
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780321993724
Author: Richard Wolfson
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 80P
A 200-g block is released from rest at a height of 25 cm on a frictionless 30° incline. It slides down the incline and then along a frictionless surface until it collides elastically with an 800-g block at rest 1.4 m from the bottom of the incline (Fig. 9.29). How much later do the two blocks collide again?
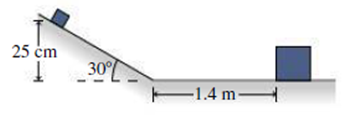
FIGURE 9.29 Problem 80
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A Jamin interferometer is a device for measuring or for comparing the indices of refraction of gases. A beam
of monochromatic light is split into two parts, each of which is directed along the axis of a separate cylindrical
tube before being recombined into a single beam that is viewed through a telescope. Suppose we are given the
following,
•
Length of each tube is L = 0.4 m.
• λ= 598 nm.
Both tubes are initially evacuated, and constructive interference is observed in the center of the field of view. As
air is slowly let into one of the tubes, the central field of view changes dark and back to bright a total of 198
times.
(a) What is the index of refraction for air?
(b) If the fringes can be counted to ±0.25 fringe, where one fringe is equivalent to one complete cycle of
intensity variation at the center of the field of view, to what accuracy can the index of refraction of air be
determined by this experiment?
1. An arrangement of three charges is shown below where q₁ = 1.6 × 10-19 C, q2 = -1.6×10-19 C,
and q3 3.2 x 10-19 C.
2 cm
Y
93
92
91
X
3 cm
(a) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the net force on q₁.
(b) Sketch the direction of the forces on qi
(Figure 1)In each case let w be the weight of the suspended crate full of priceless art objects. The strut is uniform and also has weight w
Find the direction of the force exerted on the strut by the pivot in the arrangement (a).
Express your answer in degrees.
Find the tension Tb in the cable in the arrangement (b).
Express your answer in terms of w.
Find the magnitude of the force exerted on the strut by the pivot in the arrangement (b).
Express your answer in terms of w.
Chapter 9 Solutions
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 9.1GICh. 9.2 - A 500-g fireworks rocket is moving with velocity...Ch. 9.2 - Two skaters toss a basketball back and forth on...Ch. 9.3 - Which of the following systems has (1) zero...Ch. 9.4 - Which of the following qualifies as a collision?...Ch. 9.5 - Which of the following collisions qualify as...Ch. 9.6 - One ball is at rest on a level floor. A second...Ch. 9 - Roughly where is your center of mass when youre...Ch. 9 - Prob. 2FTDCh. 9 - Prob. 3FTD
Ch. 9 - The momentum of a system of pool balls is the same...Ch. 9 - An hourglass is inverted and placed on a scale....Ch. 9 - Why are cars designed so that their front ends...Ch. 9 - Give three everyday examples of inelastic...Ch. 9 - Is it possible to have an inelastic collision in...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9FTDCh. 9 - Why dont we need to consider external forces...Ch. 9 - How is it possible to have a collision between...Ch. 9 - A pitched baseball moves no faster than the...Ch. 9 - Two identical satellites are going in opposite...Ch. 9 - Prob. 14ECh. 9 - Two particles of equal mass m are at the vertices...Ch. 9 - Rework Example 9.1 with the origin at the center...Ch. 9 - Three equal masses lie at the corners of an...Ch. 9 - Prob. 18ECh. 9 - A popcorn kernel at rest in a hot pan bursts into...Ch. 9 - A 60-kg skater, at rest on frictionless ice,...Ch. 9 - A plutonium-239 nucleus at rest decays into a...Ch. 9 - A toboggan of mass 8.6 kg is moving horizontally...Ch. 9 - A 150-g trick baseball is thrown at 60 km/h. It...Ch. 9 - An object with kinetic energy K explodes into two...Ch. 9 - Two 140-kg satellites collide at an altitude where...Ch. 9 - High-speed photos of a 220-g flea jumping...Ch. 9 - Youre working in mission control for