
Physics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780321625915
Author: Douglas C. Giancoli
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 5Q
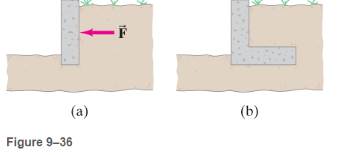
A ground retaining wall is shown in Fig. 9-36a .The ground, particularly when wet, can exert a significant force F on the wall, (a) What force produces the torque to keep the wall upright? (b)Explain why the retaining wall in Fig. 9-36bwould be much less likely to overturn than that in Fig. 9-36a
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
d
need help with the one i got wrong
Identify which of the following vectors are parallel to A.
Vector
Vector A
70°
60°
20°
AAZA!
30°
20°
20°
70°
20°
20°
70°
20°
Chapter 9 Solutions
Physics
Ch. 9 - Prob. 1OQCh. 9 - Describe several situations in which an object is...Ch. 9 - Prob. 2QCh. 9 - You can find the center of gravity of a meter...Ch. 9 - Prob. 4QCh. 9 - A ground retaining wall is shown in Fig. 9-36a...Ch. 9 - Can the sum of the torques on an object be zero...Ch. 9 - A ladder, leaning against a wall, makes a 60°...Ch. 9 - A uniform meter stick supported at the 25-cm mark...Ch. 9 - Why do you tend to lean backward when carrying a...
Ch. 9 - Figure 9-38 shows a cone. Explain how to lay it on...Ch. 9 - Prob. 11QCh. 9 - Why is it not possible to sit upright in a chair...Ch. 9 - Why is it more difficult to do sit-ups when your...Ch. 9 - Explain why touching your toes while you are...Ch. 9 - Prob. 15QCh. 9 - Name the type of equilibrium for each position of...Ch. 9 - (
17.
)
Is the Young's modulus for a bungee cord...Ch. 9 - Prob. 18QCh. 9 - Prob. 19QCh. 9 - A 60-kg woman stands on the very end of a uniform...Ch. 9 - Prob. 2MCQCh. 9 - Prob. 3MCQCh. 9 - Prob. 4MCQCh. 9 - Two children are balanced on opposite sides of a...Ch. 9 - Prob. 6MCQCh. 9 - Prob. 7MCQCh. 9 - Prob. 8MCQCh. 9 - Prob. 9MCQCh. 9 - Prob. 10MCQCh. 9 - Three forces are applied to a tree sapling, as...Ch. 9 - Prob. 2PCh. 9 - 3(I) A tower crane ( Fig. 9-48a) must always be...Ch. 9 - What is the mass of the diver in Fig. 9-49 if she...Ch. 9 - Prob. 5PCh. 9 - Figure 9-50 shows a pair of forceps used to hold a...Ch. 9 - Prob. 7PCh. 9 - The two trees in Fig. 9-51 are 6.6 m apart. A...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9PCh. 9 - Prob. 10PCh. 9 - Prob. 11PCh. 9 - Find the tension in the two cords shown in Fig....Ch. 9 - Prob. 13PCh. 9 - Prob. 14PCh. 9 - The force required to pull the cork out of the top...Ch. 9 - Prob. 16PCh. 9 - Three children are trying to balance on a seesaw,...Ch. 9 - A shop sign weighing 215 N hangs from the end of a...Ch. 9 - Prob. 19PCh. 9 - Prob. 20PCh. 9 - Prob. 21PCh. 9 - 22 (II) A 20.0-m-long uniform beam weighing 650 N...Ch. 9 - Prob. 23PCh. 9 - Prob. 24PCh. 9 - Prob. 25PCh. 9 - Prob. 26PCh. 9 - A uniform rod AB of length 5.0 m and mass M=3.S kg...Ch. 9 - You are on a pirate ship and being forced to walk...Ch. 9 - Prob. 29PCh. 9 - Prob. 30PCh. 9 - Prob. 31PCh. 9 - Prob. 32PCh. 9 - Prob. 33PCh. 9 - Prob. 34PCh. 9 - Prob. 35PCh. 9 - 36 (II) The Achilles tendon is attached to the...Ch. 9 - If 25 kg is the maximum mass m that a person can...Ch. 9 - Prob. 38PCh. 9 - Prob. 39PCh. 9 - Prob. 40PCh. 9 - A marble column of cross-sectional area 1.4 m2...Ch. 9 - Prob. 42PCh. 9 - A sign (mass 1700 kg) hangs from the bottom end of...Ch. 9 - Prob. 44PCh. 9 - Prob. 45PCh. 9 - Prob. 46PCh. 9 - A steel wire 2.3 mm in diameter stretches by...Ch. 9 - Prob. 48PCh. 9 - Prob. 49PCh. 9 - Prob. 50PCh. 9 - Prob. 51PCh. 9 - Prob. 52PCh. 9 - (a) What is the minimum cross-sectional area...Ch. 9 - Prob. 54PCh. 9 - Prob. 55PCh. 9 - Prob. 56PCh. 9 - Prob. 57PCh. 9 - Prob. 58GPCh. 9 - Prob. 59GPCh. 9 - Prob. 60GPCh. 9 - Prob. 61GPCh. 9 - Prob. 62GPCh. 9 - Prob. 63GPCh. 9 - Prob. 64GPCh. 9 - When a mass of 25 kg is hung from the middle of a...Ch. 9 - Prob. 66GPCh. 9 - Prob. 67GPCh. 9 - Prob. 68GPCh. 9 - Prob. 69GPCh. 9 - Prob. 70GPCh. 9 - Prob. 71GPCh. 9 - Prob. 72GPCh. 9 - Prob. 73GPCh. 9 - A 2.0-m-high box with a 1.0-m-square base is moved...Ch. 9 - Prob. 75GPCh. 9 - Prob. 76GPCh. 9 - Prob. 77GPCh. 9 - Prob. 78GPCh. 9 - In a mountain-climbing technique called the...Ch. 9 - Prob. 80GPCh. 9 - A cubic crate of side s=20m is top-heavy: its cgis...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
In mice, black coat color is dominant to white coat color. In the pedigree shown here, mice with a black coat a...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Q2. A graduated cylinder has markings every milliliter. Which measurement is accurately reported for this gradu...
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Match each of the following items with all the terms it applies to:
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
27. Consider the reaction.
Express the rate of the reaction in terms of the change in concentration of each of...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
2. Define equilibrium population. Outline the conditions that must be met for a population to stay in genetic e...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Acetobacter is necessary for only one of the steps of vitamin C manufacture. The easiest way to accomplish this...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3aarrow_forward44 please help with the this.arrow_forward4a Which of the following values COULD NOT be a magnitude? Choose all that apply. 626 0 -0.806 8.63 -48.5 72 131 156 4b Px = -1248 & Py = 261. Determine P.P = Qx = -1540 & Qy = 375. Determine Q.Q = 4c. T = 1105 & Ty = 425. Determine the two possible values for Tx. 4d. Uy = -38. Which of the following COULD NOT be the value of U? Choose all that apply. 10 70 72 31 47 0 75 38 4e. R has a magnitude of 165. Which of the following COULD be Rx? Choose all that apply. 165 -171 155 0 -156 -165 172 -130arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University
What is Torque? | Physics | Extraclass.com; Author: Extraclass Official;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zXxrAJld9mo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY