
To find: The
Introduction:
The variation between the present value of the cash outflows and the present value of the cash inflows is known as net present value. In capital budgeting, the net present value is utilized to analyze the profitability of a project or investment. The rate of return which equates the initial investment and the present value of net cash inflows are referred to as internal rate of return. This is also called as actual rate of return.
Answer to Problem 25QP
The net
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Company a projects the unit sale for the new 7-octave voice emulation implant as follows:
- The year 1 unit sales is 87,500.
- The year 2 unit sales is 105,000.
- The year 3 unit sales is 119,000.
- The year 4 unit sales is 108,000.
- The year 5 unit sales is 92,000.
The production implant needs $1,500,000 in the net working capital to begin their production activities. The extra net working capital investment for every year is equivalent to the 15% of the projected sales, which has to rise for the following year. The total fixed cost is $1,450,000 for a year, the unit price is $230, and the variable production cost is $355. The installation cost of the equipment is $24,000,000.
The equipment is qualified in the 7-Year MACRS
MACRS depreciation table for year 7:
| MACRS Depreciation table for seven year | |
| Year | Seven year |
| 1 | 14.29% |
| 2 | 24.49% |
| 3 | 17.49% |
| 4 | 12.49% |
| 5 | 8.93% |
| 6 | 8.92% |
| 7 | 8.93% |
| 8 | 4.46% |
Computation of the
Calculations:
The sales figure for every year along with the unit price is given. The variable cost for a unit is utilized to compute the total variable cost and the fixed cost are stated as $1,450,000 for a year.
The depreciation is calculated by using the initial cost of the equipment, which is $24,000,000 times the actual MACRS depreciation for every year. At the bottom of the of the income statement, the depreciation is added back to determine the operating cash flow for every year.
Table showing the cash inflows:
| Year | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Ending book value | $20,570,400 | $14,692,800 | $10,495,200 | $7,497,600 | $5,354,400 | ||
| Sales | $31,062,500 | $37,275,000 | $42,245,000 | $38,340,000 | $32,660,000 | ||
| Less: Variable costs | 20,125,000 | 24,150,000 | 27,370,000 | 24,840,000 | 21,160,000 | ||
| Fixed costs | 1,450,000 | 1,450,000 | 1,450,000 | 1,450,000 | 1,450,000 | ||
| Depreciation | 3,429,600 | 5,877,600 | 4,197,600 | 2,997,600 | 2,143,200 | ||
| EBIT | $6,057,900 | $5,797,400 | $9,227,400 | $9,052,400 | $7,906,800 | ||
| Less: Taxes | 2,120,265 | 2,029,090 | 3,229,590 | 3,168,340 | 2,767,380 | ||
| Net income | $3,937,635 | $3,768,310 | $5,997,810 | $5,884,060 | $5,139,420 | ||
| Add: Depreciation | 3,429,600 | 5,877,600 | 4,197,600 | 2,997,600 | 2,143,200 | ||
| Operating cash flow | $7,367,235 | $9,645,910 | $10,195,410 | $8,881,660 | $7,282,620 | ||
| Net cash inflows: | |||||||
| Operating cash flow | $7,367,235 | $9,645,910 | $10,195,410 | $8,881,660 | $7,282,620 | ||
| Change in net working capital | (931,875) | (745,500) | 585,750 | 852,000 | 1,739,625 | ||
| Capital spending | - | - | - | - | 4,994,040 | ||
| Total cash inflows | $6,435,360 | $8,900,410 | $10,781,160 | $9,733,660 | $14,016,285 | ||
After the calculations of the operating cash flows for every year, it is essential to account for other cash flows. The other cash flows are the net working capital and the capital spending, that is, the after-tax salvage of the equipment.
Formula to calculate the net working capital:
Computation of the net working capital:
Note: The total net working capital in year 1 will be 15% of the sales, which may increase in year 1 or year 2. The net working capital cash flow is negative because of the increasing sales; thus the company will spend more money on the net working capital to maximize it. In year 3, the net working capital is positive because of the decline in sales. In year 5, the net working capital is the recovery of all the net working capital of the project.
Computation of the ending book value:
Formula to calculate the after-tax salvage value:
Computation of the after-tax salvage value:
Note: The market value of the equipment is 20% of the purchase price of the equipment and it is $4,800,000.
Formula to calculate the net present value:
Computation of the net present value:
Hence, the net present value is $6,448,564.092.
Computation of the internal rate of return:
The internal rate of return is calculated by the spreadsheet method.
Step 1:

- Type the formula of the internal rate of return in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the IRR value as H8.
Step 2:
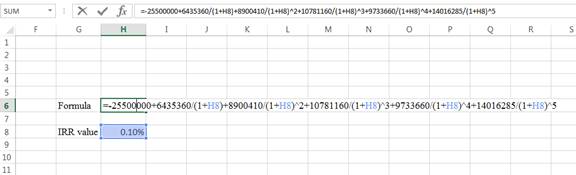
- Assume the IRR value as 0.10%.
Step 3:
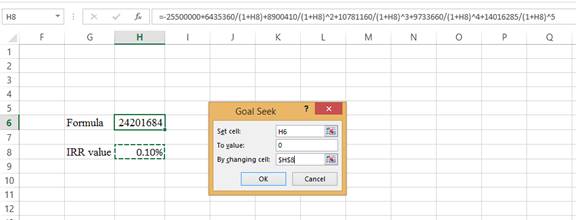
- In the spreadsheet, go to data and select What-if analysis.
- In What-if analysis, select Goal Seek.
- In ‘Set cell’ select H6 (the formula).
- The ‘To value’ is considered as 0.
- The H8 cell is selected for ‘By changing cell’.
Step 4:
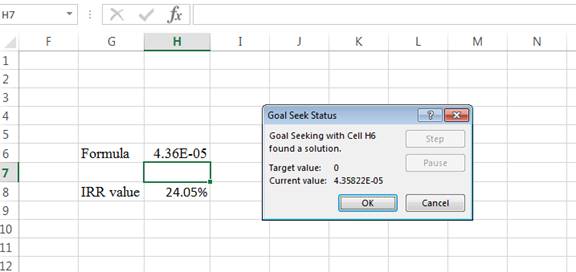
- Following the previous step, click OK in the Goal Seek Status. The Goal Seek Status appears.
Step 5:
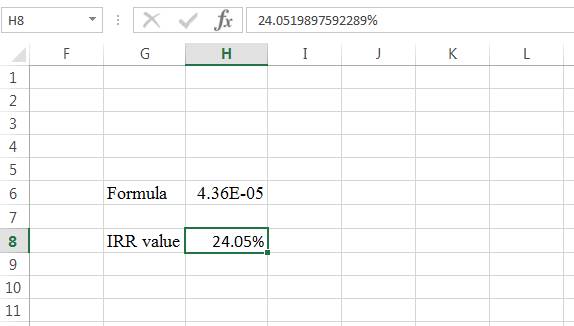
- The IRR value appears to be 24.0519897592289%.
Hence, the internal rate of return is 24.05%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Essentials of Corporate Finance
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