an...Ch. 9 - In a railroad switchyard, a 56-ton freight car is...Ch. 9 - In a totally inelastic collision between two equal...Ch. 9 - Prob. 30ECh. 9 - Two identical trucks have mass 5500 kg when empty,...Ch. 9 - An alpha particle (4He) strikes a stationary gold...Ch. 9 - Playing in the street, a child accidentally tosses...Ch. 9 - A block of mass m undergoes a one-dimensional...Ch. 9 - A proton moving at 6.9 Mm/s collides elastically...Ch. 9 - A head-on, elastic collision between two particles...Ch. 9 - Find the center of mass of a pentagon with five...Ch. 9 - Wildlife biologists fire 20-g rubber bullets to...Ch. 9 - Consider a system of three equal-mass particles...Ch. 9 - Youre with 19 other people on a boat at rest in...Ch. 9 - A hemispherical bowl is at rest on a frictionless...Ch. 9 - Physicians perform needle biopsies to sample...Ch. 9 - Find the center of mass of the uniform, solid cone...Ch. 9 - A firecracker, initially at rest, explodes into...Ch. 9 - An 11,000-kg freight car rests against a spring...Ch. 9 - On an icy road, a 1200-kg car moving at 50 km/h...Ch. 9 - A 1250-kg car is moving with velocity...Ch. 9 - Masses m and 3m approach at the same speed v and...Ch. 9 - A 238U nucleus is moving in the x-direction at 5.0...Ch. 9 - A cylindrical concrete silo is 4.0 m in diameter...Ch. 9 - A 42-g firecracker is at rest at the origin when...Ch. 9 - A 60-kg astronaut floating in space simultaneously...Ch. 9 - Assuming equal-mass pieces in Exercise 24, find...Ch. 9 - A 62-kg sprinter stands on the left end of a...Ch. 9 - Youre a production engineer in a cookie factory,...Ch. 9 - Mass m, moving at speed 2v, approaches mass 4m,...Ch. 9 - Verify explicitly that kinetic energy is conserved...Ch. 9 - While standing on frictionless ice, you (mass 65.0...Ch. 9 - Youre an accident investigator at a scene where a...Ch. 9 - A fireworks rocket is launched vertically upward...Ch. 9 - Two objects moving in opposite directions with the...Ch. 9 - Explosive bolts separate a 950-kg communications...Ch. 9 - Youre working in quality control for a model...Ch. 9 - Youre investigating an accident in which a 1040-kg...Ch. 9 - A 400-mg popcorn kernel is skittering across a...Ch. 9 - Two identical objects with the same initial speed...Ch. 9 - A proton (mass 1 u) moving at 6.90 Mm/s collides...Ch. 9 - Two objects, one initially at rest, undergo a...Ch. 9 - Blocks B and C have masses 2m and m, respectively,...Ch. 9 - Derive Equation 9.15b.Ch. 9 - An object collides elastically with an equal-mass...Ch. 9 - A proton (mass 1 u) collides elastically with a...Ch. 9 - Two identical billiard balls are initially at rest...Ch. 9 - Find an expression for the impulse imparted by a...Ch. 9 - A 32-u oxygen molecule (O2) moving in the...Ch. 9 - A 114-g Frisbee is lodged on a tree branch 7.65 m...Ch. 9 - You set a small ball of mass m atop a large ball...Ch. 9 - A car moving at speed v undergoes a...Ch. 9 - A 200-g block is released from rest at a height of...Ch. 9 - A 14-kg projectile is launched at 380 m/s at a 55...Ch. 9 - During a crash test, a car moving at 50 km/h...Ch. 9 - Use numerical or graphical techniques to estimate...Ch. 9 - A block of mass m1 undergoes a one-dimensional...Ch. 9 - Two objects of unequal mass, one initially at...Ch. 9 - Prob. 86PCh. 9 - Find the center of mass of a uniform slice of...Ch. 9 - In a ballistic pendulum demonstration gone bad, a...Ch. 9 - An 80-kg astronaut has become detached from the...Ch. 9 - Prob. 90PCh. 9 - A thin rod extends from x = 0 to x = L. It carries...Ch. 9 - Model rocket motors are specified by giving the...Ch. 9 - A block of mass M is moving at speed r0 on a...Ch. 9 - Youre interested in the intersection of physics...Ch. 9 - Youre interested in the intersection of physics...Ch. 9 - Youre interested in the intersection of physics...Ch. 9 - Youre interested in the intersection of physics...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Which coastal area experiences the largest tidal range difference in height between the high tide and low tide?...
