
(a)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction and the structure of any intermediate are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Substitution reactions are the reactions in which there is a replacement of an atom or a
Elimination reactions are the reaction in which
(a)
Answer to Problem 8.46SP
The structure of an intermediate is shown in Figure 1.
The major product of the given reaction is shown in Figure 2.
Explanation of Solution
When
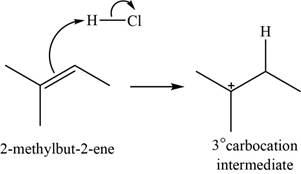
Figure 1
The chloride ion acts as a nucleophile that attacks on the electrophilic tertiary carbocation and results in the formation of
The major product of the given reaction is,
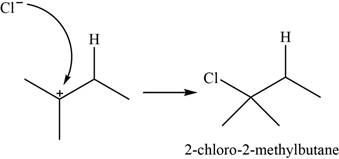
Figure 2
(b)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction and the structure of any intermediate are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Substitution reactions are the reactions in which there is a replacement of an atom or a functional group by another atom or a functional group.
Elimination reactions are the reaction in which alkenes are prepared. In this two substituents are eliminated by either one step or two step mechanism.
(b)
Answer to Problem 8.46SP
The structure of an intermediate is shown in Figure 3.
The major product of the given reaction is shown in Figure 4.
Explanation of Solution
When
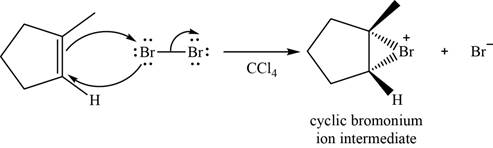
Figure 3
Bromide ion opens the bromonium ion intermediate at the more substituted carbon atom and forms
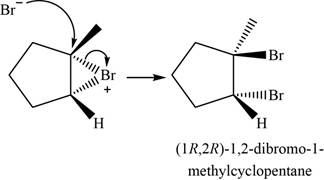
Figure 4
(c)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction and the structure of any intermediate are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Substitution reactions are the reactions in which there is a replacement of an atom or a functional group by another atom or a functional group.
Elimination reactions are the reaction in which alkenes are prepared. In this two substituents are eliminated by either one step or two step mechanism.
(c)
Answer to Problem 8.46SP
The structure of an intermediate is shown in Figure 5.
The major product of the given reaction is shown in Figure 6.
Explanation of Solution
When
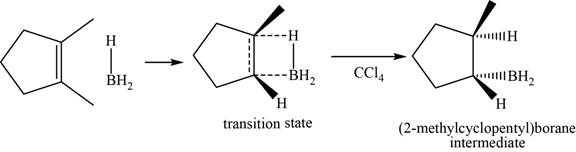
Figure 5
When
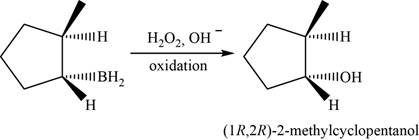
Figure 6
(d)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction and the structure of any intermediate are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Substitution reactions are the reactions in which there is a replacement of an atom or a functional group by another atom or a functional group.
Elimination reactions are the reaction in which alkenes are prepared. In this two substituents are eliminated by either one step or two step mechanism.
(d)
Answer to Problem 8.46SP
The structure of an intermediate is shown in Figure 7.
The major product of the given reaction is shown in Figure 8.
Explanation of Solution
When
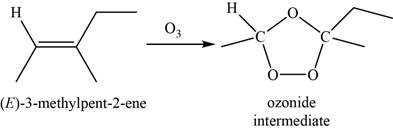
Figure 7
Now, the ozonide intermediate reacts with dimethyl sulfide and forms acetaldehyde and
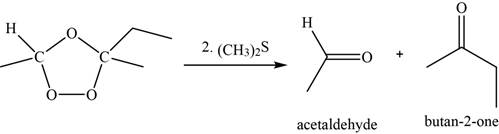
Figure 8
(e)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction and the structure of any intermediate are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Substitution reactions are the reactions in which there is a replacement of an atom or a functional group by another atom or a functional group.
Elimination reactions are the reaction in which alkenes are prepared. In this two substituents are eliminated by either one step or two step mechanism.
(e)
Answer to Problem 8.46SP
The major product of the given reaction is shown in Figure 9.
Explanation of Solution
When alkene reacts with
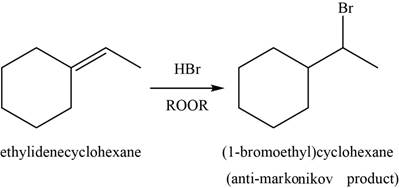
Figure 9
(f)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction and the structure of any intermediate are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Substitution reactions are the reactions in which there is a replacement of an atom or a functional group by another atom or a functional group.
Elimination reactions are the reaction in which alkenes are prepared. In this two substituents are eliminated by either one step or two step mechanism.
(f)
Answer to Problem 8.46SP
The major product of the given reaction is shown in Figure 10.
Explanation of Solution
When alkene reacts with
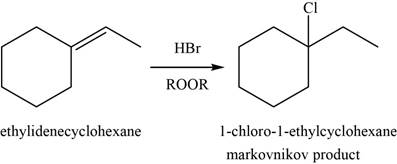
Figure 10
(g)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction and the structure of any intermediate are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Substitution reactions are the reactions in which there is a replacement of an atom or a functional group by another atom or a functional group.
Elimination reactions are the reaction in which alkenes are prepared. In this two substituents are eliminated by either one step or two step mechanism.
(g)
Answer to Problem 8.46SP
The major product of the given reaction is shown in Figure 11.
Explanation of Solution
When an alkene reacts with peroxyacid, it forms an
The major product of the given reaction is,
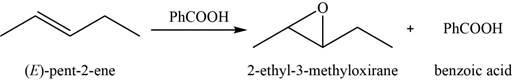
Figure 11
(h)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction and the structure of any intermediate are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Substitution reactions are the reactions in which there is a replacement of an atom or a functional group by another atom or a functional group.
Elimination reactions are the reaction in which alkenes are prepared. In this two substituents are eliminated by either one step or two step mechanism.
(h)
Answer to Problem 8.46SP
The structure of an intermediate is shown in Figure 12.
The major product of the given reaction is shown in Figure 13.
Explanation of Solution
Alkene undergoes
The structure of an intermediate is given as,
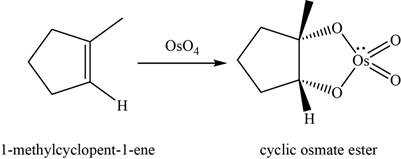
Figure 12
Now, the cyclic osmate undergoes oxidation in the presence of
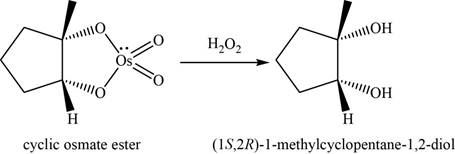
Figure 13
(i)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction and the structure of any intermediate are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Substitution reactions are the reactions in which there is a replacement of an atom or a functional group by another atom or a functional group.
Elimination reactions are the reaction in which alkenes are prepared. In this two substituents are eliminated by either one step or two step mechanism.
(i)
Answer to Problem 8.46SP
The major product of the given reaction is shown in Figure 14.
Explanation of Solution
The major product of the given reaction is,
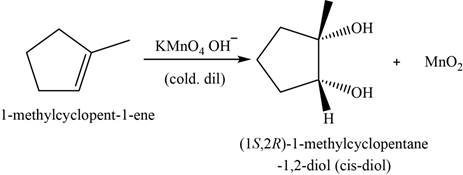
Figure 14
(j)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction and the structure of any intermediate are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Substitution reactions are the reactions in which there is a replacement of an atom or a functional group by another atom or a functional group.
Elimination reactions are the reaction in which alkenes are prepared. In this two substituents are eliminated by either one step or two step mechanism.
(j)
Answer to Problem 8.46SP
The structure of an intermediate is shown in Figure 15.
The major product of the given reaction is shown in Figure 16.
Explanation of Solution
When an alkene reacts with peroxyacid, it forms an epoxide or oxirane. Here,
The structure of an intermediate is given as,
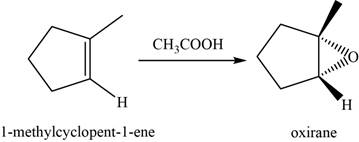
Figure 15
The oxirane is opened at more substituted carbon atom in the presence of an acid
The major product of the given reaction is,
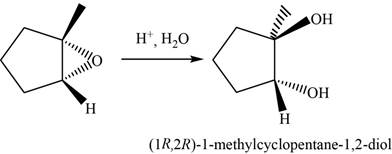
Figure 16
(k)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction and the structure of any intermediate are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Substitution reactions are the reactions in which there is a replacement of an atom or a functional group by another atom or a functional group.
Elimination reactions are the reaction in which alkenes are prepared. In this two substituents are eliminated by either one step or two step mechanism.
(k)
Answer to Problem 8.46SP
The major product of the given reaction is shown in Figure 17.
Explanation of Solution
Alkene undergoes oxidative cleavage in the presence of hot concentrated
The major product of the given reaction is,
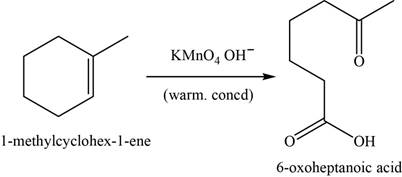
Figure 17
(l)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction and the structure of any intermediate are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Substitution reactions are the reactions in which there is a replacement of an atom or a functional group by another atom or a functional group.
Elimination reactions are the reaction in which alkenes are prepared. In this two substituents are eliminated by either one step or two step mechanism.
(l)
Answer to Problem 8.46SP
The major product of the given reaction is shown in Figure 18.
Explanation of Solution
Alkene undergoes ozonolysis to form carbonyl compounds. Here,
The major product of the given reaction is,
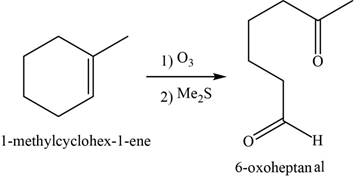
Figure 18
(m)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction and the structure of any intermediate are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Substitution reactions are the reactions in which there is a replacement of an atom or a functional group by another atom or a functional group.
Elimination reactions are the reaction in which alkenes are prepared. In this two substituents are eliminated by either one step or two step mechanism.
(m)
Answer to Problem 8.46SP
The major product of the given reaction is shown in Figure 19.
Explanation of Solution
In this reaction,
The major product of the given reaction is,
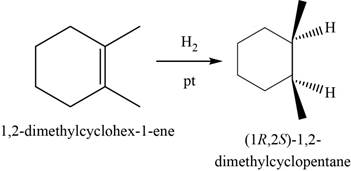
Figure 19
(n)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction and the structure of any intermediate are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Substitution reactions are the reactions in which there is a replacement of an atom or a functional group by another atom or a functional group.
Elimination reactions are the reaction in which alkenes are prepared. In this two substituents are eliminated by either one step or two step mechanism.
(n)
Answer to Problem 8.46SP
The structure of an intermediate and the major product of the given reaction are shown in Figure 20.
Explanation of Solution
This reaction is an acid catalyzed hydration of alkene and forms
The structure of an intermediate and the major product of the given reaction is,
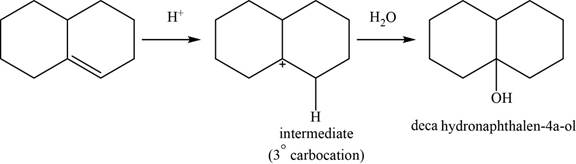
Figure 20
(o)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction and the structure of any intermediate are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Substitution reactions are the reactions in which there is a replacement of an atom or a functional group by another atom or a functional group.
Elimination reactions are the reaction in which alkenes are prepared. In this two substituents are eliminated by either one step or two step mechanism.
(o)
Answer to Problem 8.46SP
The major product of the given reaction is shown in Figure 21.
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is an olefin metathesis. The major product of the given reaction is,
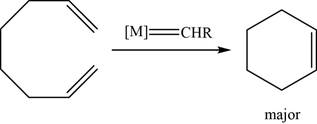
Figure 21
(p)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction and the structure of any intermediate are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Substitution reactions are the reactions in which there is a replacement of an atom or a functional group by another atom or a functional group.
Elimination reactions are the reaction in which alkenes are prepared. In this two substituents are eliminated by either one step or two step mechanism.
(p)
Answer to Problem 8.46SP
The structure of an intermediate is shown in Figure 22.
The major product of the given reaction is shown in Figure 24.
Explanation of Solution
Alkene reacts with mercuric acetate and forms mercurinium ion intermediate.
The structure of an intermediate is given as,
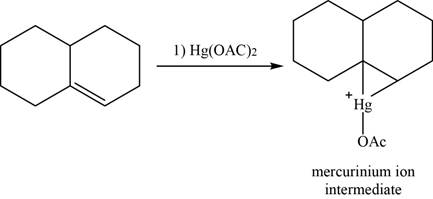
Figure 22
Now, water molecule acts as a nucleophile that opens the mercurinium ion at the most substituted carbon atom.
