
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780134605197
Author: Dee Unglaub Silverthorn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8.3, Problem 7CC
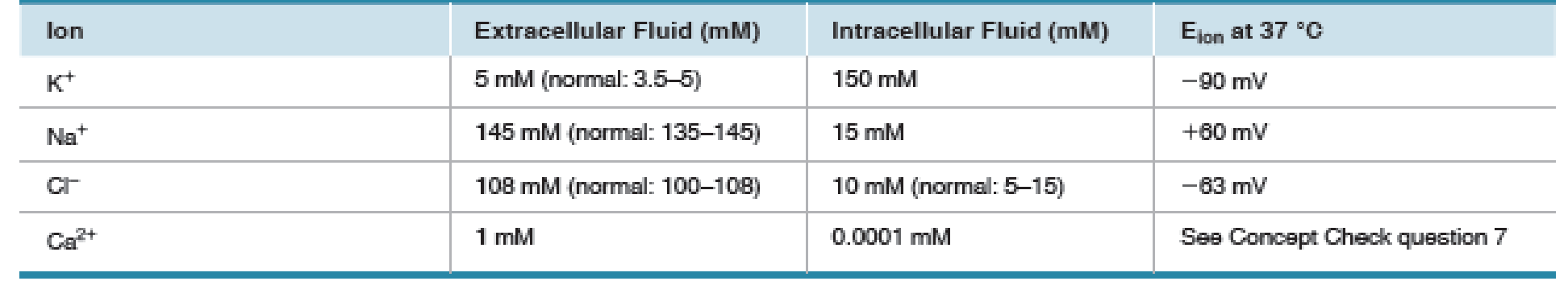
Given the values in Table 8.2, use the Nernst equation to calculate the equilibrium potential for Ca2+. Express the concentrations as powers of 10 and use your knowledge of logarithms [p. A-00] to try the calculations without a calculator.
TABLE 8.2 Ion Concentrations and Equilibrium Potentials
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
please draw in what the steps are given.
Thank you!
please draw in and fill out the empty slots from image below.
thank you!
There is a species of eagle, which lives in a tropical forest in Brazil. The alula pattern of its wings is determined by a single autosomal gene with four alleles that exhibit an unknown hierarchy of dominance. Genetic testing shows that individuals 1-1, 11-4, 11-7, III-1, and III-4 are each homozygous.
How many possible genotypes among checkered eagles in the population?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Ch. 8.1 - Organize the following terms describing functional...Ch. 8.2 - Where do neurohormone-secreting neurons terminate?Ch. 8.2 - What is the difference between a nerve and a...Ch. 8.2 - Draw a chain of three neurons that synapse on one...Ch. 8.2 - What is the primary function of each of the...Ch. 8.2 - Name the two glial cell types that form myelin....Ch. 8.3 - Given the values in Table 8.2, use the Nernst...Ch. 8.3 - Would a cell with a resting membrane potential of...Ch. 8.3 - Would the cell membrane depolarize or...Ch. 8.3 - Match each ions movement with the type of graded...
Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 11CCCh. 8.3 - What is the difference between conductance and...Ch. 8.3 - If you put ouabain, an inhibitor of the Na+-K+...Ch. 8.3 - The pyrethrin insecticides, derived from...Ch. 8.3 - When Na+ channel gates are resetting, is the...Ch. 8.3 - A stimulating electrode placed halfway down an...Ch. 8.3 - Place the following neurons in order of their...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 18CCCh. 8.4 - Prob. 19CCCh. 8.4 - Prob. 20CCCh. 8.4 - Prob. 21CCCh. 8.4 - Prob. 22CCCh. 8.4 - Classify the H+-neurotransmitter exchange as...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 24CCCh. 8.4 - Prob. 25CCCh. 8.4 - Is Na+-dependent neurotransmitter reuptake...Ch. 8.5 - In Figure 8.24e, assume the postsynaptic neuron...Ch. 8.5 - In the graphs of Figure 8.24a, b, why doesnt the...Ch. 8.5 - Prob. 29CCCh. 8.5 - Prob. 30CCCh. 8 - List the three functional classes of neurons, and...Ch. 8 - Somatic motor neurons control __________, and...Ch. 8 - Prob. 3RQCh. 8 - Prob. 4RQCh. 8 - Prob. 5RQCh. 8 - Prob. 6RQCh. 8 - Axonal transport refers to the (a) release of...Ch. 8 - Match the numbers of the appropriate...Ch. 8 - Arrange the following events in the proper...Ch. 8 - List the four major types of ion channels found in...Ch. 8 - Prob. 11RQCh. 8 - An action potential is (circle all correct...Ch. 8 - Choose from the following ions to fill in the...Ch. 8 - What is the myelin sheath?Ch. 8 - List two factors that enhance conduction speed.Ch. 8 - Prob. 16RQCh. 8 - Draw and label a graph of an action potential....Ch. 8 - Prob. 18RQCh. 8 - Prob. 19RQCh. 8 - Create a map showing the organization of the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 21RQCh. 8 - Prob. 22RQCh. 8 - Prob. 23RQCh. 8 - Prob. 24RQCh. 8 - The presence of myelin allows an axon to (choose...Ch. 8 - Define, compare, and contrast the following...Ch. 8 - Prob. 27RQCh. 8 - Prob. 28RQCh. 8 - Prob. 29RQCh. 8 - Prob. 30RQCh. 8 - An unmyelinated axon has a much greater...Ch. 8 - The GHK equation is sometimes abbreviated to...Ch. 8 - In each of the following scenarios, will an action...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- students in a science class investiged the conditions under which corn seeds would germinate most successfully. BAsed on the results which of these factors appears most important for successful corn seed germination.arrow_forwardI want to write the given physician orders in the kardex formarrow_forwardAmino Acid Coclow TABle 3' Gly Phe Leu (G) (F) (L) 3- Val (V) Arg (R) Ser (S) Ala (A) Lys (K) CAG G Glu Asp (E) (D) Ser (S) CCCAGUCAGUCAGUCAG 0204 C U A G C Asn (N) G 4 A AGU C GU (5) AC C UGA A G5 C CUGACUGACUGACUGAC Thr (T) Met (M) lle £€ (1) U 4 G Tyr Σε (Y) U Cys (C) C A G Trp (W) 3' U C A Leu בוט His Pro (P) ££ (H) Gin (Q) Arg 흐름 (R) (L) Start Stop 8. Transcription and Translation Practice: (Video 10-1 and 10-2) A. Below is the sense strand of a DNA gene. Using the sense strand, create the antisense DNA strand and label the 5' and 3' ends. B. Use the antisense strand that you create in part A as a template to create the mRNA transcript of the gene and label the 5' and 3' ends. C. Translate the mRNA you produced in part B into the polypeptide sequence making sure to follow all the rules of translation. 5'-AGCATGACTAATAGTTGTTGAGCTGTC-3' (sense strand) 4arrow_forward
- What is the structure and function of Eukaryotic cells, including their organelles? How are Eukaryotic cells different than Prokaryotic cells, in terms of evolution which form of the cell might have came first? How do Eukaryotic cells become malignant (cancerous)?arrow_forwardWhat are the roles of DNA and proteins inside of the cell? What are the building blocks or molecular components of the DNA and proteins? How are proteins produced within the cell? What connection is there between DNA, proteins, and the cell cycle? What is the relationship between DNA, proteins, and Cancer?arrow_forwardWhy cells go through various types of cell division and how eukaryotic cells control cell growth through the cell cycle control system?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College


Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781337711067
Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna Balac
Publisher:Cengage Learning



Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:OpenStax College
Enzyme Kinetics; Author: MIT OpenCourseWare;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FXWZr3mscUo;License: Standard Youtube License