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Describe the 1H NMR spectrum you would expect for each of the following compounds, indicating the relative posi...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Q1. What is the empirical formula of a compound with the molecular formula
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
81. Choose the element with the larger atoms from each pair.
a. Al or In
b. Si or N
c. P or Pb
d. C or F
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
1. How many significant figures does each of the following numbers have?
a. 0.73 b. 7.30 c. 73 d. 0.073
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
2 Of the uterus, small intestine, spinal cord, and heart, which is/are in the dorsal body cavity?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (Figure 1)In each case let ww be the weight of the suspended crate full of priceless art objects. The strut is uniform and also has weight w. Find the direction of the force exerted on the strut by the pivot in the arrangement (b). Express your answer in degrees.arrow_forwardA 70.0 cm, uniform, 40.0 N shelf is supported horizontally by two vertical wires attached to the sloping ceiling (Figure 1). A very small 20.0 N tool is placed on the shelf midway between the points where the wires are attached to it. Find the tension in the left-hand wire. Express your answer with the appropriate units.arrow_forwardFind the total bind Mev. binding energy for 13 Carbon, 6C (atomic mass = 13.0033554)arrow_forward
- What is the 27 energy absorbed in this endothermic Auclear reaction 2] Al + 'n → 27 Mg + ! H? (The atom mass of "Al is 26.981539u. and that of 11 Mg is 26.984341u) MeVarrow_forwardWhat is the energy released in this nuclear reaction 1 F + "', H-1 O+ He? 19 19 16 (The atomic mass of 1F is 18.998403 u, and that of 20 is 15.9949154) MeV.arrow_forwardWhat is the energy released in this B+ nuclear reaction خالد 2½ Al w/ Mg + ie? (The atomic mass of 11 Al is 23.9999394 and that > of 12 Mg is 23.985041 u) MeV.arrow_forward
- What is the energy released / absorbed in this nuclear reaction 14 N+ & He → » O + ! N? (The atomic mass of 14 N is 14.003074u. 17N+ and that of 10 is 16.9991324). MeVarrow_forwardCan someone help me answer this question thanks.arrow_forwardCan someone help me with this question thanks.arrow_forward
- 4B. Four electrons are located on the corners of a square, one on each corner, with the sides of the square being 25 cm long. a) Draw a sketch of the scenario and use your sketch to b) Determine the total force (magnitude and direction) on one of the electrons from the other three?arrow_forwardPortfolio Problem 3. A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a speed vo from the floor of a room of height h. It hits the ceiling and then returns to the floor, from which it rebounds, managing just to hit the ceiling a second time. Assume that the coefficient of restitution between the ball and the floor, e, is equal to that between the ball and the ceiling. Compute e.arrow_forwardPortfolio Problem 4. Consider two identical springs, each with natural length and spring constant k, attached to a horizontal frame at distance 2l apart. Their free ends are attached to the same particle of mass m, which is hanging under gravity. Let z denote the vertical displacement of the particle from the hori- zontal frame, so that z < 0 when the particle is below the frame, as shown in the figure. The particle has zero horizontal velocity, so that the motion is one dimensional along z. 000000 0 eeeeee (a) Show that the total force acting on the particle is X F-mg k-2kz 1 (1. l k. (b) Find the potential energy U(x, y, z) of the system such that U x = : 0. = O when (c) The particle is pulled down until the springs are each of length 3l, and then released. Find the velocity of the particle when it crosses z = 0.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Elastic and Inelastic Collisions; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M2xnGcaaAi4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY