
1.
Journalize the transactions for the year 2016-2018 in the books of Incorporation CA.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Warranty:
Warranty is a written guarantee that is given by the seller to the buyer for the product against product’s defect.
Prepare the
| Date | Account titles and explanation | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 2016 | Cash or | 500,000 | |
| Sales | 500,000 | ||
| (To record the sale revenue) |
Table (1)
- Cash or an account receivable is an asset account and it is increased. Thus, debit cash or accounts receivable with $500,000.
- Sales are a revenue account and it increases the shareholders’ equity. Thus, credit sales with $500,000.
Prepare the journal entry to record the estimated warranty liability for the year 2016:
| Date | Account titles and explanation | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 2016 | Warranty expense (1) | 75,000 | |
| Estimated warranty liability | 75,000 | ||
| (To record the estimated warranty liability) |
Table (2)
Working note (1):
Determine the amount of estimated warranty liability.
- Warranty expense is an expense account and it decreases the value of shareholders’ equity. Thus, debit warranty expense with $75,000.
- Estimated warranty liability is a liability and it is increased. Thus, credit estimated warranty liability with $75,000.
Prepare the journal entry to record the warranty cost incurred during the year 2016:
| Date | Account titles and explanation | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 2016 | Estimated warranty liability | 62,000 | |
| Cash or other assets | 62,000 | ||
| (To record the warranty cost incurred during the year) |
Table (3)
- Estimated warranty liability is a liability and it is decreased. Thus, debit estimated warranty liability with $62,000.
- Cash or other asset is an asset account and it is decreased. Thus, credit cash or other assets with $62,000.
Prepare the journal entry to record the sales for the year 2017:
| Date | Account titles and explanation | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 2017 | Cash or Accounts receivable | 650,000 | |
| Sales | 650,000 | ||
| (To record the sale revenue) |
Table (4)
- Cash or an account receivable is an asset account and it is increased. Thus, debit cash or accounts receivable with $650,000.
- Sales are a revenue account and it increases the shareholders’ equity. Thus, credit sales with $650,000.
Prepare the journal entry to record the estimated warranty liability for the year 2017:
| Date | Account titles and explanation | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 2017 | Warranty expense (2) | 97,500 | |
| Estimated warranty liability | 97,500 | ||
| (To record the estimated warranty liability) |
Table (5)
Working note (2):
Determine the amount of estimated warranty liability.
- Warranty expense is an expense account and it decreases the value of shareholders’ equity. Thus, debit warranty expense with $97,500.
- Estimated warranty liability is a liability and it is increased. Thus, credit estimated warranty liability with $97,500.
Prepare the journal entry to record the warranty cost incurred during the year 2017:
| Date | Account titles and explanation | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 2017 | Estimated warranty liability | 82,000 | |
| Cash or other assets | 82,000 | ||
| (To record the warranty cost incurred during the year) |
Table (6)
- Estimated warranty liability is a liability and it is decreased. Thus, debit estimated warranty liability with $82,000.
- Cash or other asset is an asset account and it is decreased. Thus, credit cash or other assets with $82,000.
Prepare the journal entry to record the sales for the year 2018:
| Date | Account titles and explanation | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 2018 | Cash or Accounts receivable | 700,000 | |
| Sales | 700,000 | ||
| (To record the sale revenue) |
Table (7)
- Cash or an account receivable is an asset account and it is increased. Thus, debit cash or accounts receivable with $700,000.
- Sales are a revenue account and it increases the shareholders’ equity. Thus, credit sales with $700,000.
Prepare the journal entry to record the estimated warranty liability for the year 2018:
| Date | Account titles and explanation | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 2018 | Warranty expense (3) | 105,000 | |
| Estimated warranty liability | 105,000 | ||
| (To record the estimated warranty liability) |
Table (8)
Working note (3):
Determine the amount of estimated warranty liability.
- Warranty expense is an expense account and it decreases the value of shareholders’ equity. Thus, debit warranty expense with $105,000.
- Estimated warranty liability is a liability and it is increased. Thus, credit estimated warranty liability with $105,000.
Prepare the journal entry to record the warranty cost incurred during the year 2018:
| Date | Account titles and explanation | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 2018 | Estimated warranty liability | 85,000 | |
| Cash or other assets | 85,000 | ||
| (To record the warranty cost incurred during the year) |
Table (9)
- Estimated warranty liability is a liability and it is decreased. Thus, debit estimated warranty liability with $85,000.
- Cash or other asset is an asset account and it is decreased. Thus, credit cash or other assets with $85,000.
2.
Determine the amount of liability that would be reported by Incorporation CA on its December 31, 2018
2.
Explanation of Solution
Liabilities: The claims creditors have over assets or resources of a company are referred to as liabilities. These are the debt obligations owed by company to creditors. Liabilities are classified on the balance sheet as current liabilities and long-term liabilities.
Prepare the T-account to determine the amount of estimated warranty liability:
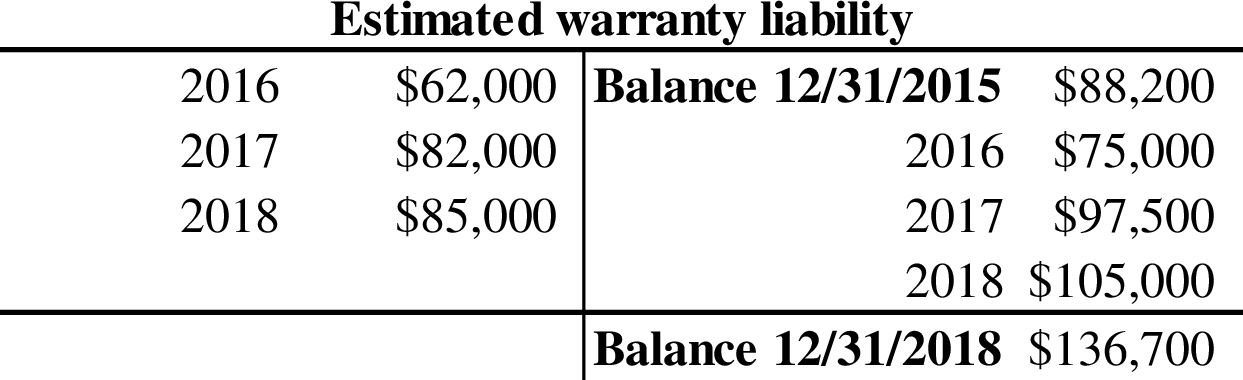
The amount of liability that would be reported by Incorporation CA on its December 31, 2018 balance sheet is $136,700.
3.
Explain the manner in which the financial statements are affected for not recognizing the
3.
Explanation of Solution
According to the recognition principle, recognition of loss contingencies is to record the loss during the current period in which it is incurred. Thus, a loss must be recognized in the same period in which it is incurred and that would result in the probable decrease in an asset or the probable increase in the value of liability. If the loss contingencies are not recognized during the particular period, then it would understate the expense, overstate the earnings, overstate the shareholders’ equity, understate the liabilities in the beginning period and understate the earning of the future period.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Cengagenowv2, 1 Term Printed Access Card For Wahlen/jones/pagach’s Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis, 2017 Update, 2nd
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





