
Concept explainers
Write Lewis structures for the following species, including all resonance forms, and show formal charges: (a)
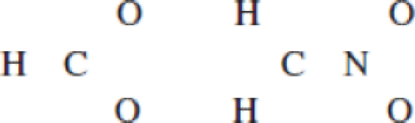
(a)
Interpretation: The resonance structure of
Concept Introduction: Sometimes the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. In these cases, the chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons and is known as resonance.
In some molecules, there is possibility of more than one Lewis structure where all the structures are equally acceptable. One of the acceptable Lewis structures of these molecules is called resonance structure.
All the possible resonance structures are imaginary whereas the resonance hybrid is real.
Any of the possible structure does not exist as such like a stable real molecule. So it is not possible to isolate one resonance structure.
These structures will differ only in the arrangement of the electrons not in the relative position of the atomic nuclei.
Structure with greater number of covalent bonds are more stable comparing to that with lower number of covalent bonds.
Structure which does not involve charge separation is more stable when comparing with structure having positive and negative charge separation.
While drawing resonance structure of a molecule some rules should be followed where the position, over whole charge and chemical framework remains intact. Also only π and nonbonding electron has been moved in all the three resonance structures
Formal charge:
A formal charge (FC) is the charge assigned to an atom in a molecule, irrespective of relative electronegativity by thinking that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally among atoms.
This method is used to identify the most probable Lewis structures if more than one possibility exists for a compound.
The Lewis structure with formal charge on each of the atoms close to zero is taken as the most plausible structure.
Formal charge of an atom can be determined by the given formula.
Answer to Problem 9.51QP
Resonance structure:
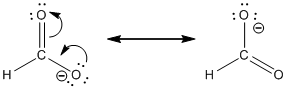
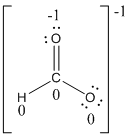
Formal charges:
Explanation of Solution
Determine the resonance structure for

In the case of chlorate ion, the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. The chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons forming 2 possible resonance structures. Both the resonance structures are similar. In all the 2 resonance structures the position, over whole charge and chemical framework remains intact.
Structure of the chlorate ion chlorate ion is given below.
The formal charge of the given compound is calculated,
- Hydrogen atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Carbon atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- First oxygen atom having double bond with carbon
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Oxygen atom which having single bond with carbon
Substituting these values to the equation,
(b)
Interpretation: The resonance structure of
Concept Introduction: Sometimes the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. In these cases, the chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons and is known as resonance.
In some molecules, there is possibility of more than one Lewis structure where all the structures are equally acceptable. One of the acceptable Lewis structures of these molecules is called resonance structure.
All the possible resonance structures are imaginary whereas the resonance hybrid is real.
Any of the possible structure does not exist as such like a stable real molecule. So it is not possible to isolate one resonance structure.
These structures will differ only in the arrangement of the electrons not in the relative position of the atomic nuclei.
Structure with greater number of covalent bonds are more stable comparing to that with lower number of covalent bonds.
Structure which does not involve charge separation is more stable when comparing with structure having positive and negative charge separation.
While drawing resonance structure of a molecule some rules should be followed where the position, over whole charge and chemical framework remains intact. Also only π and nonbonding electron has been moved in all the three resonance structures
Formal charge:
A formal charge (FC) is the charge assigned to an atom in a molecule, irrespective of relative electronegativity by thinking that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally among atoms.
This method is used to identify the most probable Lewis structures if more than one possibility exists for a compound.
The Lewis structure with formal charge on each of the atoms close to zero is taken as the most plausible structure.
Formal charge of an atom can be determined by the given formula.
Answer to Problem 9.51QP
Resonance structure:
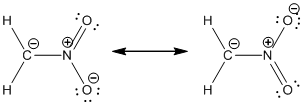
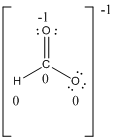
Formal charges:
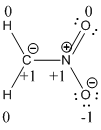
Explanation of Solution
Resonance structure of

In the case of chlorate ion, the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. The chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons forming 2 possible resonance structures. Both the resonance structures are similar. In all the 2 resonance structures the position, over whole charge and chemical framework remains intact.
Structure of the chlorate ion chlorate ion is given below.

The formal charge of the given compound is calculated,
- First hydrogen atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Second hydrogen atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Carbon atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Nitrogen atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- First oxygen atom having double bond with nitrogen
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Oxygen atom which having single bond with nitrogen
Substituting these values to the equation,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning




