
(a)
Interpretation:
The Haworth projections for
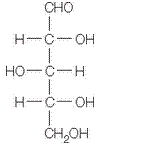
in a-furanose form should be identified along with the name of the sugar.
Concept introduction:
A Haworth projection is common way to represent the cyclic structure of monosaccharides.
Five and six membered hemiacetals are represented as planar pentagons or hexagons.
In the Haworth projection
In the Haworth projection
For example:
Haworth projections of glucose:
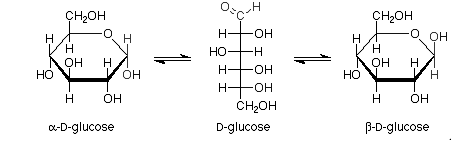
Pictorial representation:
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is as follows.
Above structure has 5 carbons and on 3rd carbon
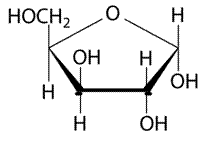
Let’s draw the Haworth projection of
In the D form of Haworth projection, the exocyclic O group at the anomeric centre is on the opposite face as to the
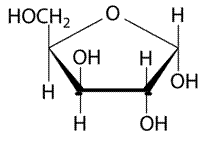
(b)
Interpretation:
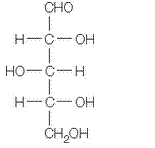
The Haworth projections for L isomer of (a) should be drawn.
Concept introduction:
A Haworth projection is common way to represent the cyclic structure of monosaccharides.
Five and six membered hemiacetals are represented as planar pentagons or hexagons.
In the Haworth projection
In the Haworth projection
For example:
Haworth projections of glucose:
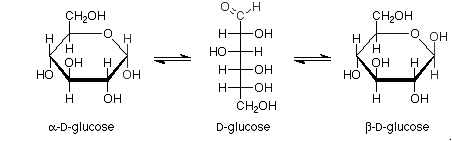
Pictorial representation:
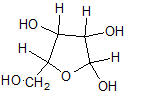
(b)
Explanation of Solution
In L form of Haworth projection, the exocyclic O group at the anomeric centre is on the same face as to the
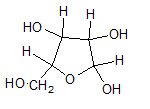
(c)
Interpretation:
The Haworth projections for a-D-Glc-NAc should be drawn.
Concept introduction:
A Haworth projection is common way to represent the cyclic structure of monosaccharides.
Five and six membered hemiacetals are represented as planar pentagons or hexagons.
In the Haworth projection
In the Haworth projection
For example:
Haworth projections of glucose:
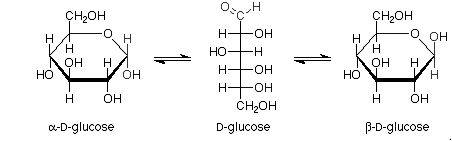
Pictorial representation:
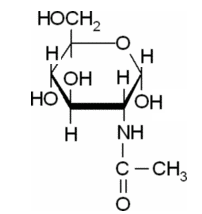
(c)
Explanation of Solution
In this compound,
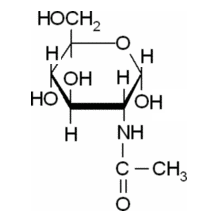
(d)
Interpretation:
The Haworth projections for a-D-Fructofuranose should be drawn.
Concept introduction:
A Haworth projection is common way to represent the cyclic structure of monosaccharides.
Five and six membered hemiacetals are represented as planar pentagons or hexagons.
In the Haworth projection
In the Haworth projection
For example:
Haworth projections of glucose:
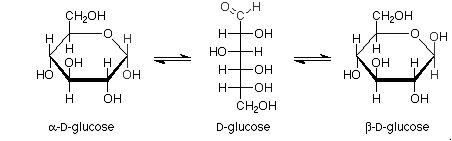
Pictorial representation:
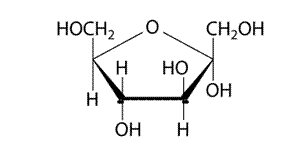
(d)
Explanation of Solution
It has 5 member furanose ring. The structure is as follows.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
BIOCHEMISTRY BOOKS ALC&MOD MST/ET PKG
- The following data were recorded for the enzyme catalyzed conversion of S -> P. Question: Estimate the Vmax and Km. What would be the rate at 2.5 and 5.0 x 10-5 M [S] ?arrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forwardThe following data were recorded for the enzyme catalyzed conversion of S -> P Question: what would the rate be at 5.0 x 10-5 M [S] and the enzyme concentration was doubled? Also, the rate given in the table is from product accumulation after 10 minuets of reaction time. Verify these rates represent a true initial rate (less than 5% turnover). Please helparrow_forward
- The following data was obtained on isocitrate lyase from an algal species. Identify the reaction catalyzed by this enzyme, deduce the KM and Vmax , and determine the nature of the inhibition by oxaloacetate. Please helparrow_forwardIn the table below, there are sketches of four crystals made of positively-charged cations and negatively-charged anions. Rank these crystals in decreasing order of stability (or equivalently increasing order of energy). That is, select "1" below the most stable (lowest energy) crystal. Select "2" below the next most stable (next lowest energy) crystal, and so forth. A B 鹽 (Choose one) +2 C +2 +2 (Choose one) D 鹽雞 (Choose one) (Choose one)arrow_forward1. Draw the structures for the fats A. 16:2: w-3 and B. 18:3:49,12,15 2. Name each of the molecules below (image attached)arrow_forward
- draw the structures for the fats A. 16:2:w-3 B 18:3:9,12,15arrow_forward1. Below is a template strand of DNA. Show the mRNA and protein that would result. label the ends of the molecules ( refer to attached image)arrow_forwardAttach the followina labels to the diagram below: helicase, single stranded binding proteins, lagging strand, leading strand, DNA polymerase, primase, 5' ends (3), 3' ends (3) (image attached)arrow_forward
- 1. How much energy in terms of ATP can be obtained from tristearin (stearate is 18:0) Show steps pleasearrow_forwardMultiple choice urgent!!arrow_forward1. Write the transamination reaction for alanine. Indicate what happens next to each of the molecules in the reaction, and under what conditions it happens. 2.arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON





