
a.
To prepare: Payroll register.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Given,
Wage rate is $10/hour.
Overtime rate is $15/hour.
Normal working hours are 40 hours.
FICA Social security tax is 6.2% of first $118,500.
FICA Medicare tax is 1.45% of gross pay.
FUTA is 0.6% of first $7000
SUTA is 5.4% of first $7000.
Payroll register
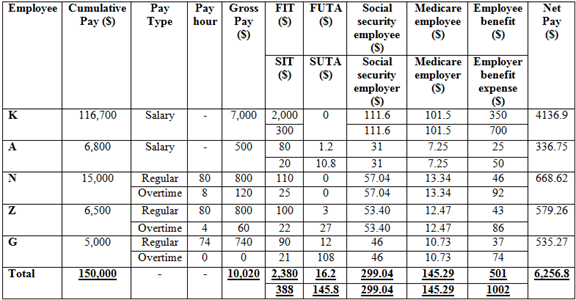
Table (1)
Working notes:
Calculation of FUTA of A,
Calculation of FUTA of Z,
Calculation of FUTA of G,
Calculation of SUTA of A,
Calculation of SUTA of Z,
Calculation of SUTA of G,
Calculation of security tax of K,
Calculation of security tax of A,
Calculation of security tax of N,
Calculation of security tax of Z,
Calculation of security tax of G,
Calculation of Medicare tax of K,
Calculation of Medicare tax of A,
Calculation of Medicare tax of N,
Calculation of Medicare tax of Z,
Calculation of Medicare tax of G,
Calculation of employee benefit of K,
Calculation of employee benefit of A,
Calculation of employee benefit of N
Calculation of employee benefit of Z,
Calculation of employee benefit of G,
Calculation of net pay of K,
Calculation of net pay of A,
Calculation of net pay of N,
Calculation of net pay of Z,
Calculation of net pay of G,
(b)
To prepare:
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Journal Entry for accrued biweekly payroll
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| August 31 | Salaries Expense | 10,020 | ||
| FICA- Social security taxes payable | 299.04 | |||
| FICA Medicare taxes payable | 145.29 | |||
| Employee federal taxes payable | 2,380 | |||
| Employee state taxes payable | 388 | |||
| Employee benefits plan payable | 501 | |||
| Salaries Payable | 6306.67 | |||
| (To record payroll for August) | ||||
| Table (2) | ||||
- Salaries expense is an expense account for company. Since the balance of this account is increased it is debited.
- FICA Social security taxes payable is a liability to company. Its balance is increasing, so it is credited.
- FICA Medicare taxes payable is a liability to company. Its balance is increasing, so it is credited.
- Employee federal taxes payable is a liability to company. Its balance is increasing, so it is credited.
- Employee state taxes payable is a liability to company. Its balance is increasing, so it is credited.
- Salaries payable is a liability to company. Its balance is increasing, so it is credited.
(c)
To prepare: Journal Entry to record employer’s cash payment of the net payroll
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Journal Entry to record employer’s cash payment of the net payroll
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| August 31 | Salaries Payable | 6306.67 | ||
| Cash | 6306.67 | |||
| (To record payment for August) | ||||
| Table (3) | ||||
- Salaries Payable is a liability to company. Its balance is decreasing, so it is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since company is paying salaries, cash is reducing. Hence cash is credited.
(d)
To prepare: Journal Entry to record employer’s payroll taxes
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Journal Entry to record employer’s payroll taxes
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| August 31 | Payroll Taxes expense | 3212.33 | ||
| Employee benefit plan expenses | 1,002 | |||
| Employee benefit plan payable | 1,002 | |||
| FICA- Social security taxes payable | 299.04 | |||
| FICA Medicare taxes payable | 145.29 | |||
| Employee federal taxes payable | 2,380 | |||
| Employee state taxes payable | 388 | |||
| (To record employer’s payroll taxes) | ||||
| Table (4) | ||||
- Payroll taxes are an expense account for company. Since the balance of this account is increased it is debited.
- Employee benefit plan expenses is an expense account for company. Since the balance of this account is increased it is debited.
- Employee benefit plan payable is a liability to company. Its balance is increasing, so it is credited.
- FICA social security taxes payable is a liability to company. Its balance is increasing, so it is credited.
- FICA Medicare taxes payable is a liability to company. Its balance is increasing, so it is credited.
- Employee federal taxes payable is a liability to company. Its balance is increasing, so it is credited.
- Employee state taxes payable is a liability to company. Its balance is increasing, so it is credited.
(e)
To prepare: Journal Entry to pay all liabilities.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Journal Entry to pay all liabilities
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| August 31 | FICA- Social security taxes payable | 598.08 | ||
| FICA Medicare taxes payable | 290.58 | |||
| Employee federal taxes payable | 2,380 | |||
| Employee state taxes payable | 388 | |||
| Employee benefits plan payable | 1,503 | |||
| FUTA payable | 16.2 | |||
| SUTA payable | 145.8 | |||
| Cash | 5321.66 | |||
| (To record payment of all liabilities) | ||||
| Table (5) | ||||
- FICA Social security taxes payable is a liability to company Its balance is increasing, so it is credited.
- FICA Medicare taxes payable is a liability to company. Its balance is increasing, so it is credited.
- Employee federal taxes payable is a liability to company. Its balance is increasing, so it is credited.
- Employee state taxes payable is a liability to company. Its balance is increasing, so it is credited.
- Employee benefit plan payable is a liability to company. Its balance is increasing, so it is credited.
- FUTA payable is a liability to company. Its balance is increasing, so it is credited.
- SUTA payable is a liability to company. Its balance is increasing, so it is credited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since company is paying salaries, cash is reducing. Hence cash is credited.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
GEN COMBO FINANCIAL AND MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING; CONNECT ACCESS CARD
- Compare the cost model vs. revaluation model, including pros, cons, and theoretical implications (e.g., relevance vs. reliability).arrow_forwardGeneral accounting questionarrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid accounting standards.arrow_forward
- If the project's cost of capital is 11%, what is the NPV of the project? What is the Year-0 net cash flow? $ -85,000 What are the net operating cash flows in Years 1, 2, and 3? Year 1: $25,403 Year 2: $27,682 Year 3: $21,606arrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this general accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate explanations.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





