
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The pH values after the addition of each proportion of the base to the acid is to be determined. Also, the titration curve needs to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Titration curve is drawn to determine the change in pH of an acid or base with respect to the added volume of base or acid to it.
The titration curve can be drawn between a strong/weak acid and strong/weak base. The change in pH shows different patterns for different combinations of acids and bases.
Explanation of Solution
Initial pH of the analyte solution can be calculated as follows:
Lactic acid is a weak acid that forms an equilibrium mixture when dissolved in water. The equilibrium is as follows.
The initial molarity of lactic acid is 0.1 M.
The amount of lactic acid at the beginning can be calculated from. By constructing an ICE table, the concentration of lactate ion in the solution after the acid dissociation can be determined.
| Reaction | Lactic acid | Lactate | H+ |
| Initial | 0.1 | 0 | 0 |
| Change | -x | +x | +x |
| Equilibrium | (0.1-x) | x | x |
The acid dissociation constant can be represented as follows:
Solving this quadratic equation gives the amount of hydrogen ions in the solution.
Thus, the concentration of hydrogen ion is 0.00185 and pH of the solution can be calculated as follows:
Addition of
Total amount of lactic acid to be neutralized can be calculated from its molarity and volume as follows:
Or,
Now, the amount of base added can be calculated as follows:
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Lactic acid | OH- | Lactate | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.0004 | ||
| Change | -0.0004 | -0.0004 | 0.0004 | 0.0004 |
| Equilibrium | 0.0021 | 0 | 0.0004 | 0.0004 |
Concentration of lactic acid after addition of base
Concentration of lactate ion
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of lactic acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Lactic acid | OH- | Lactate | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.0008 | ||
| Change | -0.0008 | -0.0008 | 0.0008 | 0.0008 |
| Equilibrium | 0.0017 | 0 | 0.0008 | 0.0008 |
Concentration of lactic acid after addition of base
Concentration of lactate ion
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of lactic acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Lactic acid | OH- | Lactate | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.00125 | ||
| Change | -0.00125 | -0.00125 | 0.00125 | 0.00125 |
| Equilibrium | 0.00125 | 0 | 0.00125 | 0.00125 |
Concentration of lactic acid after addition of base
Concentration of lactate ion
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of lactic acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Lactic acid | OH- | Lactate | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.002 | ||
| Change | -0.002 | -0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| Equilibrium | 0.0005 | 0 | 0.002 | 0.002 |
Concentration of lactic acid after addition of base
Concentration of lactate ion
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of lactic acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Lactic acid | OH- | Lactate | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.0024 | ||
| Change | -0.0024 | -0.0024 | 0.0024 | 0.0024 |
| Equilibrium | 0.0001 | 0 | 0.0024 | 0.0024 |
Concentration of lactic acid after addition of base
Concentration of lactate ion
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of lactic acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Lactic acid | OH- | Lactate | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.00245 | ||
| Change | -0.00245 | -0.00245 | -0.00245 | -0.00245 |
| Equilibrium | 0.00005 | 0 | -0.00245 | -0.00245 |
Concentration of lactic acid after addition of base
Concentration of lactate ion
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of lactic acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Lactic acid | OH- | Lactate | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.00249 | ||
| Change | -0.00249 | -0.00249 | -0.00249 | -0.00249 |
| Equilibrium | 0.00001 | 0 | -0.00249 | -0.00249 |
Concentration of lactic acid after addition of base
Concentration of lactate ion
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of lactic acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Lactic acid | OH- | Lactate | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.0025 | ||
| Change | -0.0025 | -0.0025 | -0.0025 | -0.0025 |
| Equilibrium | 0.0000 | 0 | -0.0025 | -0.0025 |
Concentration of lactic acid after addition of base
Concentration of lactate ion
At this point, there is no excess acid or base. Therefore, the only possible reaction here is the dissociation of the conjugate base of the lactic acid (that is lactate ion).
Thereafter, by obtaining the Kb value for lactate ion, the amount of hydroxide ions in the solution can be determined to get the pH value at this point.
| Reaction | Lactic acid | Lactate | OH- |
| Initial | 0.05 | 0 | 0 |
| Change | -X | x | x |
| Equilibrium | (0.05-x) | x | x |
Then the pH can be calculated as follows:
Thereafter, this quadratic equation can be solved to determine the hydroxide ion concentration, thereby, the pOH and the pH can be determined.
The calculated value of x is concentration of hydroxide ion. The pOH of the solution will be:
Addition of
Total amount of lactic acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Lactic acid | OH- | Lactate | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.0028 | ||
| Change | -0.0025 | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 |
| Equilibrium | 0 | 0.0003 | 0 | 0 |
Concentration of hydroxide
Addition of
Total amount of lactic acid to be neutralized
Amount of base added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Lactic acid | OH- | Lactate | H+ |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Add | 0 | 0.0030 | ||
| Change | -0.0025 | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 |
| Equilibrium | 0 | 0.0005 | 0 | 0 |
Concentration of hydroxide
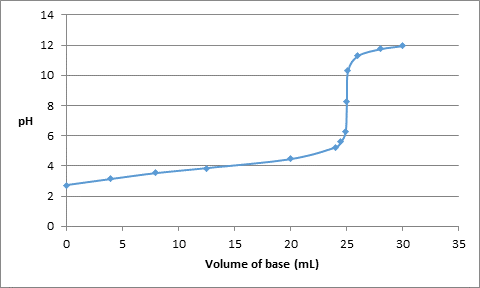
Thus, the value of pH with respect to added volume of base is as follows:
| Volume (in mL) | pH |
| 0 | 2.73 |
| 4 | 3.14 |
| 8 | 3.53 |
| 12.5 | 3.86 |
| 20 | 4.46 |
| 24 | 5.24 |
| 24.5 | 5.6 |
| 24.9 | 6.3 |
| 25.0 | 8.28 |
| 25.1 | 10.3 |
| 26.0 | 11.30 |
| 28.0 | 11.75 |
| 30.0 | 11.96 |
The titration curve can be drawn as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK WEBASSIGN FOR ZUMDAHL'S CHEMICAL PR
- ¿Qué the product is obtained from tetraethoxypropano and hidrazina?. Indicate the reason why the corresponding dial is used.arrow_forwardIf CH3COCH2CH(OCH3)2 is reacted with hydrazine, two isomeric products are formed. Indicate their structures and the major product.arrow_forwardIs it possible to obtain addition derivatives to nitrogen in position 2 of pyrazoles by reaction with electrophilic agents? Reason for this.arrow_forward
- Starting from 1,3-dicarbonyl derivatives to obtain isooxazoles and isothiazoles. Indicate whether synthetic methods exist.arrow_forwardIn the synthesis of benzotriazole, adding NaNO2 heats the solution. State the reason.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by treating benzotriazole with dimethyl sulfate or methyl iodide in a basic medium.arrow_forward
- What is the significance of selecting a "representative" sample for chemical analysis, and how does this practice ensure accurate and reliable results with respect to chemical analyses?arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation of the differences between homogeneous and heterogeneous sampling in the context of sampling methods.arrow_forwardГ C-RSA CHROMATOPAC CH=1 DATA 1: @CHRM1.C00 ATTEN=10 SPEED= 10.0 0.0 b.092 0.797 1.088 1.813 C-RSA CHROMATOPAC CH=1 Report No. =13 ** CALCULATION REPORT ** DATA=1: @CHRM1.000 11/03/05 08:09:52 CH PKNO TIME 1 2 0.797 3 1.088 4 1.813 AREA 1508566 4625442 2180060 HEIGHT 207739 701206 V 287554 V MK IDNO CONC NAME 18.1447 55.6339 26.2213 TOTAL 8314067 1196500 100 C-R8A CHROMATOPAC CH=1 DATA 1: @CHRM1.C00 ATTEN=10 SPEED= 10.0 0. 0 087 337. 0.841 1.150 C-R8A CHROMATOPAC CH=1 Report No. =14 DATA=1: @CHRM1.000 11/03/05 08:12:40 ** CALCULATION REPORT ** CH PKNO TIME AREA 1 3 0.841 1099933 41.15 4039778 HEIGHT MK IDNO 170372 649997¯¯¯ CONC NAME 21.4007 78.5993 TOTAL 5139711 820369 100 3 C-R8A CHROMATOPAC CH=1 DATA 1: @CHRM1.C00 ATTEN=10 SPEED= 10.0 0.100 0:652 5.856 3 1.165 C-RSA CHROMATOPAC CH-1 Report No. =15 DATA=1: @CHRM1.000 11/03/05 08:15:26 ** CALCULATION REPORT ** CH PKNO TIME AREA HEIGHT MK IDNO CONC NAME 1 3 3 0.856 4 1.165 TOTAL 1253386 4838738 175481 708024 V 20.5739 79.4261 6092124…arrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





