
(a)
To find:a
(a)
Explanation of Solution
A Vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. A vector PQ is represented as a directed line segment and an arrow with initial point

A vector is indicated by writing an arrow over the designated points
Vector PQ is the vector from
Conclusion:
Therefore, a Vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
(b)
To find: a scalar.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
A scalar is a quantity that has only magnitude, not direction. In context of vectors, a scalar is described as a real number.
For example,
Conclusion:
Therefore, a scalar is a quantity that has only magnitude, not direction.
(c)
To give: an algebraic and a geometric interpretation of multiplication of a vector by a scalar.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
When a scalar number c is multiplied by a vector v , the scalar multiple cv will be parallel to the vector v and has length
The scalar multiple cv points in the same direction as v if
Geometrically, assume that vector v has a magnitude of 3 units and its direction is from point P to point Q .

The scalar multiple 2v will have a magnitude of


Conclusion:
Therefore,when a scalar number c is multiplied by a vector v , the scalar multiple cv will be parallel to the vector v and has length
Geometrically, the scalar multiple 2v will have a magnitude of
(d)
To find: parallelogram rule for vector sums
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The Parallelogram rule states that
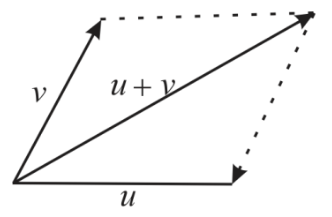
Conclusion:
Therefore, the Parallelogram rule states that
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Calculus
- Calculus lll May I please have the statements with blank lines completed; furthermore, may I please have the text box completed? Thank youarrow_forwardCalculus lll May I please have the statements completed for the following text lines and box? Thank you so much,arrow_forwardCalculus lll May I please have the solution for the following exercise? Thank you so mucharrow_forward
- Calculus lll May I please have the statement completed for the following box? Thank you so much,arrow_forwardCalculus lll May I please have the solution for the following exercise? Thank you so mucharrow_forwardUse a graphing calculator to find where the curves intersect and to find the area between the curves. y=ex, y=-x²-4x a. The left point of intersection is (Type integers or decimals rounded to the nearest thousandth as needed. Type an ordered pair.)arrow_forward
- Find the area between the curves. x= -5, x=3, y=2x² +9, y=0 The area between the curves is (Round to the nearest whole number as needed.)arrow_forwardcan you solve these questions with step by step with clear explaination pleasearrow_forwardFind the area between the following curves. x=-1, x=3, y=x-1, and y=0 The area between the curves is (Simplify your answer.)arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning  Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning



