (x,y,z) of the wire bent in...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 8FPCh. 9.2 - Prob. 9FPCh. 9.2 - Prob. 10FPCh. 9.2 - Prob. 11FPCh. 9.2 - Prob. 12FPCh. 9.2 - Prob. 51PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 52PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 53PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 54PCh. 9.2 - Locate the centroid (x,y) of the metal cross...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 56PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 57PCh. 9.2 - Determine the location of the centroidal axis xx...Ch. 9.2 - Locate the centroid (x,y) of the shaded area....Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 60PCh. 9.2 - Determine the location of the centroid C of the...Ch. 9.2 - Locate the centroid (x,y) of the shaded area....Ch. 9.2 - Determine the location of the centroid of the...Ch. 9.2 - Locate the centroid (x,y) of the shaded area....Ch. 9.2 - Determine the location (x,y) of the centroid C of...Ch. 9.2 - Determine the location of the centroid C for a...Ch. 9.2 - Locate the centroid of the cross-sectional area...Ch. 9.2 - A triangular plate made of homogeneous material...Ch. 9.2 - A triangular plate made of homogeneous material...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 70PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 71PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 72PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 73PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 74PCh. 9.2 - Locate the center of mass (x,y,z) of the...Ch. 9.2 - The sheet metal part has the dimensions shown....Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 77PCh. 9.2 - The wooden table is made from a square board...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 79PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 80PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 81PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 82PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 83PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 84PCh. 9.2 - Determine the distance z to the centroid of the...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 86PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 87PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 88PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 89PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 13FPCh. 9.3 - Prob. 14FPCh. 9.3 - Prob. 15FPCh. 9.3 - Prob. 16FPCh. 9.3 - Prob. 90PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 91PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 92PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 93PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 94PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 95PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 96PCh. 9.3 - Determine the volume of concrete needed to...Ch. 9.3 - Determine the surface area of the curb. Do not...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 99PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 100PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 101PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 102PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 103PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 104PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 105PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 106PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 107PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 108PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 109PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 110PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 111PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 112PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 113PCh. 9.3 - Prob. 114PCh. 9.5 - Determine the magnitude of the hydrostatic force...Ch. 9.5 - Determine the magnitude of the hydrostatic force...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 19FPCh. 9.5 - Prob. 20FPCh. 9.5 - Prob. 21FPCh. 9.5 - The pressure loading on the plate varies uniformly...Ch. 9.5 - The load over the plate varies linearly along the...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 117PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 118PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 119PCh. 9.5 - When the tide water A subsides, the tide gate...Ch. 9.5 - The tank is filled with water to a depth of d = 4...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 122PCh. 9.5 - The factor of safety for tipping of the concrete...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 124PCh. 9.5 - The tank is used to store a liquid having a...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 126PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 127PCh. 9.5 - Prob. 128PCh. 9.5 - Determine the magnitude of the resultant force...Ch. 9.5 - The semicircular drainage pipe is filled with...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 1RPCh. 9.5 - Prob. 2RPCh. 9.5 - Prob. 3RPCh. 9.5 - Prob. 4RPCh. 9.5 - Prob. 5RPCh. 9.5 - Prob. 6RPCh. 9.5 - Prob. 7RPCh. 9.5 - Prob. 8RPCh. 9.5 - The gate AB is 8 m wide. Determine the horizontal...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 10RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please sovle this for me and please don't use aiarrow_forwardPlease sovle this for me and please don't use aiarrow_forward3. The cold-drawn AISI 1040 steel bar shown in the figure is subjected to a completely reversed axial load fluctuating between 28 kN in compression to 28 kN in tension. Estimate the fatigue factor of safety based on achieving infinite life (using Goodman line) and the yielding factor of safety. If infinite life is not predicted, estimate the number of cycles to failure. 25 mm + 6-mm D. 10 mmarrow_forward
- CORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE 1. The truss shown is supported by hinge at A and cable at E.Given: H = 4m, S = 1.5 m, α = 75⁰, θ = 33⁰.Allowable tensile stress in cable = 64 MPa.Allowable compressive stress in all members = 120 MPaAllowable tensile stress in all members = 180 MPa1.Calculate the maximum permissible P, in kN, if the diameter of the cable is 20 mm.2.If P = 40 kN, calculate the required area (mm2) of member BC.3. If members have solid square section, with dimension 15 mm, calculate the maximum permissible P (kN) based on the allowable strength of member HI.ANSWERS: (1) 45.6 kN; (2) 83.71 mm2; (3) 171.76 kNarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE 2: A wire 4 meters long is stretched horizontally between points 4 meters apart. The wire is 25 mm2 in cross-section with a modulus of elasticity of 200 GPa. A load W placed at the center of the wire produces a sag Δ.1.Calculate the tension (N) in the wire if sag Δ = 30 mm.2.Calculate the magnitude of W, in N, if sag Δ = 54.3 mm.3. If W is 60 N, what is the sag (in mm)?ANSWERS: (1) 562 N, (2) 100 N, (3) 45.8 Narrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE 4 : A cable and pulley system at D is used to bring a 230-kg pole (ACB) to a vertical position as shown. The cable has tensile force T and is attached at C. The length of the pole is 6.0 m, the outer diameter is d = 140 mm, and the wall thickness t = 12 mm. The pole pivots about a pin at A. The allowable shear stress in the pin is 60 MPa and the allowable bearing stress is 90 MPa. The diameter of the cable is 8 mm.1.Find the minimum diameter (mm) of the pin at A to support the weight of the pole in the position shown.2.Calculate the elongation (mm) of the cable CD.3.Calculate the vertical displacement of point C, in mm.ANSWERS: (1) 6 mm, (2) 1.186 mm, (3) 1.337 mm--arrow_forward
- 1. Derive an expression for H(w) filter or bandpass/reject filter. = for the circuit below. Qualitatively determine if it's a high/lowpass L ell R ww Voarrow_forward2. Obtain the transfer function, H(w) = 0 for the circuit below for R₁ = 1 kQ2, R2 = 10 kQ, and Vi C = 1 μF. What role, if any, does the capacitor play? Explain. R₁ R2 + C + Voarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE 3 (15 points): A 12-meter-long precast pile segment is to be lifted from a trailer down to the ground and then set in place prior to driving by a crane.1. If two slings are to be used in lifting the pile to the ground, at what distance from the ends must the slings be placed for minimum bending due to its own weight?2. At what distance from the ends must the slings be placed for minimum shear due to its own weight?3. Using one sling to set the pile in a vertical position before driving at what distance from one end must the sling be placed for minimum bending due to its own weight?ANSWERS: (1) 2.48 m, (2) 3.00 m, (3) 3.51 marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Mechanical Engineering: Centroids & Center of Gravity (1 of 35) What is Center of Gravity?; Author: Michel van Biezen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Tkyk-G1rDQg;License: Standard Youtube License