
(a)
To explain: The
(a)
Explanation of Solution
A line segment with a particular direction running from initial point to terminal point is called a vector in the plane. A vector in the plane is denoted by
The vector
Where,
A vector represents a magnitude and a direction.
(b)
To find: The vector with initial point
(b)
Answer to Problem 1RCC
The vector with initial point
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The initial point is
Formula used:
The formula to calculate the vector
Calculation:
Substitute 2 for
Thus, the vector with initial point
(c)
The terminal point of the vector
(c)
Answer to Problem 1RCC
The terminal point of the vector
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The vector
Calculation:
Section (a):
The terminal point of
Substitute x for
Compare both sides,
Thus, the terminal point of the vector
Section (b):
Draw the graph of vector as shown below,
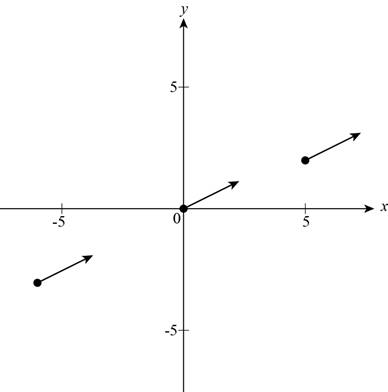
Figure (1)
Thus, Figure (1) shows various representations of the vector
(d)
The definition of magnitude of vector and the value of the vector
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The length of the line segment is called the magnitude of the vector and it is denoted by
The magnitude of the vector
Thus, magnitude of vector
(e)
The vectors
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
A vector of length 1 is called a unit vector. The vectors
The vector
Thus, the vector
(f)
The direction
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The smallest positive angle in standard position formed by the positive x-axis and the vector
The vector
And
Where,
The vector
The graph for the above equation is,
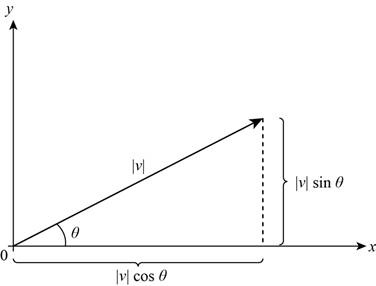
Figure (2)
Thus, Figure (2) shows the graph of the coordinates of a vector in terms of length and direction.
(g)
To find: The vector
(g)
Answer to Problem 1RCC
The vector
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The length
Calculation:
The vector
And
Substitute 5 for
And
Substitute
Thus, the coordinates of the vector
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
PRECALCULUS: MATHEMATICS FOR CALCULUS
- Please focus on ix.arrow_forwardPlease focus on vi.arrow_forward的 v If A is an n x n matrix that is not invertible, then A. rank(A) = n C. det(A) = 0 B. Reduced row-echelon form of A = In D. AB BA= In for some matrix B 63°F Partly sunny Q Search 3 $ 4 40 FS 96 S W E A S T FG S Y & コ B ㅁ F G H J 4 Z X C V B N M 9 H V FIB - FIB ㅁ P L ว DELETE BACHSPACE LOCK L ? PAUSE ALT CTRL ENTER 7 2:20 PM 4/14/2025 HOME J INSERT SHIFT END 5arrow_forward
- i Compute the given determinant by cofactor expansions. At each step, choose a row or columnthat involves the least amount of computation.7 6 8 40 0 0 68 7 9 30 4 0 5arrow_forwardi Compute the inverse of the matrix below using row operations. Please show your work.1 0 −2−3 1 42 −3 4 This is a 3*3 matrix. First row is 1 0 -2.arrow_forwardSolve the system of equations below by applying row operations on the corresponding aug-mented matrix to convert it to the reduced row-echelon form. Write the solutions using freevariables as parameters.x1 + 3x2 + x3 = 1−4x1 − 9x2 + 2x3 = −1−3x2 − 6x3 = −3arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning  Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,




