
Determine the vertical displacement of joint A. Assume the members are pin connected at their end points. Take A = 3 in2 and E = 29(103) ksi for each member. Use the method of virtual work.
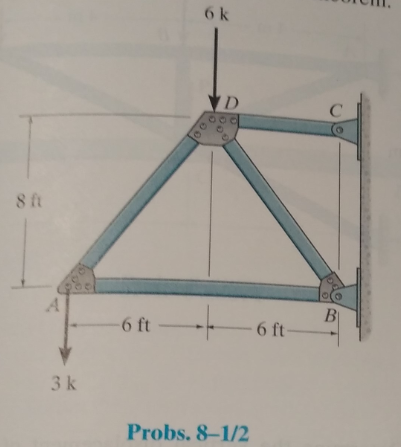
Vertical displacement of Joint A
Answer to Problem 8.1P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The members are pin connected at end points.
A = 3 in2
E = 29(103) ksi
Virtual Work Method
Virtual external work done = Sum of the internal work done
Calculation:
The virtual and real member forces are calculated by method of joints.
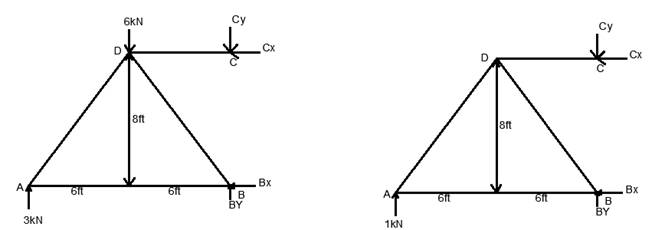
Member forces when original load is applied:
Taking moment about B, we get,
Joint A:
Joint B:
Joint D:
Member forces when virtual load is applied:
Taking moment about B, we get,
Joint A:
Joint B:
Joint D:
Conclusion:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
Modern Database Management
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- C 7-33. The beam is constructed from two boards fastened together at the top and bottom with three rows of nails spaced every 8 in. If an internal shear force of V = 800 lb is applied to the boards, determine the shear force resisted by each nail. Temps to rise Sunday **SW4 88AN SID IDI FI 2 F2 # * F3 3 日 $ 4 Q W A S F4 B Q Search F7 40 F5 F6 & Jo % 5 6 7 E R T Y ப * F G H J FB IA F9 IAA FIO FII ( B 9 ㅁ Z X C V B N M ALT H FI2 8 in. =1 } ㅁ P [ ] L 8 in. 2 in. 4 in. V 9 in. DELETE BACKSPACE NUM LOCK I T ENTER PAUSE SHIFT ALT CTRL V 7 HOME الحاد E I ENDarrow_forwardG 6-114. The cantilever wide-flange steel beam is subjected to the concentrated force of P = 600 N at its end. Determine the maximum bending stress developed in the beam at section A. 10 mm 150 mm 10 mm y Temps to rise Sunday @ 2 *F3 *F2 $ # 4 3 Q Search 1+ F7 48 F5 FB F4 & % 5 6 7 4 W E R T Y ப IAA FB * 8 9 ► I 30° FIO Q FII FI2 + == 200 mm HI [ ] A 5 ㅁ F G H J K L ? PAUSE Z X C V B N M ALT ALT CTRL -10 mm DELETE 2 m A BACKSPACE NUM LOCK 2:27 PM 4/10/2025 INSERT PE 7 日 9 HOME PG U ENTER 4 S SHIFT 2 END INSarrow_forward*7-16. allow The beam has a square cross section and is made of wood having an allowable shear stress of T - 1.4 ksi. If it is subjected to a shear of V = 1.5 kip, determine the smallest dimension a of its sides. 2 Temps to rise Sunday Fl BID (0) 4 3 2 Q Search F4 40 FS * & % S 6 7 D W E R T Y ப A S ㅁ F G H J Z X C V B N ALT の 日 Σ H FID FII FIE L ALT CTAL [ ] PAUSE V-1.5 kip BELETE BACKSPACE NUM LOCA 7 HOME ENTER F SHIFT ENDarrow_forward
- 1. Determine the reaction at supports and forces acting on each member. (5 pts each) 35 kN 60 kN 10 kN 1m 2m -3m -3m 3m 3m 25 kN 50 kN 10 kNarrow_forwardProblem 7 Water is flowing in a channel with a rectangular cross-section. The channel has a uniform width of b 10 m, and it is equipped with a broad-crested weir. The height of flow in a channel far upstream of the weir is h₁ 2 m, while the weir is == hweir = 0.8 m above the bed of the channel. = 1. Assuming the flow over the weir is critical, calculate the flow rate in the channel by iteratively solving for the critical depth he. Perform at least 3 iterations. Did the flow rate converge? 2. Given the water depth immediately downstream of the weir is 90% of the critical depth hc, what is the water depth after the flow experiences a hydraulic jump further downstream? 3. How much energy is dissipated by the hydraulic jump? h₁ hweir Figure 7: A subcritical flow goes over a broad-crested weir, and it experiences a hydraulic jump downstream of the weir. Figure not to scale.arrow_forwardmasonry worksarrow_forward
- A cantilever beam ABC is fixed at legment AB is 2m long and BC is 3m long. Segmen BC is loaded with a triangular load ranging from 0 at Calculate the maximum slope of the beam. Compute the maximum deflection.arrow_forwardSTRUCTURAL ANALYSISarrow_forwardA 6m simply supported beam is loaded with a 12 kN-m concentrated moment placed 2m from the left support and a concentrated load of 24 kN located 2m from the right support. The flexural rigidity of the beam is EI. Calculate the slope of the tangent at the left support. Determine the rotation at the right support. Find the deflection at the point of application of concentrated moment. What is the maximum deflection of the beam?arrow_forward
- GROUP 1 Design a simply supported prestressed beam to support a parking space with a harped tendon using the ACI 318 Building Code allowable stresses. The span length will be decided by the pair. The pair has to choose a suitable sustained service live load (from 300-1500plf) and superimposed dead load (50-150plf) and has no concrete topping. Assume the beam is made of normal-weight concrete with fc'= 5,000 psi and that the concrete strength f'ci at transfer is 70 percent of the cylinder strength. . Also, the pair must assume a justifiable time-dependent loss. • Assume that that fu = 260,000 psi for stress-relieved tendons, ft = 12sqrt(fc'). THE PAIR MUST BE ABLE TO DEFEND THE LENGTH OF BEAM, AND THE LOADINGS APPLIED ON THE BEAM. DEFEND THE USAGE OF YOUR SELECTED SECTION TYPEarrow_forwardA trapezoidal drainage ditch along a highway system has a side slope of 2:1 anda bottom width of 8.0 ft. The ditch is to be used to discharge a flow of 500 ft3/sec.If the ditch slope (longitudinal) is 1.0% and the Manning coefficient is 0.02,determine the minimum depth required for the ditch. Is the flow supercritical orsubcritical? Justify your answer.arrow_forwardDetermine the global stiffness matrix of the beam shown in Fig. 3. Assume supports at 1 and 3 are rollers and the support at 2 is a pinned support. Indicate the degrees of freedom in all the stiffness matrices. EI is constant, w=60kN/m, L1=1.25m and L2=3.45marrow_forward
 Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337094740Author:Segui, William T.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337094740Author:Segui, William T.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning
Engineering Fundamentals: An Introduction to Engi...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305084766Author:Saeed MoaveniPublisher:Cengage Learning





