
(a)
The coordinates in table form for the holes by using absolute programming.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The length A is
The length B is
The length C is
The length D is
The length E is
The length F is
The length G is
The length H is
The length J is
The length K is
The length L is
The length M is
The length N is
Pitch diameter of circular pattern with holes is
Angle 1 is
Concept Used:
Draw the diagram for the location of holes as shown below:
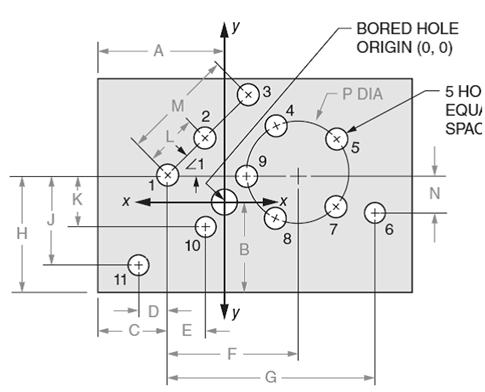
Write the expression for the location of first hole in absolute programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of second hole in absolute programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of third hole in absolute programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of fourth hole in absolute programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of fifth hole in absolute programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of sixth hole in absolute programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of seventh hole in absolute programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of eighth hole in absolute programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of ninth hole in absolute programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of tenth hole in absolute programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of eleventh hole in absolute programming.
Here,
Calculation:
Substitute
The coordinates of first hole in absolute programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of second hole in absolute programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of third hole in absolute programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of fourth hole in absolute programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of fifth hole in absolute programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of sixth hole in absolute programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of seventh hole in absolute programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of eighth hole in absolute programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of ninth hole in absolute programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of tenth hole in absolute programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of eleventh hole in absolute programming is
Conclusion:
The coordinate of each hole is shown in below table:
| Hole | X-coordinate (in mm) | Y-coordinate (in mm) |
| 1 | | |
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| 7 | | |
| 8 | ||
| 9 | ||
| 10 | ||
| 11 |
(b)
The coordinates in table form for the holes by using incremental programming.
Explanation of Solution
Concept Used:
Write the expression for the location of first hole in incremental programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of second hole in incremental programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of third hole in incremental programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of fourth hole in incremental programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of fifth hole in incremental programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of sixth hole in incremental programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of seventh hole in incremental programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of eighth hole in incremental programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of ninth hole in incremental programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of tenth hole in incremental programming.
Here,
Write the expression for the location of eleventh hole in incremental programming.
Here,
Calculation:
Substitute
The coordinates of first hole in incremental programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of second hole in incremental programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of third hole in incremental programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of fourth hole in incremental programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of fifth hole in incremental programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of sixth hole in incremental programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of seventh hole in incremental programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of eighth hole in incremental programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of ninth hole in incremental programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of tenth hole in incremental programming is
Substitute
The coordinates of eleventh hole in incremental programming is
Conclusion:
The coordinate of each hole is shown in below table:
| Hole | X-coordinate (in mm) | Y-coordinate (in mm) |
| 1 | | |
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 6 | ||
| 7 | | |
| 8 | ||
| 9 | ||
| 10 | ||
| 11 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 82 Solutions
Mathematics For Machine Technology
- Remix 4. Direction Fields/Phase Portraits. Use the given direction fields to plot solution curves to each of the given initial value problems. (a) x = x+2y 1111 y = -3x+y with x(0) = 1, y(0) = -1 (b) Consider the initial value problem corresponding to the given phase portrait. x = y y' = 3x + 2y Draw two "straight line solutions" passing through (0,0) (c) Make guesses for the equations of the straight line solutions: y = ax.arrow_forwardIt was homeworkarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 18) Find all the complex cube roots of -2i. Leave your answers in polar form with the argument in degrees.arrow_forward9) Write an equation for the hyperbola. 2+ -6-5-4-3-2 -2- -4- -5+ + 23 45 6xarrow_forward8) Find an equation for the hyperbola with vertices at vertices at (±7, 0) and foci at (±9, 0).arrow_forward
 Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal LittellAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal LittellAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,





