
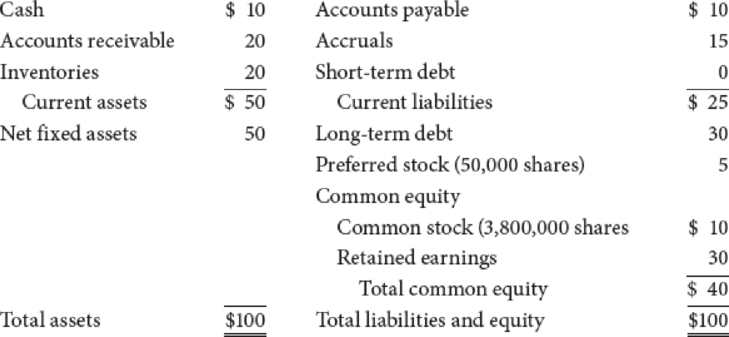
The following table gives the current
Travellers Inn (Millions of Dollars)
The following facts also apply to TII.
- (1) The long-term debt consists of 29,412 bonds, each having a 20-year maturity, semiannual payments, a coupon rate of 7.6%, and a face value of $1,000. Currently, these bonds provide investors with a yield to maturity of 11.8%. If new bonds were sold, they would have an 11.8% yield to maturity.
- (2) TII’s perpetual
preferred stock has a $100 par value, pays a quarterly dividend per share of $2, and has a yield to investors of 10%. New perpetual preferred stock would have to provide the same yield to investors, and the company would incur a 3.85% flotation cost to sell it. - (3) The company has 3.8 million shares of common stock outstanding, a price per share = P0 = $20, dividend per share = D0 = $1, and earnings per share = EPS0 = $5. The
return on equity (ROE) is expected to be 10%. - (4) The stock has a beta of 1.6%. The T-bond rate is 6%, and RPM is estimated to be 5%.
- (5) TII’s financial vice president recently polled some pension fund investment managers who hold TII’s securities regarding what minimum
rate of return on TII’s common would make them willing to buy the common rather than TII bonds, given that the bonds yielded 11.8%. The responses suggested a risk premium over TII bonds of 3 percentage points. - (6) TII is in the 25% federal-plus-state tax bracket.
Assume that you were recently hired by TII as a financial analyst and that your boss, the treasurer, has asked you to estimate the company’s WACC under the assumption that no new equity will be issued. Your cost of capital should be appropriate for use in evaluating projects that are in the same risk class as the assets TII now operates. Based on your analysis, answer the following questions.
- a. What are the current market value weights for debt, preferred stock, and common stock? (Hint: Do your work in dollars, not millions of dollars. When you calculate the market values of debt and preferred stock, be sure to round the market price per bond and the market price per share of preferred to the nearest penny.)
- b. What is the after-tax cost of debt?
- c. What is the cost of preferred stock?
- d. What is the required return on common stock using
CAPM ? - e. Use the retention growth equation to estimate the expected growth rate. Then use the expected growth rate and the dividend growth model to estimate the required return on common stock.
- f. What is the required return on common stock using the own-bond-yield-plus-judgmental-risk-premium approach?
- g. Use the required return on stock from the CAPM model, and calculate the WACC.
a.
To determine: The market value weights of debt, common stock and preferred stock.
Answer to Problem 17P
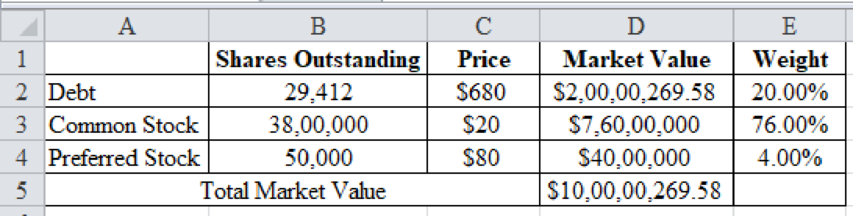
The market value weights of debt are 20%, common stock is 76% and preferred stock is 4%.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the market value weights of debt, common stock and preferred stock
Excel Spreadsheet:
Excel Workings:
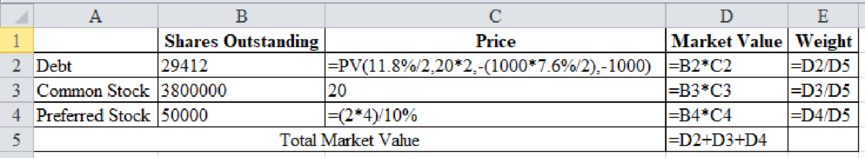
Therefore, the market value weights of debt are 20%, common stock is 76% and preferred stock is 4%.
b.
