
Complete the accounting cycle using current liability transcations (LO 8–1, 8–2, 8–4, 8–6)
On January 1, 2018. the general ledger of ACME Fireworks includes the following account balance:
| Accounts | Debit | Credit |
| Cash | $ 25,100 | |
| 46,200 | ||
| Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts | $ 4,200 | |
| Inventory | 20,000 | |
| Land | 46,000 | |
| Equipment | 15,000 | |
| 1,500 | ||
| Accounts Payable | 28,500 | |
| Notes Payable (6%. due April 1, 2019) | 50,000 | |
| Common Stock | 35,000 | |
| 33,100 | ||
| Totals | $152,300 | $152,300 |
During January 2018, the following transactions occur:
January 2 Sold gift cards totaling $8,000. The cards are redeemable for merchandise within one year of the purchase date.
January 6 Purchase additional inventory on account, $147,000.
January 15 Firework sales for the first half of the month total $135,000. All of these sales are on account. The cost of the units sold is $73,800.
January 23 Receive $125,400 from customers on accounts receivable.
January 25 Pay $90,000 to inventory suppliers on accounts payable.
January 28 Write off accounts receivable as uncollectible, $4,800.
January 30 Firework sales for the second half of the month total $143,000. Sales include $11,000 for cash and $132,000 on account. The cost of the units sold is $79,500.
January 31 Pay cash for monthly salaries, $52,000.
Required:
1. Record each of the transactions listed above.
2. Record
a. Depreciation on the equipment for the month of January is calculated using the straight-line method. At the time the equipment was purchased, the company estimated a residual value of $3,000 and a two-year service life.
b. At the end of January. $11,000 of accounts receivable are past due, and the company estimates that 30% of these accounts will not be collected. Of the remaining accounts receivable, the company estimates that 5% will not be collected.
c. Accrued interest expense on notes payable for January.
d. Accrued income taxes at the end of January are $13,000.
e. By the end of January, $3,000 of the gift cards sold on January 2 have been redeemed.
3. Prepare an adjusted
4. Prepare a multiple-step income statement for the period ended January 31, 2018.
5. Prepare a classified
6. Record closing entries.
7. Analyze the following for ACME Fireworks:
a. Calculate the
b. Calculate the acid-test ratio at the end of January. If the average acid-test ratio for the industry is 1.5, is ACME Fireworks more or less likely to haw difficulty paving its currently maturing debts (compared to the industry average)?
c. Assume the notes payable were due on April 1, 2018, rather than April 1, 2019. Calculate the revised current ratio at the end of January, and indicate whether the revised ratio would increase, decrease. or remain unchanged compared to your answer in (a).
1.
To record: The journal entries for given transactions.
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
The journal entries for given transactions of Company ACME are as follows:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit($) | Credit($) | |||
| 2018 | Cash | 8,000 | ||||
| January 2 | Deferred Revenue | 8,000 | ||||
| (To record the sale of gift cards for cash) | ||||||
| 2018 | Inventory | 147,000 | ||||
| January, 6 | Accounts payable | 147,000 | ||||
| (To record purchase of inventory on account) | ||||||
| 2018 | Accounts Receivable | 135,000 | ||||
| January 15 | Sales Revenue | 135,000 | ||||
| (To record sales of inventory on account) | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | 73,800 | |||||
| Inventory | 73,800 | |||||
| (To record the cost of inventory sold) | ||||||
| 2018 | ||||||
|
January 23 | Cash | 125,400 | ||||
| Accounts Receivable | 125,400 | |||||
| (To record cash on account) | ||||||
| 2018 | Accounts Payable | 90,000 | ||||
| January 25 | Cash | 90,000 | ||||
| (To record pay of cash ) | ||||||
| 2018 | Allowance for uncollectible accounts | 4,800 | ||||
| January 28 | Accounts Receivable | 4,800 | ||||
| (To record the written off of uncollectible accounts) | ||||||
| 2018 | Cash | 11,000 | ||||
| January 30 | Accounts Receivable | 132,000 | ||||
| Sales Revenue | 143,000 | |||||
| ( To record sale of inventory for cash) | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | 79,500 | |||||
| Inventory | 79,500 | |||||
| (To record of cost of inventory sold) | ||||||
| 2018 | Salaries Expense | 52,000 | ||||
| January 31 | Cash | 52,000 | ||||
| (To record payment of salaries) | ||||||
Table (1)
2.
To record: The given adjusting entries of Company ACME.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries:
Adjusting entries refers to the entries that are made at the end of an accounting period in accordance with revenue recognition principle, and expenses recognition principle. The purpose of adjusting entries is to adjust the revenue, and the expenses during the period in which they actually occurs.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
Adjusting entries of Company ACME are as follows:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit($) | Credit($) | |||
| 2018 | Depreciation Expense (1) | 500 | ||||
| January 31 | Accumulated Depreciation | 500 | ||||
| (To record the depreciation for January) | ||||||
| 2018 | Bad Debt Expense (3) | 12,500 | ||||
| January 31 | Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts | 12,500 | ||||
| (To adjust uncollectible accounts) | ||||||
| 2018 | Interest Expense (4) | 250 | ||||
| January 31 | Interest Payable | 250 | ||||
| (To adjust interest expense) | ||||||
| 2018 | Income Tax Expense | 13,000 | ||||
| January 31 | Income Tax Payable | 13,000 | ||||
| (To adjust income taxes) | ||||||
| 2018 | Deferred Revenue | 3,000 | ||||
| January 31 | Sales Revenue | 3,000 | ||||
| (To adjust the revenue for the gift cards redeemed) | ||||||
Table (2)
Working Notes:
a .
Calculate the depreciation on the equipment.
b.
Calculate the bad debt expense.
c .
Calculate the Interest expense.
3.
To Prepare: Adjusted trial balance for the month January 31, 2018.
Explanation of Solution
| ACME Fireworks | ||
| Adjusted Trial Balance | ||
| 31-Jan-18 | ||
| Accounts (Refer table 4) | Debit (Amount in $) | Credit (Amount in $) |
| Cash | $27,500 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 183,000 | |
| Inventory | 13,700 | |
| Land | 46,000 | |
| Equipment | 15,000 | |
| Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts | $11,900 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation | 2,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | 85,500 | |
| Deferred Revenue | 5,000 | |
| Interest Payable | 250 | |
| Income Tax Payable | 13,000 | |
| Notes Payable | 50,000 | |
| Common Stock | 35,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 33,100 | |
| Sales Revenue | 281,000 | |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 153,300 | |
| Salaries Expense | 52,000 | |
| Bad Debt Expense | 12,500 | |
| Depreciation Expense | 500 | |
| Interest Expense | 250 | |
| Income Tax Expense | 13,000 | |
| Totals | $516,750 | $516,750 |
Table (3)
Calculation of adjusted trial balance of Company ACME for the month January:
| Accounts | Ending Balance |
| |
| Cash | $27,500 | = |
|
| Accounts Receivable | 183,000 | = |
|
| Inventory | 13,700 | = |
|
| Land | 46,000 | = | 46,000 |
| Equipment | 15,000 | = | 15,000 |
| Allow for Uncollectible Accounts | 11,900 | = |
|
| Accumulated Depreciation | 2,000 | = |
|
| Accounts Payable | 85,500 | = |
|
| Deferred Revenue | 5,000 | = |
|
| Interest Payable | 250 | = | 250 |
| Income Tax Payable | 13,000 | = | 13,000 |
| Notes Payable | 50,000 | = | 50,000 |
| Common Stock | 35,000 | = | 35,000 |
| Retained Earnings | 33,100 | = | 33,100 |
| Sales Revenue | 281,000 | = |
|
| Cost of Goods Sold | 153,300 | = |
|
| Salaries Expense | 52,000 | = | 52,000 |
| Bad Debt Expense | 12,500 | = | 12,500 |
| Depreciation Expense | 500 | = | 500 |
| Interest Expense | 250 | = | 250 |
| Income Tax Expense | 13,000 | = | 13,000 |
(Table 4)
4.
To Prepare: the multiple income statement for the period ended January 31, 2018.
Explanation of Solution
| ACME Fireworks | ||
| Multiple-Step Income Statement | ||
| For the year ended January 31, 2018 | ||
| Particulars | Amount in $ | Amount in $ |
| Sales revenue | $281,000 | |
| Cost of goods sold | 153,300 | |
| Gross profit | $127,700 | |
| Salaries expense | 52,000 | |
| Bad debt expense | 12,500 | |
| Depreciation expense | 500 | |
| Total operating expenses | 65,000 | |
| Operating income | 62,700 | |
| Interest expense | 250 | |
| Income before taxes | 62,450 | |
| Income tax expense | 13,000 | |
| Net income | $49,450 | |
Table (5)
5.
To Prepare: classified balance sheet as on January 31, 2018.
Explanation of Solution
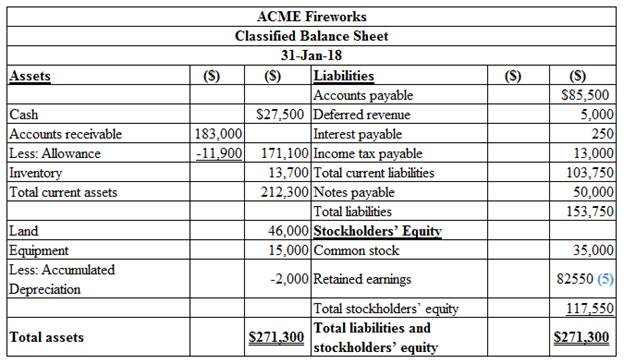
Figure (1)
Working Notes:
6.
To Record: the closing entries.
Explanation of Solution
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit($) | Credit($) | |
| 2018 | Sales Revenue | 281,000 | ||
| January 31 | Retained Earnings | 281,000 | ||
| (To record the closing revenue accounts) | ||||
| Retained Earnings | 231,550 | |||
| Cost of goods sold | 153,300 | |||
| Salaries Expense | 52,000 | |||
| Bad debt Expense | 12,500 | |||
| Depreciation Expense | 500 | |||
| Interest Expense | 250 | |||
| Income Tax Expense | 13,000 | |||
| (To close the expense accounts) | ||||
Table (6)
7. a
To Calculate: the current ratio at the end of January.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the current ratio at the end of January.
Company ACME has liquidity more than the average level required by industry. They have high portion of current assets to meet out their current liabilities which is comparatively higher than the industry average of 1.8.
7. b.
To Calculate: the acid-test ratio at the end of January.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the acid –test ratio at the end of January.
Company ACME has less difficulty in its paying its currently maturing debts. They have high portion of quick assets to meet out their current liabilities which is comparatively higher than the industry average of 1.5.
7. c.
To Indicate: whether the revised ratio would increase, decrease or remain unchanged compared to the requirement a.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate current ratio assuming notes payable as current liabilities.
Notes payable would be included in the current liabilities as the notes payable are to be due on April. This would decrease the value of the current assets and increase the value of current liabilities because ratio gets reduced when they are divided by larger number.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- I need help with this general accounting question using standard accounting techniques.arrow_forwardI need help finding the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem using appropriate accounting principles?arrow_forward
- Rahul Consulting Services expects its consultants to work 25,000 direct labor hours per year. The company's estimated total indirect costs are $350,000. The direct labor rate is $95 per hour. The company uses direct labor hours as the allocation base for indirect costs. If Rahul performs a job requiring 40 hours of direct labor, what is the total job cost?arrow_forwardAccounting?arrow_forwardPlease give me correct answer this financial accounting questionarrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
