
a.
To prepare:
The payroll register by filling in the empty cells.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the payroll register as shown below.
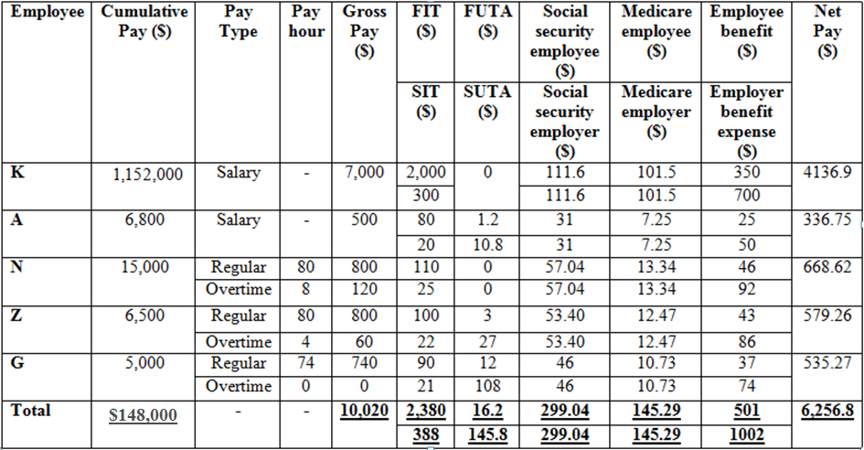
Table 1
Working notes:
1. Calculation of FUTA of A.
2. Calculation of FUTA of Z.
3. Calculation of FUTA of G.
4. Calculation of SUTA of A.
5. Calculation of SUTA of Z.
6. Calculation of SUTA of G.
7. Calculation of security tax of K.
8. Calculation of security tax of A.
9. Calculation of security tax of N.
10. Calculation of security tax of Z.
11. Calculation of security tax of G.
12. Calculation of Medicare tax of K.
13. Calculation of Medicare tax of A.
14. Calculation of Medicare tax of N.
15. Calculation of Medicare tax of Z.
16. Calculation of Medicare tax of G.
17. Calculation of employee benefit of K.
18. Calculation of employee benefit of A.
19. Calculation of employee benefit of N.
20. Calculation of employee benefit of Z.
21. Calculation of employee benefit of G.
22. Calculation of net pay of K.
23. Calculation of net pay of A.
24. Calculation of net pay of N.
25. Calculation of net pay of Z.
26. Calculation of net pay of G.
b.
To prepare:
The
b.
Answer to Problem 17E
Prepare the journal entry for accrued biweekly payroll as shown below.
| Date | Particulars | L/F | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aug 31 | Salaries expense | 10,020 | ||
| FICA - Social security taxes payable | 299.04 | |||
| FICA - Medicare taxes payable | 145.29 | |||
| Employee federal taxes payable | 2,380 | |||
| Employee state taxes payable | 388 | |||
| Employee benefits plan payable | 501 | |||
| Salaries payable | 6306.67 | |||
| (To record the payroll for August) |
Table 2
Explanation of Solution
• Salaries expense is an expense account for a company. Since the balance of this account increases, it is debited.
• FICA social security taxes payable is a liability to a company. Its balance increases, so it is credited.
• FICA Medicare taxes payable is a liability to a company. Its balance increases, so it is credited.
• Employee federal taxes payable is a liability to a company. Its balance increases, so it is credited.
• Employee state taxes payable is a liability to a company. Its balance increases, so it is credited.
• Salaries payable is a liability to a company. Its balance increases, so it is credited.
c.
To prepare:
The journal entry to record employer’s cash payment of the net payroll
c.
Answer to Problem 17E
Prepare the journal entry to record employer’s cash payment of the net payroll as shown below.
| Date | Particulars | L/F | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aug 31 | Salaries payable | 6306.67 | ||
| Cash | 6306.67 | |||
| (To record the payment for August) |
Table 3
Explanation of Solution
• Salaries payable is a liability to company. Its balance decreases, so it is debited.
• Cash is an asset account. Since the company is paying salaries, cash is reducing. Hence, cash is credited.
d.
To prepare:
The journal entry to record employer’s payroll taxes.
d.
Answer to Problem 17E
Prepare the journal entry to record employer’s payroll taxes as shown below.
| Date | Particulars | L/F | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aug31 | Payroll taxes expense | 3212.33 | ||
| Employee benefit plan expenses | 1,002 | |||
| Employee benefit plan payable | 1,002 | |||
| FICA - Social security taxes payable | 299.04 | |||
| FICA - Medicare taxes payable | 145.29 | |||
| Employee federal taxes payable | 2,380 | |||
| Employee state taxes payable | 388 | |||
| (To record the employer’s payroll taxes) |
Table 4
Explanation of Solution
• Payroll taxes are an expense account for a company. Since the balance of this account increases, it is debited.
• Employee benefit plan is an expense account for a company. Since the balance of this account increases, it is debited.
• Employee benefit plan is a liability to a company. Its balance increases, so it is credited.
• FICA social security taxes payable is a liability to a company. Its balance increases, so it is credited.
• FICA Medicare taxes payable is a liability to a company. Its balance increases, so it is credited.
• Employee federal taxes payable is a liability to a company. Its balance increases, so it is credited.
• Employee state taxes payable is a liability to a company. Its balance increases, so it is credited.
e.
To prepare:
The journal entry to pay all liabilities.
e.
Answer to Problem 17E
Prepare the journal entry to pay all liabilities as shown below.
| Date | Particulars | L/F | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aug 31 | FICA - Social security taxes payable | 598.08 | ||
| FICA - Medicare taxes payable | 290.58 | |||
| Employee federal taxes payable | 2,380 | |||
| Employee state taxes payable | 388 | |||
| Employee benefits plan payable | 1,503 | |||
| FUTA payable | 16.2 | |||
| SUTA payable | 145.8 | |||
| Cash | 5321.66 | |||
| (To record the payment of all liabilities) |
Table 5
Explanation of Solution
• FICA Social security taxes payable is a liability to a company. Its balance decreases, so it is debited.
• FICA Medicare taxes payable is a liability to a company. Its balance decreases, so it is debited.
• Employee federal taxes payable is a liability to a company. Its balance decreases, so it is debited.
• Employee state taxes payable is a liability to a company. Its balance decreases, so it is debited.
• Employee benefit plan is a liability to a company. Its balance decreases, so it is debited.
• FUTA payable is a liability to a company. Its balance decreases, so it is debited.
• SUTA payable is a liability to company. Its balance decreases, so it is debited.
• Cash is an asset account. Since company is paying salaries, its liability decreases. Hence, cash is credited.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Financial and Managerial Accounting (Looseleaf) (Custom Package)
- August's beginning and ending inventories were 24,600 and 16,200 units, respectively.arrow_forwardWhich accounting concept supports recording bad debt expense before accounts are actually uncollectible? a) Full disclosure principle b) Matching principle c) Going concern concept d) Materiality concept. Helparrow_forwardWhat is the unit product cost for job 882?arrow_forward
- Can you explain the correct approach to solve this general accounting question?arrow_forwardCameron Components Ltd. had a variable costing operating income of $82,600 in 2022. Ending inventory decreased during 2022 from 46,000 units to 43,500 units. During both 2021 and 2022, fixed manufacturing overhead was $840,000, and 105,000 units were produced. Determine the absorption costing operating income for 2022.arrow_forwardCornell Corporation plans to generate $960,000 of sales revenue if a capital project is implemented. Assuming a 30% tax rate, the sales revenue should be reflected in the analysis by:arrow_forward
- Robin, Sienna and Teagan are in partnership sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 2:2:1 respectively. At the 1 January their capital and current account balances were:Capital Account Current Account$ $Robin 32000 2400 CreditSienna 40 000 1100 DebitTeagan 48 000 1900 Credit The partners are entitled to interest on capital at the rate of 5% per annum. On 1 July, Robin increased her capital by paying a further $6,000 into the partnership bank account, while Sienna reduced her capital to $26,000 and left the value of her withdrawn capital in the partnership as a loan bearing interest at 5% per annum.Partners are allowed to withdraw from current accounts at any time during the financial year but are charged interest on the amounts involved.Details of drawings made and interest chargeable in respect of each partner for the financial year ended 31 December are:Drawings Interest on Drawings$ $Robin 6900 270Sienna 5700 220Teagan 8100 330 Sienna is paid an annual salary of $18,000. The…arrow_forwardPlease provide the answer to this general accounting question using the right approacharrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with the appropriate accounting analysis techniques?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