To determine: The after-tax cost of debt.
Answer to Problem 17P
The after-tax cost of debt is 8.85%.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the after-tax cost of debt
Therefore, the after-tax cost of debt is 8.85%.
c.
To determine: The cost of preferred stock.
Answer to Problem 17P
The cost of preferred stock is 10.40%.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the cost of preferred stock
Therefore, the cost of preferred stock is 10.40%.
d.
To determine: The required return on common stock using CAPM.
Answer to Problem 17P
The required return on common stock using CAPM is 14%.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the required return on common stock using CAPM
Therefore, the required return on common stock using CAPM is 14%.
e.
To determine: The required return on common stock using dividend growth model.
Answer to Problem 17P
The required return on common stock using dividend growth model is 13.40%.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the payout ratio
Therefore, the payout ratio is 20%.
Determine the growth rate
Therefore, the growth rate is 8%.
Determine the required return on common stock using dividend growth model
Therefore, the required return on common stock using dividend growth model is 13.40%.
f.
To determine: The required return on common stock using own-bond-yield-plus-judgmental- risk-premium approach.
Answer to Problem 17P
The required return on common stock using own-bond-yield-plus-judgmental- risk-premium approach is 14.80%.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the required return on common stock using own-bond-yield-plus-judgmental- risk-premium approach
Therefore, the required return on common stock using own-bond-yield-plus-judgmental- risk-premium approach is 14.80%.
g.
To determine: The WACC.
Answer to Problem 17P
The WACC is 12.83%.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the WACC
Therefore, the WACC is 12.83%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Bundle: Financial Management: Theory & Practice, 16th + MindTap, 1 term Printed Access Card
- Dont use chatgpt and give answer What does “liquidity” refer to in finance? a) The profitability of a companyb) The ease of converting assets into cashc) The stability of incomed) The level of debtarrow_forwardThe opportunity cost of holding cash is inversely related to the level of market interest rates. Question 9 options: True Falsearrow_forwardYour firm deals strictly with four customers. The average amount that each customer pays per month along with the collection delay associated with each payment is shown below. Given this information, what is the amount of the average daily receipts? Assume that every month has 30 days. Customer Item Amount Delay A $8,500 5 days B $12,000 2 days C $16,000 3 days D $3,600 2 days Question 8 options: $8,448 $1,337 $3,342 $1,408 $10,025arrow_forward
- Which of the following is true regarding cash management? Question 7 options: The basic objective in cash management is to keep the investment in cash as low as possible while still operating efficiently and effectively. Effective cash management results in minimization of the total interest earnings involved with holding cash. A cost of holding cash is the liquidity it gives the firm. A firm should decrease its cash holdings as long as the NPV of doing so is negative. A cost of holding cash is the interest income earned on the outstanding cash balance.arrow_forwardLow default risk is a characteristic of money market securities. Question 6 options: True Falsearrow_forwardJeep Corp. held large sums of cash during the mid-1990s primarily because it would need a large amount of cash in the event of a recession. This is a[n] _____ for holding cash. Question 5 options: Adjustment motive. Compensating balances motive. Speculative motive. Transactions motive. Precautionary motive.arrow_forward
- With respect to the workings of a lockbox system, the cheque clearing process begins before the company even knows the payments have been received. Question 4 options: True Falsearrow_forwardYou are considering implementing a lockbox system for your firm. The system is expected to reduce the collection time by 1.5 days. On an average day, your firm receives 250 checks with an average value of $400 each. The daily interest rate on Treasury bills is .02%. What is the anticipated amount of the daily savings if this system is implemented? Question 3 options: $30 $25 $15 $20 $10arrow_forwardDisbursement float is virtually eliminated when payments are made electronically. Question 2 options: True Falsearrow_forward
- According to your cheque book, you have a $3,000 balance in your account. You write cheques totaling $4,500 and make a deposit of $3,500. Determine your net float. Question 1 options: $8,000 -$1,000 $0 $1,000 $4,000arrow_forwardWhat is a blue-chip stock? a) A stock with high volatilityb) A stock of a well-established, financially sound companyc) A newly launched IPO stockd) A stock with high dividends but low growtharrow_forwardNo chatgpt! What does “liquidity” refer to in finance? a) The profitability of a companyb) The ease of converting assets into cashc) The stability of incomed) The level of debtarrow_forward

