
Concept explainers
Seasonal business cycle. Suppose that profits on the sale of swimming suits over a 2-year period are given approximately by
where P is profit (in hundreds of dollars) for a week of sales t weeks after January 1. The graph of the profit function is shown in the figure.
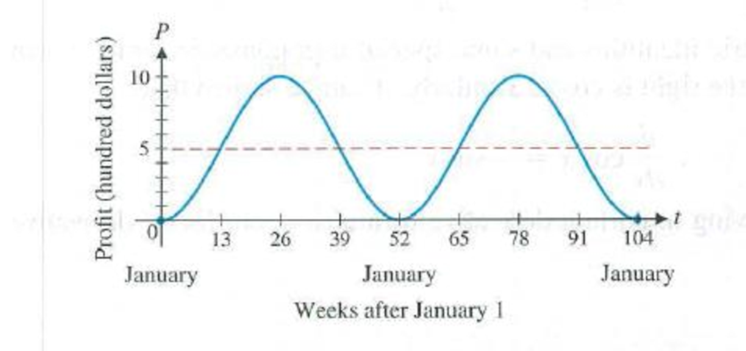
(A) Find the exact values of P(13), P(26), P(39), and P(52) without using a calculator.
(B) Use a calculator to find P(30) and P(100). Interpret the results.
(C) Use a graphing calculator to confirm the graph shown here for y = P(t).
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (13th Edition)
- x-4 For the function f(x): find f'(x), the third derivative of f, and f(4) (x), the fourth derivative of f. x+7arrow_forwardIn x For the function f(x) = find f'(x). Then find f''(0) and f''(9). 11x'arrow_forwardLet f(x) = √√x+3 and g(x) = 6x − 2. Find each of the following composite functions and state the domain: (a) fog (b) gof, (c) fof (d) gogarrow_forward
- Compute the following: (a) 8x³ + 3x dx (b) cos(2u) du (c) f² ebx dxarrow_forwardFind the following limits. (a) lim 3(x-1)² x→2 x (b) lim 0+x (c) lim 3x2-x+1 x²+3 x²+x-12 x-3 x-3arrow_forwardFor f(x) = (x+3)² - 2 sketch f(x), f(x), f(x − 2), and f(x) — 2. State the coordi- nates of the turning point in each graph.arrow_forward
- if the b coloumn of a z table disappeared what would be used to determine b column probabilitiesarrow_forwardConstruct a model of population flow between metropolitan and nonmetropolitan areas of a given country, given that their respective populations in 2015 were 263 million and 45 million. The probabilities are given by the following matrix. (from) (to) metro nonmetro 0.99 0.02 metro 0.01 0.98 nonmetro Predict the population distributions of metropolitan and nonmetropolitan areas for the years 2016 through 2020 (in millions, to four decimal places). (Let x, through x5 represent the years 2016 through 2020, respectively.) x₁ = x2 X3 261.27 46.73 11 259.59 48.41 11 257.96 50.04 11 256.39 51.61 11 tarrow_forwardFill in all the justifications to complete this formal proof, following all conventions from the textbook. 1. Ax~Q(x) 2. Ax(Q(x)vR(x)) 3. @n Premise Premise 4. | ~Q(n) 5. | Q(n)vR(n) 6. || Q(n) 7. || # 8. || R(n) 9. || R(n) 10. | R(n) 11. AxR(x)arrow_forward
- For f(x) = (x+3)² - 2 sketch f(x), f(x), f(x − 2), and f(x) — 2. State the coordi- nates of the turning point in each graph.arrow_forwardIn quadrilateral QRST, m<R=60, m<T=90, QR=RS, ST=8, TQ=8 How long is the longer diagonal of QRST? Find the ratio of RT to QS.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning