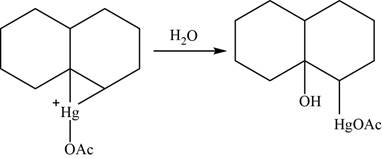
Figure 23
Now, organomercurial alcohol undergoes demercuration in the presence of
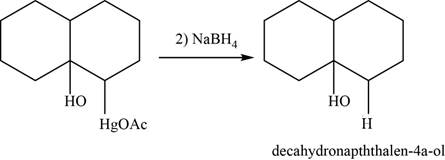
Figure 24
(q)
Interpretation:
The major product of the given reaction and the structure of any intermediate are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Substitution reactions are the reactions in which there is a replacement of an atom or a functional group by another atom or a functional group.
Elimination reactions are the reaction in which alkenes are prepared. In this two substituents are eliminated by either one step or two step mechanism.
(q)
Answer to Problem 8.46SP
The structure of an intermediate is shown in Figure 25.
The major product of the given reaction is shown in Figure 26.
Explanation of Solution
Alkene reacts with chlorine and forms chloronium ion intermediate.
The structure of an intermediate is given as,
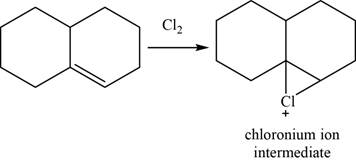
Figure 25
Now, the water molecule acts as a nucleophile that opens the chloronium ion intermediate at more substituted carbon atom. The major product of the given reaction is,
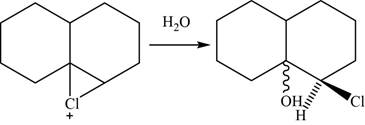
Figure 26
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Help with annotating the labeled peaks in the 'H NMR (solvent CDCls) spectra and 'H NMR (solvent Acetone-D6) spectra Also help with Calculating the keto-enol tautomerization Ka constant for the product in both solvents.Two solvents and two different Kaarrow_forwardDraw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide CH₂OH HO H HO H H OH CH₂OHarrow_forwardCan you explain how I get these here and show the steps plz?arrow_forward
- Give the IUPAC name for this compound Hydrocarbon Condensed Formulas Hint C2H5 CH2CH3 expand that in all the formula Part A: (CH3)2CHCH(C2H5)CH2CH2CH3 Give the IUPAC name for this compound. Part B: CH2=C(C2H5)CH2CH2CH3 Give the IUPAC name for this compound. Part C: (CH3)2C=CHC(C2H5)=CH2 Give the IUPAC name for this compound. Part D: CH3C=CCH(C2H5)2 Give the IUPAC name for this compound. Part E: (CH3)3CC=CCH2CH=C(CH3)2arrow_forwardSelect/ Match the correct letter from the image below for the IUPAC names given below: A B C D 3 E F G H K L Part 1. 4-methylheptane For example.mmmm Answer Letter H _for part 1 Part 2. 2,4-dimethylhexane Part 3. 2,3-dimethylpentane Part 4. 2,2-dimethylhexane Part 5. 2-ethyl-1,1,3,3-tetramethylcyclopentane Part 6. 3-ethyl-2-methylpentanearrow_forwardCan u show the process as to how to get these?arrow_forward
- Sketch the expected 'H NMR spectra for the following compound. Label all of the H's in the structure and the corresponding signal for the spectra you sketch. Make sure you include the integration value and the splitting pattern for each signal Indicate how many signals you would expect in the 13C NMRarrow_forwardUse IUPAC naming rules to name the following hydrocarbon compounds: CH2-CH3 | a) CH-CH-CH2-CH-CH-CH3 b) | CH2 CH3 | CH3 CH3 \ / C=C H 1 H CH2-CH3 c) d) CH=C-CH3 e) CH3-CH2-CH2-CH=CH-CH3 f) CH2=CH-CH2-CH=CH-CH3 g) CH3-CH2-C = C-CH2-CH3 h)arrow_forwardQ5 Name the following : a. b. C. d. e.arrow_forward
- 25. Predict the major product of the following reaction. 1 equivalent of each of the starting materials was used. H₂C CH3 CH3 H3C H3C H3C. CH2 + H3C. heat CH3 CH H.C. CH3 H.C H.C CH3 CH CH3 CH3 A B C Earrow_forwardFind chemical structures based on the below information. a) Chemical formula C6H8O Compound is aromatic plus has two 1H NMR peaks that integrated for 3 each that are singlets (it could have more peaks in the 1H NMR b) Chemical Formula: C6H100 Compounds is conjugated 'H NMR has a signal that integrates for 6 and is a doublet IR spectra has a signal at 1730 cm-1arrow_forwardJaslev Propose a synthesis of the following starting from benzene and any other reagents and chemicals. No mechanisms are required. Indicate the condition for each step plus the major product for each step. More than two steps are required. Step 1 Step 2 مہد Brarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


