
Concept explainers
To find: The 95% margin of error for the difference of two proportions for
Answer to Problem 94E
Solution: The margin of error is 0.1717.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: The assumption made that the sample size n is the common value of
Where, z* is the critical value for the standard normal variable and
Where,
Substitute the provided values
The value of
Therefore, the margin of error is obtained as 0.1717.
To find: The 95% margin of error for the difference of two proportions for sample size
Answer to Problem 94E
Solution: The margin of error is 0.1589.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: The assumption made that the sample size n is the common value of
Where z* is the critical value for the standard normal variable and
Where
Substitute the provided values
The value of
Therefore, the margin of error is obtained as 0.1589.
To find: The 95% margin of error for the difference of two proportions for sample size
Answer to Problem 94E
Solution: The margin of error is 0.1486.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: The assumption made that the sample size n is the common value of
Where z* is the critical value for the standard normal variable and
Where
Substitute the provided values
The value of
Therefore, the margin of error is obtained as 0.1486.
To find: The 95% margin of error for the difference of two proportions for sample size
Answer to Problem 94E
Solution: The margin of error is 0.1329.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: The assumption made that the sample size n is the common value of
Where z* is the value for the standard normal density curve and
Where
Substitute the provided values
The value of
Therefore, the margin of error is obtained as 0.1329.
To find: The 95% margin of error for the difference of two proportions for sample size
Answer to Problem 94E
Solution: The margin of error is 0.0665.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: The assumption made that the sample size n is the common value of
Where z* is the critical value for the standard normal variable and
Where
Substitute the provided values
The value of
Therefore, the margin of error is obtained as 0.0665.
To find: The 95% margin of error for the difference of two proportions for sample size
Answer to Problem 94E
Solution: The margin of error is 0.0595.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: The assumption made that the sample size n is the common value of
Where z* is the critical value for the standard normal variable and
Where
Substitute the provided values
The value of
Therefore, the margin of error is obtained as 0.0595.
To find: The 95% margin of error for the difference of two proportions for sample size
Answer to Problem 94E
Solution: The margin of error is 0.0420.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: The assumption made that the sample size n is the common value of
Where z* is the critical value for the standard normal variable and
Where
Substitute the provided values
The value of
Therefore, the margin of error is obtained as 0.0420.
The obtained results of margin of error for different sample sizes in a table.
Answer to Problem 94E
Solution: The obtained results of 95% margins of error for different sample sizes are tabulated as:
N |
m |
60 |
0.1717 |
70 |
0.1589 |
80 |
0.1486 |
100 |
0.1329 |
400 |
0.0665 |
500 |
0.0595 |
1000 |
0.0420 |
Explanation of Solution
n |
m |
60 |
0.1717 |
70 |
0.1589 |
80 |
0.1486 |
100 |
0.1329 |
400 |
0.0665 |
500 |
0.0595 |
1000 |
0.0420 |
So, it is observed that with an increase in the sample size the margin of error reduces. Hence, a larger sample results in more accurate results.
To graph: The 95% margins of error obtained for different sample sizes.
Explanation of Solution
Graph: To obtain the graph of 95% margins of error for different sample sizes, Minitab is used. The steps followed to construct the graph are:
Step 1: Enter the data of the sample sizes and the associated margins of error values in the worksheet.
Step 2: Select Graph-->
Step 3: Select Simple from the opened dialog and click on OK.
Step 4: Select the Y variables as margin of error column and X variable as sample size column and click on OK.
The graph is obtained as:
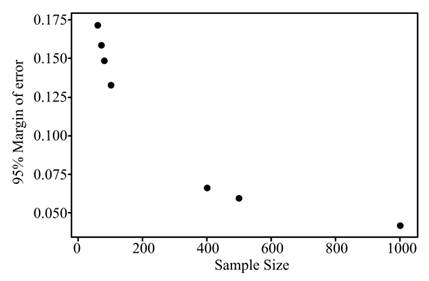
To explain: A short summary of the obtained results.
Answer to Problem 94E
Solution: The obtained results of margins of error and the graph shows that the margin of error decreases as the sample size increases. But the rate of decrease of margin of error is very less for large n.
Explanation of Solution
Hence, a larger sample is desirable for a lower error.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK INTRODUCTION TO THE PRACTICE OF STA
- Problem 4. Margrabe formula and the Greeks (20 pts) In the homework, we determined the Margrabe formula for the price of an option allowing you to swap an x-stock for a y-stock at time T. For stocks with initial values xo, yo, common volatility σ and correlation p, the formula was given by Fo=yo (d+)-x0Þ(d_), where In (±² Ꭲ d+ õ√T and σ = σ√√√2(1 - p). дго (a) We want to determine a "Greek" for ỡ on the option: find a formula for θα (b) Is дго θα positive or negative? (c) We consider a situation in which the correlation p between the two stocks increases: what can you say about the price Fo? (d) Assume that yo< xo and p = 1. What is the price of the option?arrow_forwardWe consider a 4-dimensional stock price model given (under P) by dẴ₁ = µ· Xt dt + йt · ΣdŴt where (W) is an n-dimensional Brownian motion, π = (0.02, 0.01, -0.02, 0.05), 0.2 0 0 0 0.3 0.4 0 0 Σ= -0.1 -4a За 0 0.2 0.4 -0.1 0.2) and a E R. We assume that ☑0 = (1, 1, 1, 1) and that the interest rate on the market is r = 0.02. (a) Give a condition on a that would make stock #3 be the one with largest volatility. (b) Find the diversification coefficient for this portfolio as a function of a. (c) Determine the maximum diversification coefficient d that you could reach by varying the value of a? 2arrow_forwardQuestion 1. Your manager asks you to explain why the Black-Scholes model may be inappro- priate for pricing options in practice. Give one reason that would substantiate this claim? Question 2. We consider stock #1 and stock #2 in the model of Problem 2. Your manager asks you to pick only one of them to invest in based on the model provided. Which one do you choose and why ? Question 3. Let (St) to be an asset modeled by the Black-Scholes SDE. Let Ft be the price at time t of a European put with maturity T and strike price K. Then, the discounted option price process (ert Ft) t20 is a martingale. True or False? (Explain your answer.) Question 4. You are considering pricing an American put option using a Black-Scholes model for the underlying stock. An explicit formula for the price doesn't exist. In just a few words (no more than 2 sentences), explain how you would proceed to price it. Question 5. We model a short rate with a Ho-Lee model drt = ln(1+t) dt +2dWt. Then the interest rate…arrow_forward
- In this problem, we consider a Brownian motion (W+) t≥0. We consider a stock model (St)t>0 given (under the measure P) by d.St 0.03 St dt + 0.2 St dwt, with So 2. We assume that the interest rate is r = 0.06. The purpose of this problem is to price an option on this stock (which we name cubic put). This option is European-type, with maturity 3 months (i.e. T = 0.25 years), and payoff given by F = (8-5)+ (a) Write the Stochastic Differential Equation satisfied by (St) under the risk-neutral measure Q. (You don't need to prove it, simply give the answer.) (b) Give the price of a regular European put on (St) with maturity 3 months and strike K = 2. (c) Let X = S. Find the Stochastic Differential Equation satisfied by the process (Xt) under the measure Q. (d) Find an explicit expression for X₁ = S3 under measure Q. (e) Using the results above, find the price of the cubic put option mentioned above. (f) Is the price in (e) the same as in question (b)? (Explain why.)arrow_forwardThe managing director of a consulting group has the accompanying monthly data on total overhead costs and professional labor hours to bill to clients. Complete parts a through c. Question content area bottom Part 1 a. Develop a simple linear regression model between billable hours and overhead costs. Overhead Costsequals=212495.2212495.2plus+left parenthesis 42.4857 right parenthesis42.485742.4857times×Billable Hours (Round the constant to one decimal place as needed. Round the coefficient to four decimal places as needed. Do not include the $ symbol in your answers.) Part 2 b. Interpret the coefficients of your regression model. Specifically, what does the fixed component of the model mean to the consulting firm? Interpret the fixed term, b 0b0, if appropriate. Choose the correct answer below. A. The value of b 0b0 is the predicted billable hours for an overhead cost of 0 dollars. B. It is not appropriate to interpret b 0b0, because its value…arrow_forwardUsing the accompanying Home Market Value data and associated regression line, Market ValueMarket Valueequals=$28,416+$37.066×Square Feet, compute the errors associated with each observation using the formula e Subscript ieiequals=Upper Y Subscript iYiminus−ModifyingAbove Upper Y with caret Subscript iYi and construct a frequency distribution and histogram. LOADING... Click the icon to view the Home Market Value data. Question content area bottom Part 1 Construct a frequency distribution of the errors, e Subscript iei. (Type whole numbers.) Error Frequency minus−15 comma 00015,000less than< e Subscript iei less than or equals≤minus−10 comma 00010,000 0 minus−10 comma 00010,000less than< e Subscript iei less than or equals≤minus−50005000 5 minus−50005000less than< e Subscript iei less than or equals≤0 21 0less than< e Subscript iei less than or equals≤50005000 9…arrow_forward
- The managing director of a consulting group has the accompanying monthly data on total overhead costs and professional labor hours to bill to clients. Complete parts a through c Overhead Costs Billable Hours345000 3000385000 4000410000 5000462000 6000530000 7000545000 8000arrow_forwardUsing the accompanying Home Market Value data and associated regression line, Market ValueMarket Valueequals=$28,416plus+$37.066×Square Feet, compute the errors associated with each observation using the formula e Subscript ieiequals=Upper Y Subscript iYiminus−ModifyingAbove Upper Y with caret Subscript iYi and construct a frequency distribution and histogram. Square Feet Market Value1813 911001916 1043001842 934001814 909001836 1020002030 1085001731 877001852 960001793 893001665 884001852 1009001619 967001690 876002370 1139002373 1131001666 875002122 1161001619 946001729 863001667 871001522 833001484 798001589 814001600 871001484 825001483 787001522 877001703 942001485 820001468 881001519 882001518 885001483 765001522 844001668 909001587 810001782 912001483 812001519 1007001522 872001684 966001581 86200arrow_forwarda. Find the value of A.b. Find pX(x) and py(y).c. Find pX|y(x|y) and py|X(y|x)d. Are x and y independent? Why or why not?arrow_forward
- The PDF of an amplitude X of a Gaussian signal x(t) is given by:arrow_forwardThe PDF of a random variable X is given by the equation in the picture.arrow_forwardFor a binary asymmetric channel with Py|X(0|1) = 0.1 and Py|X(1|0) = 0.2; PX(0) = 0.4 isthe probability of a bit of “0” being transmitted. X is the transmitted digit, and Y is the received digit.a. Find the values of Py(0) and Py(1).b. What is the probability that only 0s will be received for a sequence of 10 digits transmitted?c. What is the probability that 8 1s and 2 0s will be received for the same sequence of 10 digits?d. What is the probability that at least 5 0s will be received for the same sequence of 10 digits?arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





