
Concept explainers
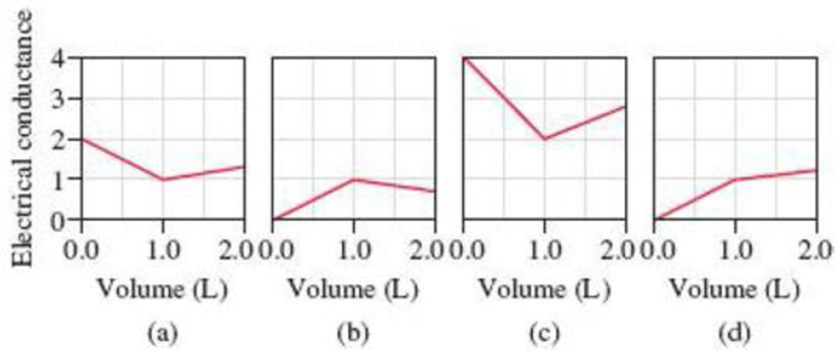
Because the acid-base and precipitation reactions discussed in this chapter all involve ionic species, their progress can be monitored by measuring the electrical conductance of the solution. Match each of the following reactions with one of the diagrams shown here. The electrical conductance is shown in arbitrary units. Explain the significance of the point at which the slope changes in each diagram.
(1) A 1.0 M KOH solution is added to 1.0 L of 1.0 M HC2H3O2.
(2) A 1.0 M NaOH solution is added to 1.0 L of 1.0 M HCl.
(3) A 1.0 M BaCl2 solution is added to 1.0 L of 1.0 M K2SO4.
(4) A 1.0 M NaCl solution is added to 1.0 L of 1.0 M AgNO3.
(5) A 1.0 M HC2H3O2 solution is added to 1.0 L of 1.0 M NH3.
(a)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance, when
Answer to Problem 9.168QP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data
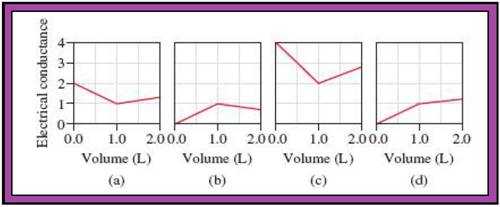
Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
If Conductance unit of
(b)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance when,
Answer to Problem 9.168QP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data

Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
(c)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance when,
Answer to Problem 9.168QP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data

Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
(d)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance, when
Answer to Problem 9.168QP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data

Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
(e)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance, when
Answer to Problem 9.168QP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data

Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
Match the calculated conductance unit of each reaction in given diagrams in Fig.1.
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry: Atoms First V1
- If the current voltage is n = 0.14 V. Indicate which of the 2 formulas must be applied a) = a T = i exp[(1 - p) F Fn Fn b) i==exp B RTarrow_forwardTopic: Photochemistry and Photophysics of Supramoleculesarrow_forwardTwo cations that exchange an electron in an interface, the exchange density is worth 1.39 mA/cm2 and the current density is worth 15 mA/cm2 at 25°C. If the overvoltage is 0.14 V, calculate the reaction rate and symmetry factor. Data: R = 8,314 J mol-1 k-1: F = 96500 Carrow_forward
- With the help of the Tafel line, it is estimated that the interchange density of the VO2+/VO2+ system on the carbon paper has a value of 3 mA cm-2. Calculate a) the current density if the voltage has a value of 1.6 mV and the temperature is 25°C. b) the beta value of the anódico process if the Tafel pendulum is 0.6 V at 25°C. Data: R = 8.314 JK-1mol-1, y F = 96485 C mol-1.arrow_forwardApply the NANSTE law to the MnO4- + 8H+ + 5e- ⇄ Mn2+ + 4H2Oarrow_forwardIn the Nernst Law, how much is RT / F?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





