
Concept explainers
The following Lewis structures for (a) HCN, (b) C2H2, (c) SnO2, (d) BF3, (e) HOF, (f) HCOF, and (g) NF3 are incorrect. Explain what is wrong with each one and give a correct structure for the molecule. (Relative positions of atoms are shown correctly.)
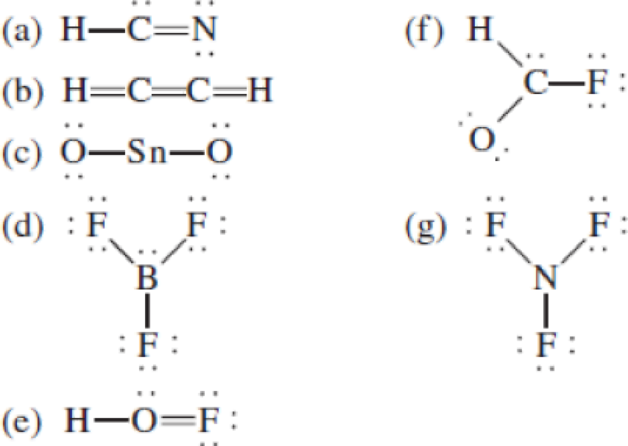
(a)
Interpretation: The Lewis structures of the molecules should be corrected with appropriate explanation.
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Dots represent the electron position around the atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent bonds between atoms.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Answer to Problem 9.47QP
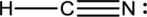
Explanation of Solution
To find: The correct Lewis structure for the given molecule.
- The given structure of the molecule is shown below.
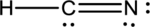
- In the given structure, the carbon contains lone pair of electrons and the bond between carbon and nitrogen is double bond. So the octets of these two atoms are not filled.
- The corrected Lewis structure of the above compound is drawn below.
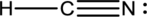
The total number of valence electrons is found to be 10, where 1 electron, 5 electrons and 4 electrons were contributed by H, C and N atoms respectively. Carbon is placed as the central atoms since its electronegativity is less than nitrogen.
The 6 electrons getting after reducing two electrons for each bond from the total valence electron are distributed on N atom to complete the octet. Sincethe octets of C atoms are not filled, a triple bond is made between C and N atoms.
(b)
Interpretation: The Lewis structures of the molecules should be corrected with appropriate explanation.
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Dots represent the electron position around the atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent bonds between atoms.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Answer to Problem 9.47QP

Explanation of Solution
To find: The correct Lewis structure of the given molecule.
- The given structure of the molecule is below.

- In the given structure there is a double bond between hydrogen and carbon which violates the octet rule and also the bond between 2 carbon atoms is double.
- The corrected Lewis structure of the above compound is drawn below.

Each carbon atom bonded with one carbon and hydrogen atom. The total number of valence electrons found to be 10, where 1 electron, 5 electrons were contributed by each H and C atoms respectively.
Sincethere are noelectrons to distribute after reducing two electrons for each bond from the total valence electron, a triple bond is made between two C atomsto fill the octets.
(c)
Interpretation: The Lewis structures of the molecules should be corrected with appropriate explanation.
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Dots represent the electron position around the atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent bonds between atoms.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Answer to Problem 9.47QP
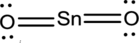
Explanation of Solution
To find: The correct Lewis structure of the given molecule.
- The given structure of the molecule is below.
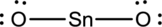
- In the given structure, tin atom does not fill the octet since the bond between tin and terminal atoms are single bond.
- The corrected Lewis structure of the above compound is drawn below.
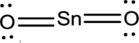
The electronegativity of tin atom is less than oxygen, so it is taken as the central atom bonded with an oxygen atom at each side. Tin atom contributes 4 and each oxygen atom contributes 6 electrons making the total number of valence electrons 16.
To obtain the remaining electrons 12, two electrons for each bond is reduced from the total number of valence electrons, which then further distributed on the terminal oxygen atoms to fill the octets.
Since the central tin atom does not complete octet, a double bond is formed between each terminal oxygen atom
(d)
Interpretation: The Lewis structures of the molecules should be corrected with appropriate explanation.
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Dots represent the electron position around the atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent bonds between atoms.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Answer to Problem 9.47QP
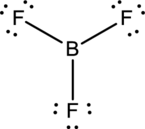
Explanation of Solution
To find: The correct Lewis structure of the given molecule.
- The given structure of the molecule is below.
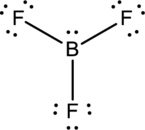
- In this structure, there is a lone pair of electron on boron atom whereas in actual structure that lone pair is no needed to fill the octet.
- The corrected Lewis structure of the above compound is drawn below.
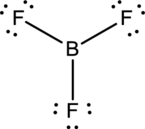
Boron atom has less electronegativity comparing to fluorine. So it is taken as the central atom with 3 terminal fluorine atoms.The boron has 4 and each fluorine atom have 7 valence electrons. Since there are 3 fluorine atoms the total valence electron of the molecule becomes 24.
The 18 electrons after reducing two electrons for each bond from the total valence electron are distributed onfluorine atom to fill the octets. So each fluorine atom gets 3 lone pairs.
(e)
Interpretation: The Lewis structures of the molecules should be corrected with appropriate explanation.
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Dots represent the electron position around the atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent bonds between atoms.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Answer to Problem 9.47QP
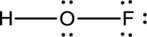
Explanation of Solution
To find: The correct Lewis structure of the given molecule
- The given structure of the molecule is below.
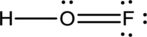
- In the given structure, there is a double bond between oxygen and fluorine which is not needed. Distributing a lone pair on oxygen is enough to fill its octet.
- The corrected Lewis structure of the above compound is drawn below.
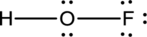
The electronegativity of oxygen atom is less than fluorine and the molecule is with hydrogen and fluorine atoms at the terminal position of oxygen.
Hydrogen, oxygen and fluorine contribute 1, 6 and 7 electrons respectively making the total number of valence electrons 14.
The 10 electrons after reducing for each bond from the total valence electron are distributed on terminal atoms, then to central oxygen atom to fill the octets.
(f)
Interpretation: The Lewis structures of the molecules should be corrected with appropriate explanation.
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Dots represent the electron position around the atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent bonds between atoms.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Answer to Problem 9.47QP
Explanation of Solution
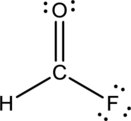
- The given structure of the molecule is below.
- Here the bond between oxygen and carbon is not given appropriately to fill the octet.
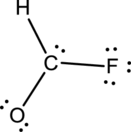
- The corrected Lewis structure of the above compound is drawn below.
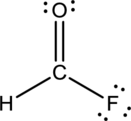
Comparing to fluorine and oxygen, carbon has the least electronegativity, so it is taken as the central atom with hydrogen, fluorine and oxygen at its terminal positions.
Hydrogen, oxygen, carbon and fluorine contribute 1, 6, 4 and 7 electrons respectively making the total number of valence electrons 18.
To fill the octets of the atoms, the 12 electrons after reducing two electrons for each bond from the total valence electron are distributed on terminal atoms.
Since the central carbon atom does not have sufficient electrons to fill the octet, a double bond is made between carbon and terminal oxygen atoms.
(g)
Interpretation: The Lewis structures of the molecules should be corrected with appropriate explanation.
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represents the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
Dots represent the electron position around the atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent bonds between atoms.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Answer to Problem 9.47QP
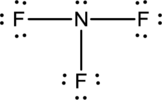
Explanation of Solution
- The given structure of the molecule is below.
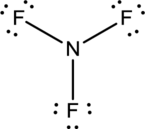
- In this structure a lone pair of electrons is missing which is sufficient to fill the octet of nitrogen.
- The corrected Lewis structure of the above compound is drawn below.
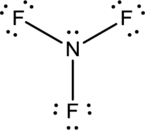
Nitrogen atom has less electronegativity comparing to fluorine. So it is taken as the central atom with 3 fluorine atoms at the terminal positions of it
The nitrogen has 5 and each fluorine atom have 7 valence electrons. Since there are 3 fluorine atoms the total number of valence electrons becomes 26.
The 20 electrons after reducing two electrons for each bond from the total valence electron are distributed on fluorine atom to fill the octets. The remaining 2 electrons are distributed to the central atom so that nitrogen fills the octet.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry
- ASP please....arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardConsider the structure of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane. Part 1 of 2 Draw the Newman projection for the anti conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. ✡ ぬ Part 2 of 2 H H F Br H H ☑ Draw the Newman projection for the gauche conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. H F Br H Harrow_forward
- Please help me answer this question. I don't understand how or where the different reagents will attach and it's mostly due to the wedge bond because I haven't seen a problem like this before. Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how it can happen and what the final product will look like.arrow_forwardWhich of the following compounds is the most acidic in the gas phase? Group of answer choices H2O SiH4 HBr H2Sarrow_forwardWhich of the following is the most acidic transition metal cation? Group of answer choices Fe3+ Sc3+ Mn4+ Zn2+arrow_forward
- Based on the thermodynamics of acetic acid dissociation discussed in Lecture 2-5, what can you conclude about the standard enthalpy change (ΔHo) of acid dissociation for HCl? Group of answer choices You cannot arrive at any of the other three conclusions It is a positive value It is more negative than −0.4 kJ/mol It equals −0.4 kJ/molarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP URGENT!arrow_forwardDraw the skeletal structure corresponding to the following IUPAC name: 7-isopropyl-3-methyldecanearrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning




