
Croyden is a calendar year, accrual basis corporation. Mr. and Mrs. Croyden (cash basis taxpayers) are the sole corporate shareholders. Mr. Croyden is president of the corporation, and Mrs. Croyden is vice president. Croyden’s financial records, prepared in accordance with GAAP, show the following information for the year.
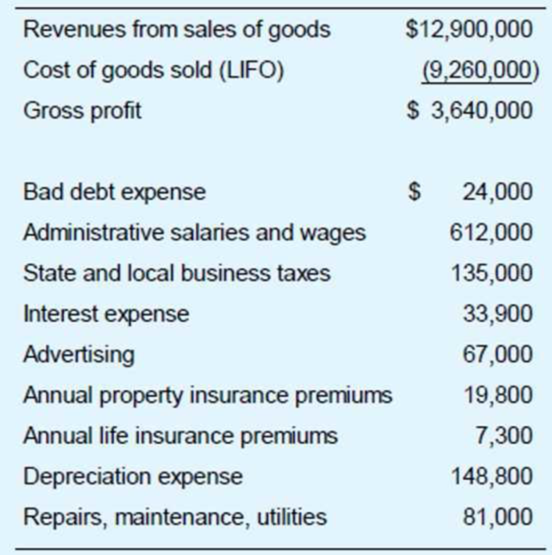
Croyden’s records reveal the following facts:
- Under the UNICAP rules, Croyden had to capitalize $142,800 of administrative wages to inventory. These wages were expensed for financial statement purposes.
- Because of the UNICAP rules, Croyden’s cost of goods sold for tax purposes exceeds cost of goods sold for financial statement purposes by $219,000.
- Bad debt expense equals the addition to the corporation’s allowance for
bad debts . Actual write-offs of uncollectible accounts during the year totaled $31,200. - Administrative salaries include an accrued $50,000 year-end bonus to Mr. Croyden and an accrued $20,000 year-end bonus to Mrs. Croyden. These bonuses were paid on January 17 of the following year.
- The life insurance premiums were on key-person policies for Mr. and Mrs. Croyden. The corporation is the policy beneficiary.
- Croyden disposed of two assets during the year. (These dispositions are not reflected in the financial statement information shown.) It sold office furnishings for $45,000. The original cost of the furnishings was $40,000, and
accumulated MACRS depreciation through date of sale was $12,700. It also exchanged transportation equipment for a 15 percent interest in apartnership . The original cost of the transportation equipment was $110,000, and accumulated MACRS depreciation through date of exchange was $38,900. - MACRS depreciation for assets placed in service in prior years (including the office furnishings and transportation equipment disposed of this year) is $187,600. The only asset acquired this year was new equipment costing $275,000. The equipment has a seven-year recovery period and was placed in service on February 11. Assume that Croyden does not elect Section 179 or bonus depreciation with respect to this acquisition.
- Croyden’s prior-year tax returns show no nonrecaptured Section 1231 losses and a $7,400 capital loss carryforward.
Solely on the basis of these facts, compute Croyden’s taxable income.
LN Consulting is a calendar year, cash basis unincorporated business. The business is not required to provide audited financial statements to any external user. LN’s accounting records show the following.
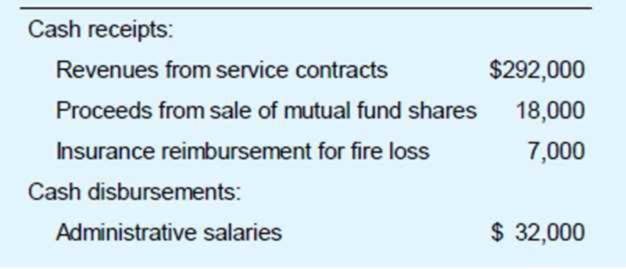
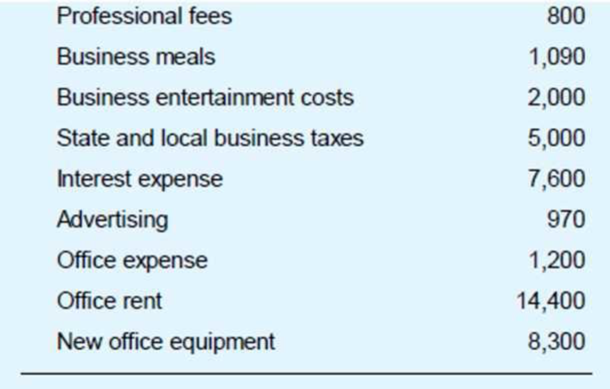
LN’s records reveal the following facts:
- In December, the bookkeeper prepaid $1,500 interest on a business debt. Tins interest is related to the next taxable year.
- LN disposed of two assets during the year. It exchanged computer equipment for office furniture. (These assets are not like-kind for federal tax purposes.) The original cost of the computer equipment was $13,000, and accumulated MACRS depreciation through date of exchange was $9,700. The office furniture has a $6,000 FMV It sold 1,200 shares in a mutual fund for $18,000. LN purchased the shares as a short-term investment of excess
working capital . The cost of the shares was $16,600. - An electrical fire completely destroyed a company car. The adjusted basis of the car was $9,100, and LN’s property insurance company paid $7,000 in complete settlement of its damage claim LN used the insurance money to pay various operating expenses.
- MACRS depreciation for assets placed in service in prior years (including the computer equipment and company car) is $4,600. The only asset acquired this year (in addition to the office furniture) was office equipment costing $8,300. The equipment was placed in service on August 19.
Based on these facts, compute the taxable income generated by LN Consulting’s activities, before any 20 percent (QBI) deduction that might be available to LN’s owners.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
PRINCIPLES OF TAXATION F/BUS.+INVEST.
- Can you help me solve this general accounting problem using the correct accounting process?arrow_forwardApplying the Accounting Equation and Assessing Financial Statement LinkagesThe following information is available for Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) and Intel for a recent fiscal year.• AMD’s assets increased by $1,004 million and its liabilities increased by $334 million.• Intel’s assets increased by $4,714 million and its liabilities decreased by $830 million.a. Complete the following table. Assets, beginning Assets, end Liabilities, Liabilities, Stockholders’ Equity, (in $ millions) of year of year beginning of year end of year end of year AMD Answer 1 $4,556 $2,956 Answer 2 Answer 3 Intel $123,249 Answer 4 Answer 5 $53,400 Answer 6 b. Calculate average assets for each company. (in $ millions) Average Assets AMD Answer 7 Intel Answer 8 c. Which company has the larger proportion of its assets financed by the company’s owners at year-end? Answer 9arrow_forwardApplying the Accounting Equation and Assessing Financial Statement LinkagesThe following information is available for Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) and Intel for a recent fiscal year.• AMD’s assets increased by $1,004 million and its liabilities increased by $334 million.• Intel’s assets increased by $4,714 million and its liabilities decreased by $830 million.a. Complete the following table. Assets, beginning Assets, end Liabilities, Liabilities, Stockholders’ Equity, (in $ millions) of year of year beginning of year end of year end of year AMD Answer 1 $4,556 $2,956 Answer 2 Answer 3 Intel $123,249 Answer 4 Answer 5 $53,400 Answer 6 b. Calculate average assets for each company. (in $ millions) Average Assets AMD Answer 7 Intel Answer 8 c. Which company has the larger proportion of its assets financed by the company’s owners at year-end? Answer 9arrow_forward
- Formulating Financial Statements from Raw Data and Calculating RatiosFollowing is selected financial information from JM Smucker Co. for a recent fiscal year ($ millions). Current assets, end of year $2,010.1 Noncurrent liabilities, end of year $5,962.1 Cash, end of year 169.9 Stockholders' equity, end of year 8,140.1 Cash for investing activities (355.5) Cash from operating activities 1,136.3 Cost of product sold 5,298.2 Total assets, beginning of year 16,284.2 Total liabilities, end of year 7,914.9 Revenue 7,998.9 Cash for financing activities (945.2) Total expenses, other than cost of product sold 2,069.0 Stockholders' equity, beginning of year 8,124.8 Dividends paid (418.1) Requireda. Prepare the income statement for the year. J.M. Smucker Company, Inc. Income Statement ($ millions) Answer 1 Answer 2 Answer 3 Answer 4 Answer 5 Answer 6 Answer 7 Answer 8 Answer 9 Answer 10 b. Prepare the balance sheet at the end of the year. J.M.…arrow_forwardCalculate Total Fixed Cost With General Accounting Methodarrow_forwardIm Waiting for Solution of this General Accounting Questionarrow_forward





