
Concept explainers
To Write:
A menu-driven program that will read in an employee data base for a company from a file and do specified operations on the data. The file stores the following information for each employee:
• Name
• Department
• Birth Date
• Date Hired
• Annual Salary
• Office Phone Extension
You are to decide exactly how this information is to be stored in the file. Design the layout of the file, and then create a sample data file in this format to use when testing your program. The format of the file is up to you. However, space is critical. Do not use any more characters in your file than you have to! Your program is to read the information from the file into a data structure, and then display a menu of options for operations to be done on the data. You may not assume in your program that you know the length of the data file. The menu options are:
1. Print all of the information in an easy-to-read format to a new file.
2. Print the information for a particular department.
3. Calculate the total payroll for the company (the sum of the salaries).
4. Find out how many employees have been with the company for N years (N might be 10, for example).
5. Exit the program.
Answer to Problem 33E
Solution:
The script is saved and executed as follows.
Explanation of Solution
MATLAB Code:
%MATLAB code to create only considers years.
%
function nyears(emps)
%Define the function to create only considers years.
hiredyears = zeros(1, length(emps));
for i = 1:length(emps)
hiredyears(i) = str2num(emps(i).hired(5:6)) + 1900;
end
current_year = 2013;
N = 20;
fy = find(current_year-hiredyears >= N);
fprintf('%d employees have worked at least %d years.\n\n', length(fy), N)
end
%end of function
%The script file should be placed in the same folder.
%MATLAB code to prints the menu of options and error-checks.
%Function file
function choice_selection = options
%Define the function to prints the menu of options and error-checks.
%until the user pushes one of the buttons
choice_selection = menu('Choose an option', 'Print all', 'Print dept', 'Payroll', 'N years', 'Exit Program');
%Define the statemnet to check the condition if the user closes the menu box rather than
%pushing one of the buttons, choice will be 0.
while choice_selection == 0
disp('Error-please choose one of the options.')
choice_selection = menu('Choose an option', 'Print all', 'Print dept', 'Payroll', 'N years', 'Exit Program');
end
end
%end of function
%The script file should be placed in the same folder.
%MATLAB code to calculate the employee payroll.
%Function file
function payroll(salaries)
fprintf('The total of the salaries is $%.2f.\n\n', ...
sum(salaries))
end
%end of function
%The script file should be placed in the same folder.
%MATLAB code to write to screen; could change to write to file.
%Function file
function printall(emp)
%Define the function to write to screen; could change to write to file.
fprintf('%-15s%-8s%11s%11s %-10s %5s\n\n', 'Name', 'Dept', ...
'Birth Date', 'Hire Date', 'salary', 'Phone')
for i = 1:length(emp)
fprintf('%-15s%-8s', emp(i).name, emp(i).dept)
b = emp(i).birth;
birthdate = sprintf('%s-%s-19%s', b(1:2), b(3:4), b(5:6));
h = emp(i).hired;
hiredate = sprintf('%s-%s-19%s', h(1:2), h(3:4), h(5:6));
fprintf('%11s%11s', birthdate, hiredate)
fprintf('$%9.2f x%s\n', emp(i).salary, emp(i).phone)
end
end
%end of function
%The script file should be placed in the same folder.
%MATLAB code to check the condition if the user closes the menu box rather than pushing one of the buttons, choice will be 0.
%Function file
function printdept(emp)
choice_selection = menu('Choose Dept', 'sales','service', 'Trucking');
%Define the instruction to check the condition if the user closes the menu box rather than
%pushing one of the buttons, choice will be 0.
while choice_selection == 0
disp('Error-please choose one of the options.')
choice_selection = menu('Choose Dept', 'sales', 'service', 'Trucking');
end
ca = {'sales','service','Trucking'};
chosen = ca{choice_selection};
fprintf('%-15s%-8s%11s%11s %-10s %5s\n\n', 'Name', 'Dept','Birth Date', 'Hire Date', 'salary', 'Phone')
for i = 1:length(emp)
if strcmp(emp(i).dept, chosen)
fprintf('%-15s%-8s', emp(i).name, emp(i).dept)
b = emp(i).birth;
birthdate = sprintf('%s-%s-19%s', b(1:2), b(3:4), b(5:6));
h = emp(i).hired;
hiredate = sprintf('%s-%s-19%s', h(1:2), h(3:4), h(5:6));
fprintf('%11s%11s', birthdate, hiredate)
fprintf('$%9.2f x%s\n', emp(i).salary, emp(i).phone)
end
end
end
%end of function
%The script file should be placed in the same folder.
%MATLAB code to read the employees.
%Function file
function emp = reademployees
%Define the function to read the employees.
emp(2).name = 'Akhilesh, Abhishek';
emp(2).dept = 'service';
emp(2).birth = '072267';
emp(2).hired = '121298';
emp(2).salary = 87333;
emp(2).phone = '5388';
emp(1).name = 'Mohit, Roy';
emp(1).dept = 'sales';
emp(1).birth = '072267';
emp(1).hired = '121288';
emp(1).salary = 77333;
emp(1).phone = '5389';
%Define the instruction to create the employee name, departemnt,
%birth date, hired department, salary and phone number.
end
%end of function
%The script file should be placed in the same folder.
%....................Start of the script file.............................
employees = reademployees;
%Define the instrcution to creates an employee data base for a company and
%performs some operations on the data.
Choice_Selection = options;
%Define the instruction to read the info from a file.
while Choice_Selection ~= 5
switch Choice_Selection
%Define the instruction to call a function to display a menu and get choice
case 1
printall(employees)
%Define the instruction to prints all of the info to a file.
case 2
printdept(employees)
%Define the instruction to prints info for one department.
case 3
payroll([employees.salary])
%Define the instruction to prints total payroll.
case 4
nyears(employees)
%Define the instruction to prints employees >= N years.
end
Choice_Selection = options;
%Define the instruction to display menu again and get user's choice.
end
Save the MATLAB script with name, chapter_9_54793_9_33E.m in the current folder. Execute the script by typing the string name at the command window to write A menu-driven program that will read in an employee data base for a company from a file and do specified operations on the data. The file stores the following information for each employee:
• Name
• Department
• Birth Date
• Date Hired
• Annual Salary
• Office Phone Extension
You are to decide exactly how this information is to be stored in the file. Design the layout of the file, and then create a sample data file in this format to use when testing your program. The format of the file is up to you. However, space is critical. Do not use any more characters in your file than you have to! Your program is to read the information from the file into a data structure, and then display a menu of options for operations to be done on the data. You may not assume in your program that you know the length of the data file. The menu options are:
1. Print all of the information in an easy-to-read format to a new file.
2. Print the information for a particular department.
3. Calculate the total payroll for the company (the sum of the salaries).
4. Find out how many employees have been with the company for N years (N might be 10, for example).
Result:
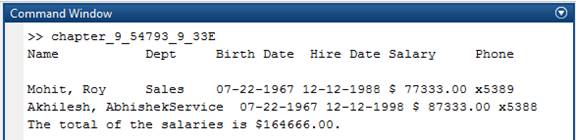
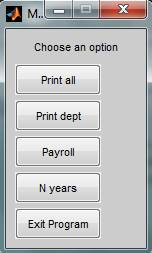
Therefore, the script is saved and executed.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
MATLAB: A Practical Introduction to Programming and Problem Solving
- Should you be confident in applying your regression equation to estimate the heart rate of a python at 35°C? Why or why not?arrow_forwardGiven your fitted regression line, what would be the residual for snake #5 (10 C)?arrow_forwardCalculate the 95% confidence interval around your estimate of r using Fisher’s z-transformation. In your final answer, make sure to back-transform to the original units.arrow_forward
- BUSINESS DISCUSSarrow_forwardA researcher wishes to estimate, with 90% confidence, the population proportion of adults who support labeling legislation for genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Her estimate must be accurate within 4% of the true proportion. (a) No preliminary estimate is available. Find the minimum sample size needed. (b) Find the minimum sample size needed, using a prior study that found that 65% of the respondents said they support labeling legislation for GMOs. (c) Compare the results from parts (a) and (b). ... (a) What is the minimum sample size needed assuming that no prior information is available? n = (Round up to the nearest whole number as needed.)arrow_forwardThe table available below shows the costs per mile (in cents) for a sample of automobiles. At a = 0.05, can you conclude that at least one mean cost per mile is different from the others? Click on the icon to view the data table. Let Hss, HMS, HLS, Hsuv and Hмy represent the mean costs per mile for small sedans, medium sedans, large sedans, SUV 4WDs, and minivans respectively. What are the hypotheses for this test? OA. Ho: Not all the means are equal. Ha Hss HMS HLS HSUV HMV B. Ho Hss HMS HLS HSUV = μMV Ha: Hss *HMS *HLS*HSUV * HMV C. Ho Hss HMS HLS HSUV =μMV = = H: Not all the means are equal. D. Ho Hss HMS HLS HSUV HMV Ha Hss HMS HLS =HSUV = HMVarrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning





