
Concept explainers
a)
To calculate: The IRR (
Introduction:
The IRR (Internal rate of return) is a rate of discount, which makes the predictable investment’s NPV equal to zero.
The NPV (
a)
Answer to Problem 12QP
As IRR is higher in Project A when compared to Project B, Project A can be accepted. However, it is not the appropriate decision because the criterion of IRR has problem in ranking for mutually exclusive projects.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Company G has identified two mutually exclusive projects where the cash flows of Project A are$14,400, $12,300, $9,200, and $5,100 for year1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The cash flows of Project B are $4,300, $9,800, $15,200, and $16,800 for year 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The initial costs for both the projects are $29,000 respectively.
Note:
- NPV is the difference between the present values of the cash inflows from the
present value of cash outflows. - The IRR is the rate of interest, which makes the project’s NPV equal to zero. Hence, using the available information, assume that NPV is equal to zero and form an equation to compute the IRR.
Equation of NPV to compute IRR assuming that NPV is equal to zero:
Compute IRR for Project A using a spreadsheet:
Step 1:
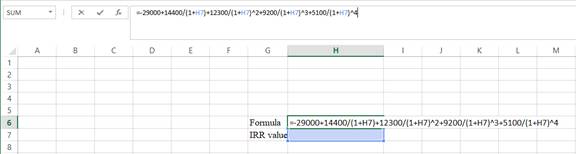
- Type the equation of NPV in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the IRR value as H7.
Step 2:
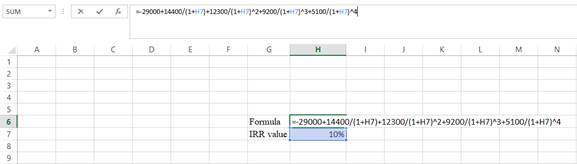
- Assume the IRRvalue as 10%.
Step 3:
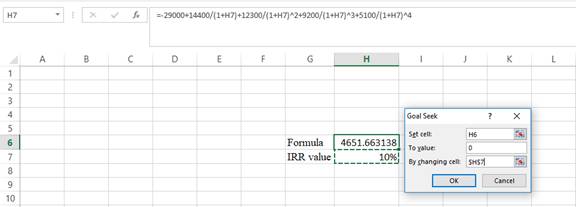
- In the spreadsheet go to data and select the what-if analysis.
- In what-if analysis select goal seek.
- In set cell select H6 (the formula).
- The “To value” is considered as 0 (the assumption value for NPV).
- The H7 cell is selected for the by changing cell.
Step 4:
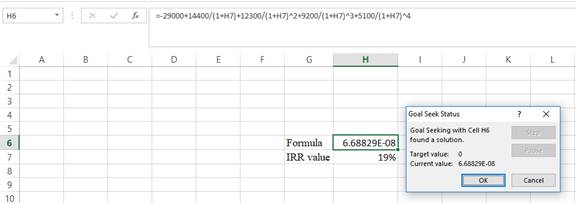
- Following the previous step click OK in the goal seek. The goal seek status appears with the IRRvalue.
Step 5:
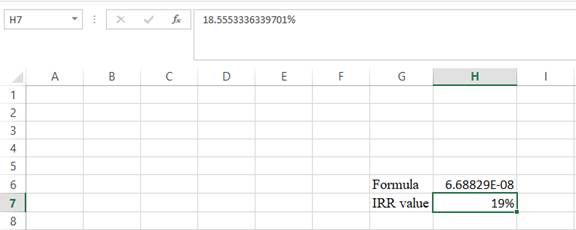
- The value appears to be 18.555336339701%.
Hence, the IRR value is 18.56%.
Compute IRR for Project B using a spreadsheet:
Step 1:
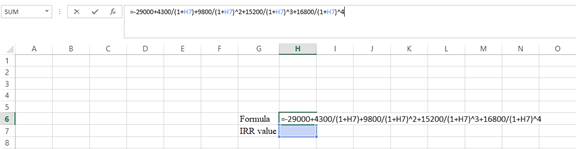
- Type the equation of NPV in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the IRR value as H7.
Step 2:
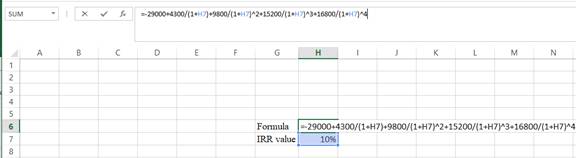
- Assume the IRRvalue as 10%.
Step 3:
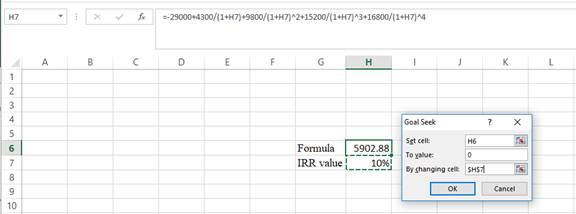
- In the spreadsheet go to data and select the what-if analysis.
- In what-if analysis select goal seek.
- In set cell select H6 (the formula).
- The “To value” is considered as 0 (the assumption value for NPV).
- The H7 cell is selected for the by changing cell.
Step 4:
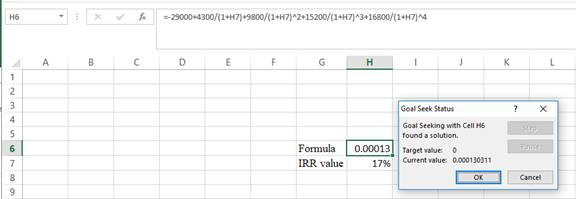
- Following the previous step click OK in the goal seek. The goal seek status appears with the IRRvalue.
Step 5:
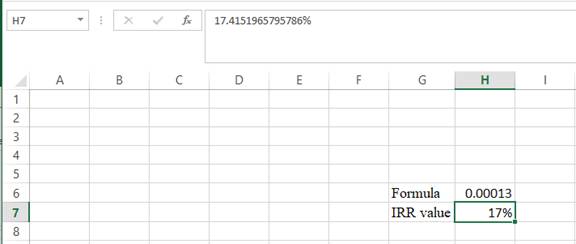
- The value appears to be 17.4151965795786%.
Hence, the IRR value is 17.42%.
b)
To calculate: The NPV for the projects to choose the best project for the company.
Introduction:
The IRR (Internal
The NPV (Net present value) is a capital budgeting technique, which is used to assess the investment that in turn, is utilized to identify the profitability in a proposed investment.
b)
Answer to Problem 12QP
As NPV is greater in Project B, the company must accept Project B.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Company G has identified two mutually exclusive projects where the cash flows of Project A are$14,400, $12,300, $9,200, and $5,100 for year1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The cash flows of Project B are $4,300, $9,800, $15,200, and $16,800 for year 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The initial costs for both the projects are $29,000 respectively.
Note:
- NPV is the difference between the present values of the cash inflows from the present value of cash outflows.
- The IRR is the rate of interest, which makes the project’s NPV equal to zero. Hence, using the available information, assume that NPV is equal to zero and form an equation to compute the IRR.
Formula to calculate the NPV:
Compute NPV for Project A:
Hence, the NPV for Project A is $4,042.42.
Compute NPV for Project B:
Note: The rate is given at 11%.
Hence, the NPV for project B is $5,008.56.
c)
To calculate: The rates of discount at which the company will select Project A and Project B and the discount rate in which the company will be indifferent in selecting between the two projects.
Introduction:
The IRR (Internal rate of return) is a rate of discount, which makes the predictable investment’s NPV equal to zero.
The NPV (Net present value) is a capital budgeting technique, which is used to assess the investment that in turn, is utilized to identify the profitability in a proposed investment.
c)
Answer to Problem 12QP
At the rate of discount above 14.83%, the company must choose Project A and for the rate below 14.83%, the company should choose Project B. Hence, it is indifferent at the discount rate of 14.83%.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Company G has identified two mutually exclusive projects where the cash flows of Project A are$14,400, $12,300, $9,200, and $5,100 for year1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The cash flows of Project B are $4,300, $9,800, $15,200, and $16,800 for year 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively. The initial costs for both the projects are $29,000 respectively.
