
EBK COLLEGE PHYSICS, VOLUME 2
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781337514644
Author: Vuille
Publisher: CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 37P
A hypodermic syringe contain a medicine with the density of water (Fig. P9.37). The barrel of the syringe has a cross-sectional area of in the absence of a force on the plunger, the pressure everywhere is 1.00 atm. A force
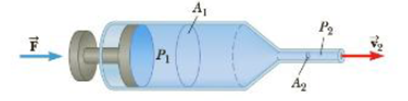
Figure P9.37
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
How can you tell which vowel is being produced here ( “ee,” “ah,” or “oo”)? Also, how would you be able to tell for the other vowels?
You want to fabricate a soft microfluidic chip like the one below. How would you go about
fabricating this chip knowing that you are targeting a channel with a square cross-sectional
profile of 200 μm by 200 μm. What materials and steps would you use and why? Disregard the
process to form the inlet and outlet.
Square Cross Section
1. What are the key steps involved in the fabrication of a semiconductor device.
2. You are hired by a chip manufacturing company, and you are asked to prepare a silicon wafer
with the pattern below. Describe the process you would use.
High Aspect
Ratio
Trenches
Undoped Si Wafer
P-doped Si
3. You would like to deposit material within a high aspect ratio trench. What approach would you
use and why?
4. A person is setting up a small clean room space to carry out an outreach activity to educate high
school students about patterning using photolithography. They obtained a positive photoresist, a
used spin coater, a high energy light lamp for exposure and ordered a plastic transparency mask
with a pattern on it to reduce cost. Upon trying this set up multiple times they find that the full
resist gets developed, and they are unable to transfer the pattern onto the resist. Help them
troubleshoot and find out why pattern of transfer has not been successful.
5. You are given a composite…
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK COLLEGE PHYSICS, VOLUME 2
Ch. 9.2 - Suppose you have one cubic meter of gold, two...Ch. 9.3 - The pressure at the bottom of a glass filled with...Ch. 9.4 - Several common barometers are built using a...Ch. 9.4 - Blood pressure is normally measured with the cuff...Ch. 9.5 - Atmospheric pressure varies from day to day. The...Ch. 9.5 - The density of lead is greater than iron, and both...Ch. 9.6 - You observe two helium balloons floating next to...Ch. 9 - The three containers in Figure CQ9.1 are filled...Ch. 9 - The density of air is 1.3 kg/m3 at sea level. From...Ch. 9 - Four solid, uniform objects are placed in a...
Ch. 9 - Figure CQ9.4 shows aerial views from directly...Ch. 9 - Prob. 5CQCh. 9 - Prob. 6CQCh. 9 - Water flows along a streamline down a river of...Ch. 9 - During inhalation, the pressure in the lungs is...Ch. 9 - The water supply for a city is often provided from...Ch. 9 - An ice cube is placed in a glass of water. What...Ch. 9 - Prob. 11CQCh. 9 - Will an ice cube float higher in water or in an...Ch. 9 - Prob. 13CQCh. 9 - Prob. 14CQCh. 9 - A person in a boat floating in a small pond throws...Ch. 9 - One of the predicted problems due to global...Ch. 9 - An 81.5kg man stands on a horizontal surface. (a)...Ch. 9 - The weight of Earths atmosphere exerts an average...Ch. 9 - Calculate the mass of a solid gold rectangular bar...Ch. 9 - Prob. 5PCh. 9 - Prob. 6PCh. 9 - Suppose a distant world with surface gravity of...Ch. 9 - Prob. 8PCh. 9 - (a) Calculate the absolute pressure at the bottom...Ch. 9 - Mercury is poured into a U-tube as shown in Figure...Ch. 9 - A collapsible plastic bag (Fig. F9.11) contains a...Ch. 9 - A hydraulic jack has an input piston of area 0.050...Ch. 9 - A container is filled to a depth of 20.0 cm with...Ch. 9 - Blaise Pascal duplicated Torricellis barometer...Ch. 9 - A sphygmomanometer is a device used to measure...Ch. 9 - Piston in Figure P9.16 has a diameter of 0.25...Ch. 9 - Buoyant Forces and Archimedes Principle A...Ch. 9 - Prob. 18PCh. 9 - A small ferryboat is 4.00 m wide and 6.00 m long....Ch. 9 - A 62.0-kg survivor of a cruise line disaster rests...Ch. 9 - A hot-air balloon consists of a basket banging...Ch. 9 - A large balloon of mass 226 kg is filled with...Ch. 9 - A spherical weather balloon is filled with...Ch. 9 - The average human has a density of 945 kg/m3 after...Ch. 9 - On October 21, 2001, Ian Ashpole of the United...Ch. 9 - The gravitational force exerted on a solid object...Ch. 9 - A cube of wood having an edge dimension of 20.0 cm...Ch. 9 - A light spring of force constant k = 160 N/m rests...Ch. 9 - A sample of an unknown material appears to weigh...Ch. 9 - An object weighing 300 N in air is immersed in...Ch. 9 - A 1.00-kg beaker containing 2.00 kg of oil...Ch. 9 - A horizontal pipe narrows from a radius of 0.250 m...Ch. 9 - A large water tank is 3.00 m high and filled lo...Ch. 9 - Wafer flowing through a garden hose of diameter...Ch. 9 - Prob. 35PCh. 9 - Prob. 36PCh. 9 - A hypodermic syringe contain a medicine with the...Ch. 9 - When a person inhales, air moves down the bronchus...Ch. 9 - A jet airplane in level flight has a mass of 8.66 ...Ch. 9 - A man attaches a divider to an outdoor faucet so...Ch. 9 - Prob. 41PCh. 9 - Prob. 42PCh. 9 - A jet of water squirts out horizontally from a...Ch. 9 - A large storage tank, open to the atmosphere at...Ch. 9 - The inside diameters of the larger portions of the...Ch. 9 - Water is pumped through a pipe of diameter 15.0 cm...Ch. 9 - Old Faithful geyser in Yellowstone Park erupts at...Ch. 9 - The Venturi tube shown in Figure P9.48 may be used...Ch. 9 - Prob. 49PCh. 9 - Prob. 50PCh. 9 - A certain fluid has a density of 1.080 kg/m3 and...Ch. 9 - Whole blood has a surface tension of 0.058 N/m and...Ch. 9 - Prob. 53PCh. 9 - Prob. 54PCh. 9 - Prob. 55PCh. 9 - Prob. 56PCh. 9 - Spherical panicles of a protein of density 1.8...Ch. 9 - A hypodermic needle is 3.0 era in length and 0.30...Ch. 9 - Prob. 59PCh. 9 - The aorta in humans has a diameter of about 2.0...Ch. 9 - Prob. 61PCh. 9 - Glycerin in water diffuses along a horizontal...Ch. 9 - Prob. 63PCh. 9 - Small spheres of diameter 1.00 mm fall through 20C...Ch. 9 - The Deformation of Solids 65. A 200.-kg load is...Ch. 9 - A 25.0-m long steel cable with a cross-sectional...Ch. 9 - A plank 2.00 cm thick and 15.0 cm wide is firmly...Ch. 9 - Artificial diamonds can be made using...Ch. 9 - For safety in climbing, a mountaineer uses a nylon...Ch. 9 - Assume that if the shear stress in steel exceeds...Ch. 9 - Bone has a Youngs modulus of 18 109 Pa. Under...Ch. 9 - A stainless-steel orthodontic: wire is applied to...Ch. 9 - A high-speed lifting mechanism supports an 800.-kg...Ch. 9 - The deepest point in the ocean is in the Mariana...Ch. 9 - Prob. 75PCh. 9 - The total cross-sectional area of the load-bearing...Ch. 9 - An iron block of volume 0.20 m5 is suspended from...Ch. 9 - Prob. 78APCh. 9 - In most species of clingfish (family...Ch. 9 - Prob. 80APCh. 9 - Prob. 81APCh. 9 - Superman attempts to drink water through a very...Ch. 9 - The human brain and spinal cord are immersed in...Ch. 9 - A Hydrometer is an instrument used to determine...Ch. 9 - Prob. 85APCh. 9 - A helium-filled balloon, whose envelope has a mass...Ch. 9 - A light spring of constant A = 90.0 N/m is...Ch. 9 - A U-tube open at both ends is partially filled...Ch. 9 - In about 1657. Otto von Guericke, inventor of the...Ch. 9 - Oil having a density of 930 kg/m3 floats on water....Ch. 9 - Prob. 91AP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find r and θ for (z1-z∗2)/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2∗)z1z2∗ Please show all stepsarrow_forwardAn electromagnetic wave is traveling through vacuum in the positive x direction. Its electric field vector is given by E=E0sin(kx−ωt)j^,where j^ is the unit vector in the y direction. If B0 is the amplitude of the magnetic field vector, find the complete expression for the magnetic field vector B→ of the wave. What is the Poynting vector S(x,t), that is, the power per unit area associated with the electromagnetic wave described in the problem introduction? Give your answer in terms of some or all of the variables E0, B0, k, x, ω, t, and μ0. Specify the direction of the Poynting vector using the unit vectors i^, j^, and k^ as appropriate. Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardAnother worker is performing a task with an RWL of only 9 kg and is lifting 18 kg, giving him an LI of 2.0 (high risk). Questions:What is the primary issue according to NIOSH?Name two factors of the RWL that could be improved to reduce risk.If the horizontal distance is reduced from 50 cm to 30 cm, how does the HM change and what effect would it have?arrow_forward
- Two complex values are z1=8 + 8i, z2=15 + 7 i. z1∗ and z2∗ are the complex conjugate values. Any complex value can be expessed in the form of a+bi=reiθ. Find r and θ for z1z2∗. Find r and θ for z1/z2∗? Find r and θ for (z1−z2)∗/z1+z2∗. Find r and θ for (z1−z2)∗/z1z2∗ Please explain all steps, Thank youarrow_forwardAn ac series circuit consists of a voltage source of frequency 60 Hz and voltage amplitude V, a 505-Ω resistor, and a capacitor of capacitance 7.2 μF. What must be the source voltage amplitude V for the average electrical power consumed in the resistor to be 236 W? There is no inductance in the circuit.arrow_forwardAn L−R−C series circuit has R= 280 Ω . At the frequency of the source, the inductor has reactance XLL= 905 Ω and the capacitor has reactance XC= 485 Ω . The amplitude of the voltage across the inductor is 445 V . What is the amplitude of the voltage across the resistor and the capacitor? What is the voltage amplitude of the source? What is the rate at which the source is delivering electrical energy to the circuit?arrow_forward
- A 0.185 H inductor is connected in series with a 98.5 Ω resistor and an ac source. The voltage across the inductor is vL=−(12.5V)sin[(476rad/s)t]vL. Derive an expression for the voltage vR across the resistor. Express your answer in terms of the variables L, R, VL (amplitude of the voltage across the inductor), ω, and t. What is vR at 2.13 ms ? Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardA worker lifts a box under the following conditions:Horizontal distance (H): 30 cmInitial height (V): 60 cmVertical travel (D): 50 cmTorso rotation (A): 30°Frequency: 3 times/minute for 1 hourGrip: Good Question:What is the RWL for this task?What does this value mean in terms of occupational safety?arrow_forwardCan someone helparrow_forward
- Can someone help mearrow_forward3. Four identical small masses are connected in a flat perfect square. Rank the relative rotational inertias (IA, IB, IC) about the three axes of rotation shown. Axes A and B are in the plane of the square, and axis C is perpendicular to the plane, through mass m1. ΙΑ IB m2 m1 m3 Ic m4 (a) IAarrow_forwardConsider the circuit shown in the figure below. (Assume L = 5.20 m and R2 = 440 Ω.) (a) When the switch is in position a, for what value of R1 will the circuit have a time constant of 15.4 µs? (b) What is the current in the inductor at the instant the switch is thrown to position b?arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Fluids in Motion: Crash Course Physics #15; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fJefjG3xhW0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY