
Concept explainers
(a)
The maximum wind speed that a blowfly can stand.
(a)
Answer to Problem 91P
The blowfly can stand a wind speed up to
Explanation of Solution
The cross-sectional area of the blowfly is
For the blowfly to stand the wind, the net torque on it will be zero. Consider the axis of the rotation to pass through the tip of the left leg.
The figure below shows the blowfly and different forces.
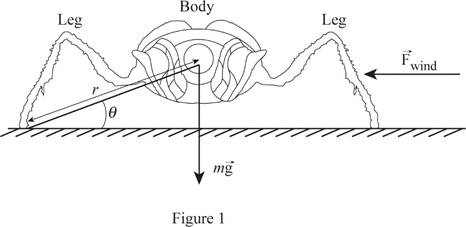
Write the formula for the condition to stand the wind.
Here,
Write the formula for the force due to wind.
Here,
Substitute equation (II) in equation (I).
Re-write the above equation to get an expression for
Conclusion:
Substitute
The blowfly can stand a wind speed up to
(b)
The maximum wind speed that a blowfly can stand when the angle is
(b)
Answer to Problem 91P
The blowfly can stand a wind speed up to
Explanation of Solution
The cross-sectional area of the blowfly is
For the blowfly to stand the wind, the net torque on it will be zero. Consider the axis of the rotation to pass through the tip of the left leg.
Write the formula for the condition to stand the wind.
Here,
Write the formula for the force due to wind.
Here,
Substitute equation (II) in equation (I).
Re-write the above equation to get an expression for
Conclusion:
Substitute
The blowfly can stand a wind speed up to
(c)
The maximum wind speed that a blowfly can stand when the angle is
(c)
Answer to Problem 91P
The blowfly can stand a wind speed up to
Explanation of Solution
The cross-sectional area of the blowfly is
For the blowfly to stand the wind, the net torque on it will be zero. Consider the axis of the rotation to pass through the tip of the left leg.
Write the formula for the condition to stand the wind.
Here,
Write the formula for the force due to wind.
Here,
Substitute equation (II) in equation (I).
Re-write the above equation to get an expression for
Conclusion:
Substitute
The blowfly can stand a wind speed up to
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Physics
- Consider a uniformly charged ring of radius R with total charge Q, centered at the origin inthe xy-plane. Find the electric field (as a vector) at a point on the z-axis at a distance z above thecenter of the ring. Assume the charge density is constant along the ring.arrow_forward3) If the slider block C is moving at 3m/s, determine the angular velocity of BC and the crank AB at the instant shown. (Use equation Vs Vc wx fuc, then use equation Vs VA + Ve/athen write it in terms of w and the appropriate r equate the two and solve) 0.5 m B 1 m 60° A 45° vc = 3 m/sarrow_forward3) If the slider block C is moving at 3m/s, determine the angular velocity of BC and the crank AB at the instant shown. (Use equation Vs Vc wxf, then use equation V, VA + Va/Athen write it in terms of w and the appropriate r equate the two and solve) f-3marrow_forward
- Pls help ASAParrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward14. A boy is out walking his dog. From his house, he walks 30 m North, then 23 m East, then 120 cm South, then 95 m West, and finally 10 m East. Draw a diagram showing the path that the boy walked, his total displacement, and then determine the magnitude and direction of his total displacement.arrow_forward
- Pls help ASAParrow_forward12. A motorboat traveling 6 m/s, West encounters a water current travelling 3.5 m/s, South. a) Draw a vector diagram showing the resultant velocity, then determine the resultant velocity of the motorboat. b) If the width of the river is 112 m wide, then how much time does it take for the boat to travel shore to shore? c) What distance downstream does the boat reach the opposite shore?arrow_forwardLake Erie contains roughly 4.00⋅10114.00⋅1011 m3 of water. Assume the density of this water is 1000. kg/m3 and the specific heat of water is 4186 J/kg˚C. It takes 2.31x10^19 J of energy to raise the temperature of that volume of water from 12.0 °C to 25.8 ˚C. An electric power plant can produce about 1110 MW. How many years would it take to supply this amount of energy by using the 1110 MW from an electric power plant?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





