
Concept explainers
(a)
To determine: The lewis structure for
(a)
Answer to Problem 8.88QP
Solution
The lewis structure for
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
Number of valence electrons in hydrogen is
Carbon is bonded to three hydrogen atoms and nitrogen atom by single bond. With one oxygen, nitrogen is bonded by single bond while with other oxygen, it is bonded by double bond. Lone pairs of electrons present on oxygen atoms are delocalized which results in the formation of another lewis structure. Hence the lewis structure of
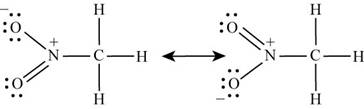
Figure 1
(b)
To determine: The lewis structure for.
(b)
Answer to Problem 8.88QP
Solution
The lewis structures for.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The two given possible skeletal for
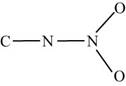
Figure 2
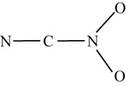
Figure 3
In the first skeletal, the nitrogen of
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
With one oxygen atom, nitrogen is bonded by single bond while with other oxygen; it is bonded by double bond. Lone pairs of electrons present on oxygen atoms are delocalized which results in the formation of another lewis structure. Hence the lewis structure of
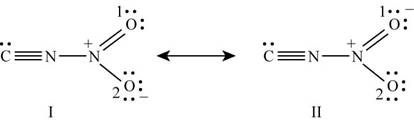
Figure 4
The formal charge on each atom of resonating structure (I) of
Formal charge is calculated as,
Number of valence electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in first nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on first nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
Number of lone pair electrons in carbon is
Number of bond pair electrons in carbon is
To calculate the formal charge on carbon, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in second nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on second nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (1), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (2), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
The formal charge on each atom of resonating structure (II) of
Number of valence electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in first nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on first nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
Number of lone pair electrons in carbon is
Number of bond pair electrons in carbon is
To calculate the formal charge on carbon, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in second nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on second nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (1), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (2), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
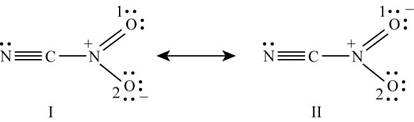
Figure 5
The formal charge on each atom of resonating structure (I) of
Number of valence electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in first nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on first nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
Number of lone pair electrons in carbon is
Number of bond pair electrons in carbon is
To calculate the formal charge on carbon, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in second nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on second nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (1), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (2), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
The formal charge on each atom of resonating structure (II) of
Number of valence electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in first nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in first nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on first nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in carbon is
Number of lone pair electrons in carbon is
Number of bond pair electrons in carbon is
To calculate the formal charge on carbon, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of lone pair electrons in second nitrogen is
Number of bond pair electrons in second nitrogen is
To calculate the formal charge on second nitrogen, substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (1) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (1), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
Number of valence electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of lone pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
Number of bond pair electrons in oxygen (2) is
To calculate the formal charge on oxygen (2), substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair electrons and bond pair electrons in the equation (1).
The resonating structure which possesses zero or minimum formal charge is preferred. The distribution of formal charges on both the molecules
(c)
To determine: Whether the given two structures of
(c)
Answer to Problem 8.88QP
Solution
The two structures of
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
In the resonating forms, the postion of atoms remains same. But in the two structures of
Conclusion
The two structures of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry: The Science in Context (Fourth Edition)
- -AG|F=2E|V 3. Before proceeding with this problem you may want to glance at p. 466 of your textbook where various oxo-phosphorus derivatives and their oxidation states are summarized. Shown below are Latimer diagrams for phosphorus at pH values at 0 and 14: Acidic solution -0.93 +0.38 -0.51 -0.06 H3PO4 →H4P206 H3PO3 H3PO2 → P→ PH3 -0.28 -0.50 → -0.50 Basic solution 3-1.12 -1.57 -2.05 -0.89 PO HPO →→H2PO2 P PH3 -1.73 a) Under acidic conditions, H3PO4 can be reduced into H3PO3 directly (-0.28V), or via the formation and reduction of H4P2O6 (-0.93/+0.38V). Calculate the values of AG's for both processes; comment. (3 points) 0.5 PH, 0.0 -0.5- 2 3 9 3 -1.5 -2.0 Pa H,PO H,PO H,PO -3 -1 0 2 4 Oxidation state, N 2 b) Frost diagram for phosphorus under acidic conditions is shown. Identify possible disproportionation and comproportionation processes; write out chemical equations describing them. (2 points) c) Elemental phosphorus tends to disproportionate under basic conditions. Use data in…arrow_forwardThese two reactions appear to start with the same starting materials but result in different products. How do the chemicals know which product to form? Are both products formed, or is there some information missing that will direct them a particular way?arrow_forwardWhat would be the best choices for the missing reagents 1 and 3 in this synthesis? 1. PPh3 3 1 2 2. n-BuLi • Draw the missing reagents in the drawing area below. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. • Do not draw the missing reagent 2. If you draw 1 correctly, we'll know what it is. • Note: if one of your reagents needs to contain a halogen, use bromine. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Priva ×arrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: Explanation Check IN NaBH3CN H+ ? Click and drag to start drawing a structure. D 5 C +arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: H3O+ + ? • Draw all the reasonable products in the drawing area below. If there are no products, because no reaction will occur, check the box under the drawing area. • Include both major and minor products, if some of the products will be more common than others. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds if you need to distinguish between enantiomers. No reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. dmarrow_forwardIarrow_forward
- Draw the anti-Markovnikov product of the hydration of this alkene. this problem. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for esc esc ☐ Explanation Check F1 1 2 F2 # 3 F3 + $ 14 × 1. BH THE BH3 2. H O NaOH '2 2' Click and drag to start drawing a structure. F4 Q W E R A S D % 905 LL F5 F6 F7 © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility < & 6 7 27 8 T Y U G H I F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 9 0 J K L P + // command option Z X C V B N M H H rol option commandarrow_forwardAG/F-2° V 3. Before proceeding with this problem you may want to glance at p. 466 of your textbook where various oxo-phosphorus derivatives and their oxidation states are summarized. Shown below are Latimer diagrams for phosphorus at pH values at 0 and 14: -0.93 +0.38 -0.50 -0.51 -0.06 H3PO4 →H4P206 →H3PO3 →→H3PO₂ → P → PH3 Acidic solution Basic solution -0.28 -0.50 3--1.12 -1.57 -2.05 -0.89 PO HPO H₂PO₂ →P → PH3 -1.73 a) Under acidic conditions, H3PO4 can be reduced into H3PO3 directly (-0.28V), or via the formation and reduction of H4P206 (-0.93/+0.38V). Calculate the values of AG's for both processes; comment. (3 points) 0.5 PH P 0.0 -0.5 -1.0- -1.5- -2.0 H.PO, -2.3+ -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 2 H,PO, b) Frost diagram for phosphorus under acidic conditions is shown. Identify possible disproportionation and comproportionation processes; write out chemical equations describing them. (2 points) H,PO 4 S Oxidation stale, Narrow_forward4. For the following complexes, draw the structures and give a d-electron count of the metal: a) Tris(acetylacetonato)iron(III) b) Hexabromoplatinate(2-) c) Potassium diamminetetrabromocobaltate(III) (6 points)arrow_forward
- 2. Calculate the overall formation constant for [Fe(CN)6]³, given that the overall formation constant for [Fe(CN)6] 4 is ~1032, and that: Fe3+ (aq) + e = Fe²+ (aq) E° = +0.77 V [Fe(CN)6]³ (aq) + e¯ = [Fe(CN)6] (aq) E° = +0.36 V (4 points)arrow_forward5. Consider the compounds shown below as ligands in coordination chemistry and identify their denticity; comment on their ability to form chelate complexes. (6 points) N N A B N N N IN N Carrow_forward1. Use standard reduction potentials to rationalize quantitatively why: (6 points) (a) Al liberates H2 from dilute HCl, but Ag does not; (b) Cl2 liberates Br2 from aqueous KBr solution, but does not liberate C12 from aqueous KCl solution; c) a method of growing Ag crystals is to immerse a zinc foil in an aqueous solution of AgNO3.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





