
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given substrate, when
Concept introduction:
As the number of alkyl groups on the carbon bonded to the leaving group increases, the
Answer to Problem 9.69P
The major E1 product for the given reaction is shown below:
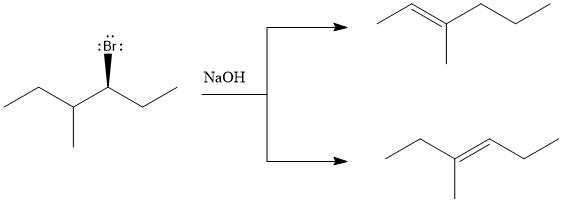
Explanation of Solution
Elimination usually takes place so as to produce the most stable, i.e., highly alkyl substituted, alkene.
The possible E1 products are obtained by eliminating the leaving group and a proton on carbon adjacent to the one bonded to the leaving group. Here the
The first and second alkene product is highly substituted than the third alkene product. Therefore, the first and second alkene products are more stable. The base in this reaction is OH, which is not bulky, so the first and second products are the major products.

From the stability of the product formed, the major E1 product is drawn.
(b)
Interpretation:
For the given substrate, when
Concept introduction:
As the number of alkyl groups on the carbon bonded to the leaving group increases, the rate of E1 reaction increases. Each additional alkyl group, which is electron donating, stabilizes the carbocation intermediate produced and thus helps the leaving group leave. The
Answer to Problem 9.69P
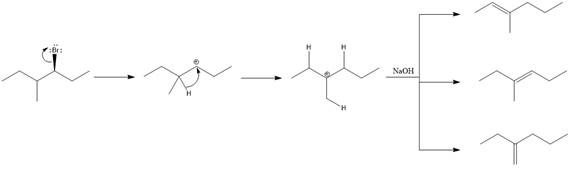
The major E1 product for the given reaction is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
Elimination usually takes place so as to produce the most stable, i.e., highly alkyl substituted, alkene.
The possible E1 products are obtained by eliminating the leaving group and a proton on carbon adjacent to the one bonded to the leaving group. Here the
From the stability of the product formed, the major E1 product is drawn.
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given substrate, when
Concept introduction:
As the number of alkyl groups on the carbon bonded to the leaving group increases, the rate of E1 reaction increases. Each additional alkyl group, which is electron donating, stabilizes the carbocation intermediate produced and thus helps the leaving group leave. The
Answer to Problem 9.69P
The major E1 product for the given reaction is shown below:
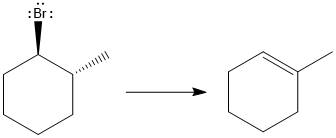
Explanation of Solution
Elimination usually takes place so as to produce the most stable, i.e., highly alkyl substituted, alkene.
The possible E1 products are obtained by eliminating the leaving group and a proton on carbon adjacent to the one bonded to the leaving group. Here the
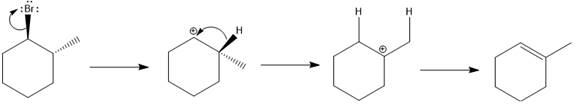
From the stability of the product formed, the major E1 product is drawn.
(d)
Interpretation:
For the given substrate, when
Concept introduction:
As the number of alkyl groups on the carbon bonded to the leaving group increases, the rate of E1 reaction increases. Each additional alkyl group, which is electron donating, stabilizes the carbocation intermediate produced and thus helps the leaving group leave. The
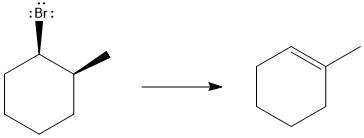
Answer to Problem 9.69P
The major E1 product for the given reaction is shown below:
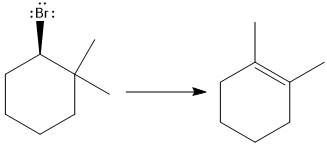
Explanation of Solution
Elimination usually takes place so as to produce the most stable that means highly alkyl substituted alkene.
The possible E1 products are obtained by eliminating the leaving group and a proton on the carbon adjacent to the one bonded to the leaving group. Here the
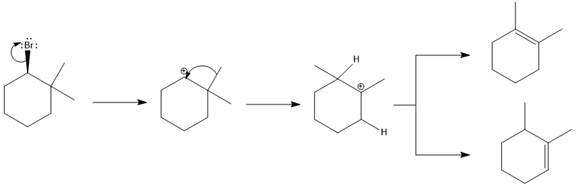
The first alkene product is highly substituted than the second alkene product. Therefore, the first alkene product is more stable. The base in this reaction is OH, which is not bulky, so the first and second products are the major products.

From the stability of the product formed, the major E1 product is drawn.
(e)
Interpretation:
For the given substrate, when
Concept introduction:
As the number of alkyl groups on the carbon bonded to the leaving group increases, the rate of E1 reaction increases. Each additional alkyl group, which is electron donating, stabilizes the carbocation intermediate produced and thus helps the leaving group leave. The
Answer to Problem 9.69P
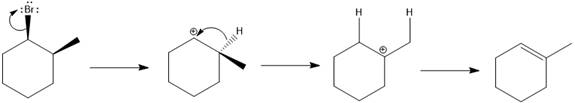
The major E1 product for the given reaction is shown below:
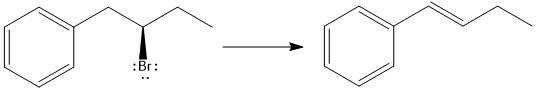
Explanation of Solution
Elimination usually takes place so as to produce the most stable that means highly alkyl substituted alkene.
The possible E1 products are obtained by eliminating the leaving group and a proton on the carbon adjacent to the one bonded to the leaving group. Here the
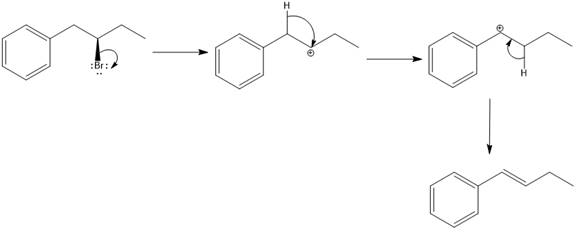
From the stability of the product formed, the major E1 product is drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- Draw the missing intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this synthesis: 1. MeO- H3O+ 1 2 2. PrBr Δ You can draw the two structures in any arrangement you like. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardWhat is the differences between: Glyceride and phosphoglyceride Wax and Fat Soap and Fatty acid HDL and LDL cholesterol Phospho lipids and sphingosine What are the types of lipids? What are the main lipid components of membrane structures? How could lipids play important rules as signaling molecules and building units? The structure variety of lipids makes them to play significant rules in our body, conclude breifly on this statement.arrow_forwardWhat is the differences between DNA and RNA for the following: - structure - function - type What is the meaning of: - replication - transcription - translation show the base pair connection(hydrogen bond) in DNA and RNAarrow_forward
- What is the IP for a amino acid- give an example what are the types of amino acids What are the structures of proteins The N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Try-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val- Tyr- Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forwardWhat is the IP for a amino acid- give an example what are the types of amino acids What are the structures of proteins The N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Try-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val- Tyr- Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forward> aw the missing intermediates 1 and 2, plus the final product 3, of this synthesis: 1. Eto 1. EtO¯ H3O+ 1 2 2. PrBr 2. PrBr Δ You can draw the three structures in any arrangement you like. 3 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Explanation Check 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacarrow_forward
- There are various factors that affect an equilibrium. Give 3 of these factors and explain using examples andequations how an equilibrium is affected by these factors. Please remember that this is a communication question so that you are communicating your understanding of the factors that affect and equilibrium.arrow_forwardEEZE LETCHUP ID Draw the most likely conjugate base resulting from this acid-base reaction. Include all lone pairs. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Drawing く NaOCH2CH3 :0: :0: 狗arrow_forwardAnswerarrow_forward
- 2. Provide a clear arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reactions. Do not skip proton transfers, do not combine steps, and make sure your arrows are clear enough to be interpreted without ambiguity. a. CH3 Ph OEt هد Ph CH3 Hint: the species on the left is an ynolate, which behaves a lot like an enolate.arrow_forwardb. CH3 H3C CH3 CH3 H3C an unexpected product, containing a single 9- membered ring the expected product, containing two fused rings H3C-I (H3C)2CuLi an enolatearrow_forwardb. H3C CH3 1. 2. H3O+ H3C MgBr H3Carrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