Note:
- NPV is the difference between the present values of the cash inflows from the present value of cash outflows.
- The IRR is the rate of interest, which makes the project’s NPV equal to zero. Hence, using the available information, assume that NPV is equal to zero and form an equation to compute the IRR.
Equation to calculate the crossover rates:
Compute the discount rate using spreadsheet
Step 1:
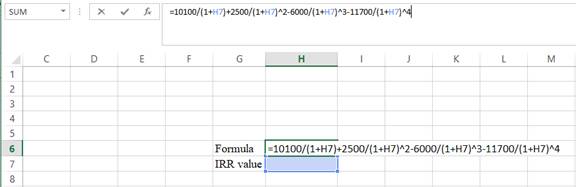
- Type the equation of NPV in H6 in the spreadsheet and consider the R value as H7.
Step 2:
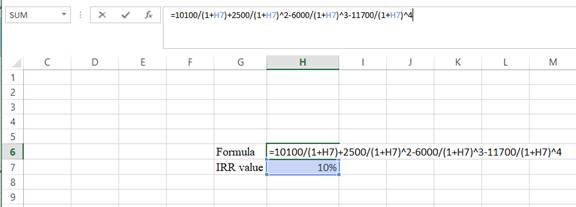
- Assume the Rvalue as 10%.
Step 3:
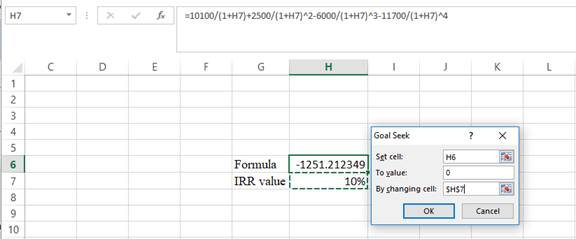
- In the spreadsheet go to data and select the what-if analysis.
- In what-if analysis select goal seek.
- In set cell select H6 (the formula).
- The “To value” is considered as 0 (the assumption value for NPV).
- The H7 cell is selected for the by changing cell.
Step 4:
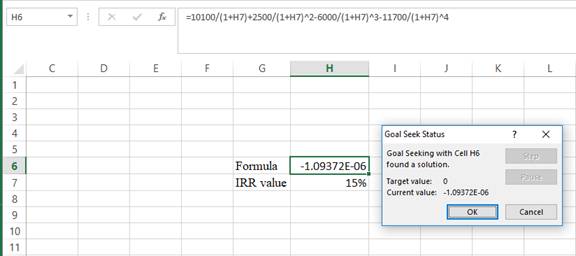
- Following the previous step click OK in the goal seek. The goal seek status appears with the Rvalue.
Step 5:
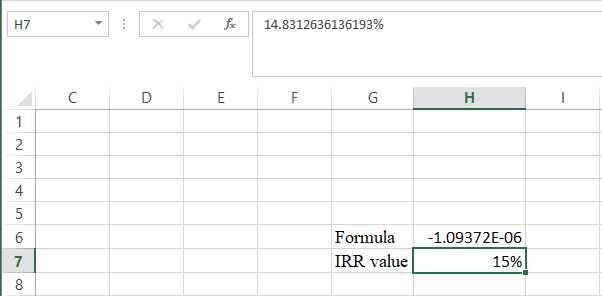
- The value appears to be 14.8312636136193%.
Hence, the R value is 14.83%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Fundamentals of Corporate Finance Standard Edition
- Imagine that the SUNY Brockport Student Government Association (SGA) is considering investing in sustainable campus improvements. These improvements include installing solar panels, updating campus lighting to energy-efficient LEDs, and implementing a rainwater collection system for irrigation. The total initial investment required for these projects is $100,000. The projects are expected to generate savings (effectively, the cash inflows in this scenario) of $30,000 in the first year, $40,000 in the second year, $50,000 in the third year, and $60,000 in the fourth year due to reduced energy and maintenance costs. SUNY Brockport’s discount rate is 8%. What is the NPV of the sustainable campus improvements? (rounded)a- $70,213b- $48,729c- $45,865d- $62,040arrow_forwardAfter many sunset viewings at SUNY Brockport, Amanda dreams of owning a waterfront home on Lake Ontario. She finds her perfect house listed at $425,000. Leveraging the negotiation skills she developed at school, she persuades the seller to drop the price to $405,000. What would be her annual payment if she opts for a 30-year mortgage from Five Star Bank with an interest rate of 14.95% and no down payment? 26,196 27,000 24,500 25,938arrow_forwardWhat is an amortized loan?arrow_forward
- 1. A bond currently has a price of $1,050. The yield on the bond is 5%. If the yield increases 30 basis points, the price of the bond will go down to $1,035. The duration of this bond is closest to: Group of answer choices None of the above 6.0 5 4.5 5.5 2. A callable corporate bond can be purchased by the bond issuer before maturity for a price specified at the time the bond is issued. Corporation X issues two bonds (bond A and bond B) at the same time with thesame maturity, par value, and coupons. However, bond A is callable and bond B is not. Which bond will sell for a higher price and why? Group of answer choices Bond B; bond B should have the value of bond A minus the value of the call option Bond A; bond A should have the value of bond B plus the value of the call option Not enough information Bond A; bond A should have the value of bond B minus the value of the call option Bond B; bond B should have the value of bond A plus the value of the call optionarrow_forwardIn plain English, what is the Agency problem?arrow_forwardHW Question 29: what is the difference between accounting and finance?arrow_forward
- 1. You are assessing the average performance of two mutual fund managers with the Fama-French 3-factor model. The fund managers and the Fama-French factors had the following performance over this periodof time: Manager 1 Manager 2 Rm − rf smb hmlAvg. (total) Ret 27% 13% 8% 2% 6%βmkt 2 1 1 0 0s 1 -0.5 0 1 0h 1 0.5 0 0 1 The risk-free rate is 2%. What kinds of stocks does Manager 1 invest in? Group of answer choices Small-cap value stocks Large-cap value stocks Large-cap growth stocks Not enough information…arrow_forward1. A hedge fund currently invests in $100 million of mortgage-backed securities (MBS) that have a duration of 15 and convexity of -500 (negative five hundred). Which of the following is closest to how much money the fund would gain or lose if interest rates decreased by 1%, using the duration+convexity approximation? Group of answer choices Lose $12 million Lose $10 million Lose $12.5 million Gain $11 million Gain $12 million 2. A hedge fund currently invests in $100 million of mortgage-backed securities (MBS) that have a duration of 15 and convexity of -500 (negative five hundred). Suppose the Hedge fund financed their $100 million of MBS by using seven-day repurchase agreements in addition to their investors’ capital. Assuming they borrow the maximum amount, the required haircut is 10%, and the interest rate is 2% per year, which of the following is closest to how much interest they will owe at the end of the first seven-day term? Group of answer choices $35,000 $40,000 $30,000…arrow_forward1. A 5-year Treasury bond with a coupon rate of 5% per year (semiannual coupons) currently has a quoted price of $100 in the Wall Street Journal. Assuming the last coupon was 60 days ago and there are 364 days per year, which of the following is closest to what you would pay to buy this bond? Group of answer choices $101.000 $100.750 $101.500 $101.250 $100.500 2. Which TWO of the following are correct reasons that could explain why most CFOs still rely on the CAPM to estimate the cost of capital in spite of the fact that it fails to explain the returns on all stocks? Group of answer choices None of the above More investors still only care about the risks captured by the CAPM, and therefore the cost-of-capital given by the CAPM, than any other model The CAPM estimates always underestimate the cost-of-capital, so CFOs can use the CAPM to deceive shareholders into believing their companies are worth more than is actually true There is not necessarily a reliably better/generally…arrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





