
Concept explainers
Complete the following table:
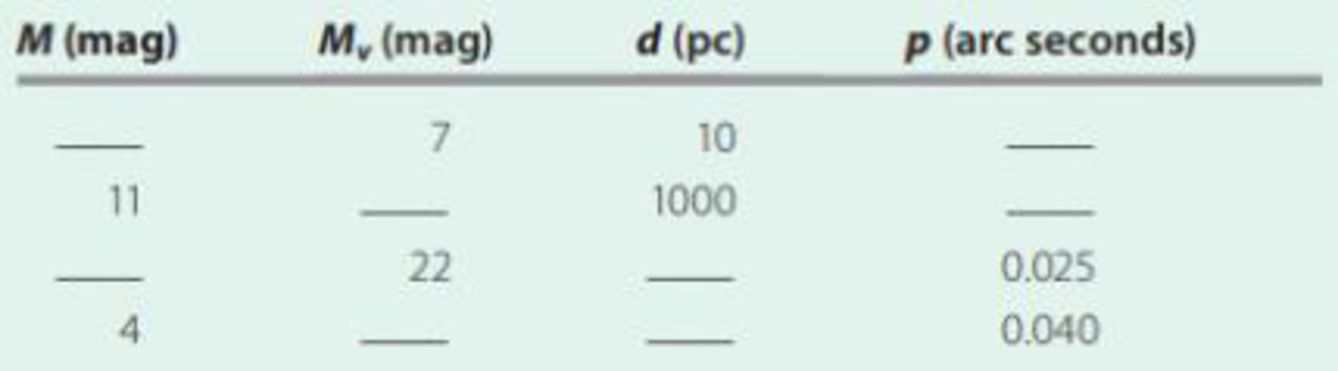
Complete the given table with proper values.
Answer to Problem 5P
The required table is given below:
| | | | |
| 7 | 7 | 10 | 0.1 |
| 11 | 1 | 1000 | 0.001 |
| 25 | 22 | 40 | 0.025 |
| 4 | 2 | 25 | 0.040 |
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for the relation between absolute and apparent visual magnitude.
Here,
Write the expression between the relation of distance and parallax distance.
Here,
Conclusion:
First table:
Substitute,
Substitute,
Second table:
Substitute,
Substitute,
Third table:
Substitute,
Substitute,
Fourth table:
Substitute,
Substitute,
Thus, the required table is given below:
| | | | |
| 7 | 7 | 10 | 0.1 |
| 11 | 1 | 1000 | 0.001 |
| 25 | 22 | 40 | 0.025 |
| 4 | 2 | 25 | 0.040 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
FOUNDATIONS OF ASTRONOMY (LL)-W/MINDTAP
- Hi! I need help with these calculations for part i and part k for a physics Diffraction Lab. We used a slit width 0.4 mm to measure our pattern.arrow_forwardExamine the data and % error values in Data Table 3 where the angular displacement of the simple pendulum decreased but the mass of the pendulum bob and the length of the pendulum remained constant. Describe whether or not your data shows that the period of the pendulum depends on the angular displacement of the pendulum bob, to within a reasonable percent error.arrow_forwardIn addition to the anyalysis of the graph, show mathematically that the slope of that line is 2π/√g . Using the slope of your line calculate the value of g and compare it to 9.8.arrow_forward
- An object is placed 24.1 cm to the left of a diverging lens (f = -6.51 cm). A concave mirror (f= 14.8 cm) is placed 30.2 cm to the right of the lens to form an image of the first image formed by the lens. Find the final image distance, measured relative to the mirror. (b) Is the final image real or virtual? (c) Is the final image upright or inverted with respect to the original object?arrow_forwardConcept Simulation 26.4 provides the option of exploring the ray diagram that applies to this problem. The distance between an object and its image formed by a diverging lens is 5.90 cm. The focal length of the lens is -2.60 cm. Find (a) the image distance and (b) the object distance.arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward
 Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
 AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax Horizons: Exploring the Universe (MindTap Course ...PhysicsISBN:9781305960961Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Horizons: Exploring the Universe (MindTap Course ...PhysicsISBN:9781305960961Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning





