
Subpart (a):
The equilibrium price and the quantity of haircuts and total surplus.
Subpart (a):
Explanation of Solution
Supply curve: The supply equation is
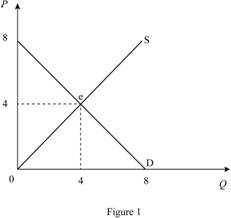
In Figure 1, horizontal axis measures quantity and vertical axis measures price. The curve D indicates demand and the curve S indicates supply. Market reaches the equilibrium at point ‘e’ where the demand curve intersects with supply curve.
Equilibrium price can be calculated as follows.
Equilibrium price is $4.
Thus, equilibrium quantity is 4 units.
Consumer surplus is $8.
Producer surplus is $8.
Total surplus can be calculated as follows.
Total surplus is $16.
Concept introduction:
Consumer surplus: It is the difference between the highest willing price of the consumer and the actual price that the consumer pays.
Producer surplus: It is the difference between the minimum accepted price for the producer and the actual price received by the producer.
Equilibrium price: It is the market price determined by equating the supply to the demand. At this equilibrium point, the supply will be equal to the demand and there will be no excess demand or
Subpart (b):
The equilibrium price and the quantity of haircuts and total surplus.
Subpart (b):
Explanation of Solution
The world price for the good is $1. Thus, when the country opens the market for trade, the price becomes $1 in domestic country too. Figure 2 describe this situation.
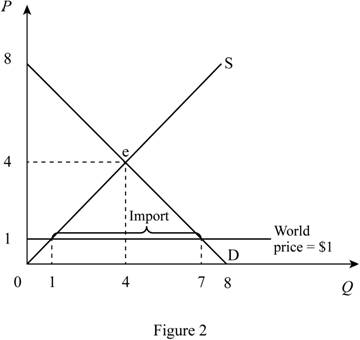
In Figure 2, horizontal axis measures quantity and vertical axis measures price. The curve D indicates demand and the curve S indicates supply. Market reaches the equilibrium at point ‘e’ where the demand curve intersects with supply curve.
When the competitor (Rest of the world) sells a good at price $1, in domestic country equilibrium price become equal to world price. Thus, equilibrium price in the domestic country is $1.
Equilibrium domestic supply can be calculated by substituting the domestic equilibrium price in to supply equation.
Thus, equilibrium quantity is 1 unit.
Equilibrium domestic demand can be calculated by substituting the domestic equilibrium price in to demand equation.
Thus, equilibrium domestic demand is 7 units.
Total imports can be calculated as follows.
Domestic imports are 6 units.
Consumer surplus can be calculated as follows.
Consumer surplus is $24.5.
Producer surplus can be calculated as follows.
Producer surplus is $0.5.
Total surplus can be calculated as follows.
Total surplus is $25.
Concept introduction:
Consumer surplus: It is the difference between the highest willing price of the consumer and the actual price that the consumer pays.
Producer surplus: It is the difference between the minimum accepted price for the producer and the actual price received by the producer.
Equilibrium price: It is the market price determined by equating the supply to the demand. At this equilibrium point, the supply will be equal to the demand and there will be no excess demand or excess supply in an economy. Thus, the economy will be at equilibrium.
Subpar (c):
The equilibrium price and the quantity of haircuts and total surplus.
Subpar (c):
Explanation of Solution
When domestic country impose tariff of $1, the price in domestic country increases from $1 to $2. This increase in price is shown in the Figure 3.
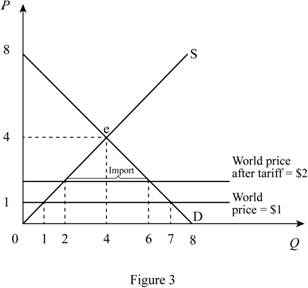
In Figure 3, horizontal axis measures quantity and vertical axis measures price. The curve D indicates demand and the curve S indicates supply. Market reaches the equilibrium at point ‘e’ where the demand curve intersects with supply curve. Price is increases from $1 to $2 due to the tariff of $1.
Domestic equilibrium price can be calculated as follows.
New domestic price is $2.
Equilibrium domestic supply can be calculated by substituting the domestic equilibrium price in to supply equation.
Thus, equilibrium quantity is 2 units.
Equilibrium domestic demand can be calculated by substituting the domestic equilibrium price in to demand equation.
Thus, equilibrium domestic demand is 6 units.
Total imports can be calculated as follows.
Domestic imports are 4 units.
Consumer surplus can be calculated as follows.
Consumer surplus is $18.
Producer surplus can be calculated as follows.
Producer surplus is $2.
Government revenue can be calculated as follows.
Government revenue is 4.
Total surplus can be calculated as follows.
Total surplus is $24.
Concept introduction:
Consumer surplus: It is the difference between the highest willing price of the consumer and the actual price that the consumer pays.
Producer surplus: It is the difference between the minimum accepted price for the producer and the actual price received by the producer.
Equilibrium price: It is the market price determined by equating the supply to the demand. At this equilibrium point, the supply will be equal to the demand and there will be no excess demand or excess supply in an economy. Thus, the economy will be at equilibrium.
Subpart (d):
Calculate total gains and deadweight loss.
Subpart (d):
Explanation of Solution
Total gains from opening up trade can be calculated as follows.
Total gains are$8.
Deadweight loss can be calculated as follows.
Deadweight loss is $1.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS
- I need help in seeing how these are the answers. If you could please write down your steps so I can see how it's done please.arrow_forwardSuppose that a random sample of 216 twenty-year-old men is selected from a population and that their heights and weights are recorded. A regression of weight on height yields Weight = (-107.3628) + 4.2552 x Height, R2 = 0.875, SER = 11.0160 (2.3220) (0.3348) where Weight is measured in pounds and Height is measured in inches. A man has a late growth spurt and grows 1.6200 inches over the course of a year. Construct a confidence interval of 90% for the person's weight gain. The 90% confidence interval for the person's weight gain is ( ☐ ☐) (in pounds). (Round your responses to two decimal places.)arrow_forwardSuppose that (Y, X) satisfy the assumptions specified here. A random sample of n = 498 is drawn and yields Ŷ= 6.47 + 5.66X, R2 = 0.83, SER = 5.3 (3.7) (3.4) Where the numbers in parentheses are the standard errors of the estimated coefficients B₁ = 6.47 and B₁ = 5.66 respectively. Suppose you wanted to test that B₁ is zero at the 5% level. That is, Ho: B₁ = 0 vs. H₁: B₁ #0 Report the t-statistic and p-value for this test. Definition The t-statistic is (Round your response to two decimal places) ☑ The Least Squares Assumptions Y=Bo+B₁X+u, i = 1,..., n, where 1. The error term u; has conditional mean zero given X;: E (u;|X;) = 0; 2. (Y;, X¡), i = 1,..., n, are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) draws from i their joint distribution; and 3. Large outliers are unlikely: X; and Y, have nonzero finite fourth moments.arrow_forward
- Asap pleasearrow_forwardTasks Exercise 1 Assess the following functions: 1. f(x)= x2+6x+2 2.f '(x)=10x-2x2+5 a. Find the stationary points. (5 marks) b. Determine whether the stationary point is a maximum or minimum. (5 marks) c. Draw the corresponding curves (5 marks)arrow_forwardProblem 2: The sales data over the last 10 years for the Acme Hardware Store are as follows: 2003 $230,000 2008 $526,000 2004 276,000 2009 605,000 2005 328,000 2010 690,000 2006 388,000 2011 779,000 2007 453,000 2012 873,000 1. Calculate the compound growth rate for the period of 2003 to 2012. 2. Based on your answer to part a, forecast sales for both 2013 and 2014. 3. Now calculate the compound growth rate for the period of 2007 to 2012. 1. Based on your answer to part e, forecast sales for both 2013 and 2014. 5. What is the major reason for the differences in your answers to parts b and d? If you were to make your own projections, what would you forecast? (Drawing a graph is very helpful.)arrow_forward
- Exercise 4A firm has the following average cost: AC = 200 + 2Q – 36 Q Find the stationary point and determine if it is a maximum or a minimum.b. Find the marginal cost function.arrow_forwardExercise 4A firm has the following average cost: AC = 200 + 2Q – 36 Q Find the stationary point and determine if it is a maximum or a minimum.b. Find the marginal cost function.arrow_forwardExercise 2A firm has the following short-run production function: Q = 30L2 -0.5L3a. Make a table with two columns: Production and Labour b. Add a third column to the table with the marginal product of labour c. Graph the values that you estimated for the production function and the marginal product oflabour Exercise 3A Firm has the following production function: Q= 20L-0.4L2a. Using differential calculus find the unit of labour that maximizes the production. b. Estimate function of Marginal product of labor c. Obtain the Average product of labor. d. Find the point at which the Marginal Product of Labour is equal to the Average Product of Labour.arrow_forward
- Problem 3 You have the following data for the last 12 months' sales for the PRQ Corporation (in thousands of dollars): January 500 July 610 February 520 August 620 March 520 September 580 April 510 October 550 May 530 November 510 June 580 December 480 1. Calculate a 3-month centered moving average. 2. Use this moving average to forecast sales for January of next year. 3. If you were asked to forecast January and February sales for next year, would you be confident of your forecast using the preceding moving averages? Why or why not? expect? Explain.arrow_forwardProblem 5 The MNO Corporation is preparing for its stockholder meeting on May 15, 2013. It sent out proxies to its stockholders on March 15 and asked stockholders who plan to attend the meeting to respond. To plan for a sufficient number of information packages to be distributed at the meeting, as well as for refreshments to be served, the company has asked you to forecast the number of attending stockholders. By April 15, 378 stockholders have expressed their intention to attend. You have available the following data for the last 6 years for total attendance at the stockholder meeting and the number of positive responses as of April 15: Year Positive Responses Attendance 2007 322 520 2008 301 550 2009 398 570 2010 421 600 2011 357 570 2012 452 650 1. What is your attendance forecast for the 2013 stockholder meeting? 2. Are there any other factors that could affect attendance, and thus make your forecast inac- curate?arrow_forwardProblem 4 Office Enterprises (OE) produces a line of metal office file cabinets. The company's economist, having investigated a large number of past data, has established the following equation of demand for these cabinets: Q=10,000+6013-100P+50C Q=Annual number of cabinets sold B = Index of nonresidential construction P = Average price per cabinet charged by OE C=Average price per cabinet charged by OE's closest competitor It is expected that next year's nonresidential construction index will stand at 160, OE's average price will be $40, and the competitor's average price will be $35. 1. Forecast next year's sales. 2. What will be the effect if the competitor lowers its price to 832? If it raises its price to $36? 3. What will happen if OE reacts to the decrease mentioned in part b by lowering its price to $37? 4. If the index forecast was wrong, and it turns out to be only 140 next year, what will be the effect on OE's sales? If not, what does it measure?arrow_forward
 Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506893Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506756Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506756Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning





