
(a)
To explain: The
(a)
Explanation of Solution
A line segment with a particular direction running from initial point to terminal point is called a vector in the plane. A vector in the plane is denoted by
The vector
Where,
A vector represents a magnitude and a direction.
(b)
To find: The vector with initial point
(b)
Answer to Problem 1RCC
The vector with initial point
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The initial point is
Formula used:
The formula to calculate the vector
Calculation:
Substitute 2 for
Thus, the vector with initial point
(c)
The terminal point of the vector
(c)
Answer to Problem 1RCC
The terminal point of the vector
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The vector
Calculation:
Section (a):
The terminal point of
Substitute x for
Compare both sides,
Thus, the terminal point of the vector
Section (b):
Draw the graph of vector as shown below,
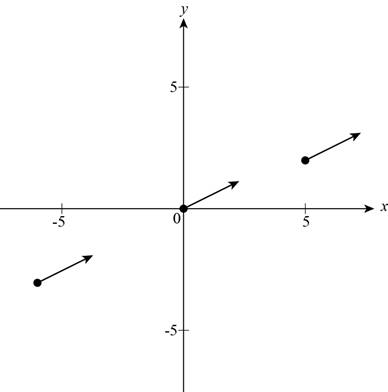
Figure (1)
Thus, Figure (1) shows various representations of the vector
(d)
The definition of magnitude of vector and the value of the vector
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The length of the line segment is called the magnitude of the vector and it is denoted by
The magnitude of the vector
Thus, magnitude of vector
(e)
The vectors
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
A vector of length 1 is called a unit vector. The vectors
The vector
Thus, the vector
(f)
The direction
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The smallest positive angle in standard position formed by the positive x-axis and the vector
The vector
And
Where,
The vector
The graph for the above equation is,
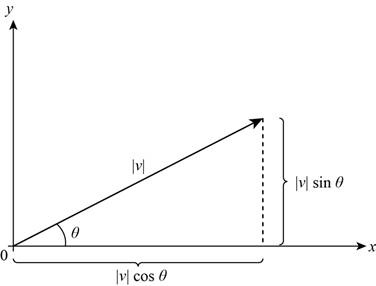
Figure (2)
Thus, Figure (2) shows the graph of the coordinates of a vector in terms of length and direction.
(g)
To find: The vector
(g)
Answer to Problem 1RCC
The vector
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The length
Calculation:
The vector
And
Substitute 5 for
And
Substitute
Thus, the coordinates of the vector
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Bundle: Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus, 7th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Stewart/Redlin/Watson's Precalculus, Enhanced Edition, 7th Edition, Single-Term
- Assuming that the rate of change of the price P of a certain commodity is proportional to the difference between demand D and supply S at any time t, the differential equations describing the price fluctuations with respect to time can be expressed as: dP/dt = k(D - s) where k is the proportionality constant whose value depends on the specific commodity. Solve the above differential equation by expressing supply and demand as simply linear functions of price in the form S = aP - b and D = e - fParrow_forwardFind the area of the surface obtained by rotating the circle x² + y² = r² about the line y = r.arrow_forward1) Find the equation of the tangent line to the graph y=xe at the point (1, 1).arrow_forward
- 3) Suppose that f is differentiable on [0, 5], and f'(x) ≤ 3 over this interval. If f(0) = −1, what is the maximum possible value of f(5)?arrow_forward2) Find the maximum value of f(x, y) = x - y on the circle x² + y² - 4x - 2y - 4 = 0.arrow_forwardFor the system consisting of the lines: and 71 = (-8,5,6) + t(4, −5,3) 72 = (0, −24,9) + u(−1, 6, −3) a) State whether the two lines are parallel or not and justify your answer. b) Find the point of intersection, if possible, and classify the system based on the number of points of intersection and how the lines are related. Show a complete solution process.arrow_forward
- 3. [-/2 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES SESSCALCET2 7.4.013. Find the exact length of the curve. y = In(sec x), 0 ≤ x ≤ π/4arrow_forwardH.w WI M Wz A Sindax Sind dy max Утах at 0.75m from A w=6KN/M L=2 W2=9 KN/m P= 10 KN B Make the solution handwritten and not artificial intelligence because I will give a bad rating if you solve it with artificial intelligencearrow_forwardSolve by DrWz WI P L B dy Sind Ⓡ de max ⑦Ymax dx Solve by Dr ③Yat 0.75m from A w=6KN/M L=2 W2=9 kN/m P= 10 KN Solve By Drarrow_forward
- How to find the radius of convergence for the series in the image below? I'm stuck on how to isolate the x in the interval of convergence.arrow_forwardDetermine the exact signed area between the curve g(x): x-axis on the interval [0,1]. = tan2/5 secx dx andarrow_forwardSet up the partial fraction expansion of the function below. Do not explicitly solve for the variables 5 x²(x − 2)(x − 3)³ (24 - 81)² -arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning  Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,




