
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure that contributes most to the bonding in
Concept introduction: The Lewis structures are diagrams that give information about the bonding electron pairs and the lone pairs of electrons in a molecule. Similar to electron dot structure in Lewis diagram the lone pair electrons are represented as dots and they also contain lines which represent bonding electron pairs in a bond.
To determine: If the given Lewis structure contributes to the bonding in
(a)
Answer to Problem 8.109QP
Solution
The given Lewis structure does not contribute most to the bonding in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The given Lewis structure is,
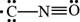
Figure 1
The charge present on each atom is known as formal charge which is calculated by using the formula,
For oxygen
The number of valence electrons in oxygen atom is six, the lone pair electrons are two and the bonding electrons are six.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
For carbon atom,
The number of valence electrons in carbon atom is four, the lone pair electrons are five and the bonding electrons are two.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
For nitrogen atom,
The number of valence electrons in nitrogen atom is five, the lone pair electron is zero and the bonding electrons are eight.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
In the given Lewis structure of
(b)
To determine: If the given Lewis structure contributes to the bonding in
(b)
Answer to Problem 8.109QP
Solution
The given Lewis structure does not contribute most to the bonding in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The given Lewis structure is,
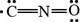
Figure 2
The formal charge is calculated by using the formula,
For oxygen atom,
The number of valence electrons in oxygen atom is six, the lone pair electrons are four and the bonding electrons are four.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
For carbon atom,
The number of valence electrons in carbon atom is four, the lone pair electrons are three and the bonding electrons are four.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
For nitrogen atom,
The number of valence electrons in nitrogen atom is five, the lone pair electron is zero and the bonding electrons are eight.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
In the given Lewis structure of
Thus, it is known that the nitrogen atom is more electronegative than carbon atom. Hence, the given Lewis structure does not contribute most to the bonding in
(c)
To determine: If the given Lewis structure contributes to the bonding in
(c)
Answer to Problem 8.109QP
Solution
The given Lewis structure does not contribute most to the bonding in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The given Lewis structure is,
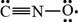
Figure 3
The formal charge is calculated by using the formula,
For oxygen atom,
The number of valence electrons in oxygen atom is six, the lone pair electrons are five and the bonding electrons are two.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
For carbon atom,
The number of valence electrons in carbon atom is four, the lone pair electrons are two and the bonding electrons are six.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
For nitrogen atom,
The number of valence electrons in nitrogen atom is five, the lone pair electron is zero and the bonding electrons are eight.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
In the given Lewis structure of
Hence, the given Lewis structure does not contribute most to the bonding in
(d)
To determine: If the given Lewis structure contributes to the bonding in
(d)
Answer to Problem 8.109QP
Solution
The given Lewis structure contributes most to the bonding in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
The given Lewis structure is,
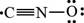
Figure 4
The formal charge is calculated by using the formula,
For oxygen atom,
The number of valence electrons in oxygen atom is six, the lone pair electrons are six and the bonding electrons are two.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
For carbon atom,
The number of valence electrons in carbon atom is four, the lone pair electron is one and the bonding electrons are six.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
For nitrogen atom,
The number of valence electrons in nitrogen atom is five, the lone pair electron is zero and the bonding electrons are eight.
Substitute the value of valence electrons, lone pair of electrons and bond pair of electrons in the above formula to calculate the formal charge.
In the given Lewis structure of
Conclusion
The Lewis structure that contributes most to the bonding in the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Smartwork5 Printed Access Card for Use with Chemistry: The Science in Context 5th Edition (SmartWork Access Printed Access Card)
- What is the final product when hexanedioic acid reacts with 1º PCl5 and 2º NH3.arrow_forwardWhat is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forward
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





