
Concept explainers
1.
Prepare the bank reconciliation for Corporation S as at December 31, 2015.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Bank reconciliation: Bank statement is prepared by bank. The company maintains its own records from its perspective. This is why the cash balance per bank and cash balance per books seldom agree. Bank reconciliation is the statement prepared by company to remove the differences and disagreement between cash balance per bank and cash balance per books.
Prepare bank reconciliation for Corporation S as at December 31, 2015.
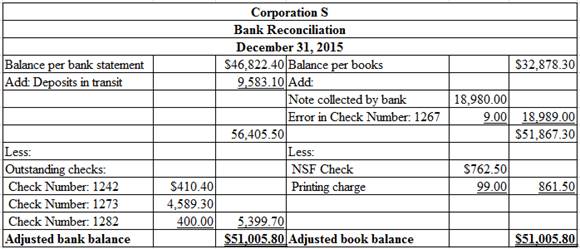
Table (1)
Working Notes:
Calculate book error in recording Check Number: 1267.
Description:
- The deposits which are not recorded by the bank are referred to as deposits in transit. Since the deposits in transit are not reflected on the bank statement, the company should add deposits in transit to cash balance per bank, while preparation of
bank reconciliation statement . - Outstanding checks are the checks that are issued by the company, but not yet paid by the bank. When the check is issued for payment, the company deducts the cash balance immediately. But the bank deducts only when the cash is paid for the issued check. So, company deducts the cash balance per bank to remove the differences.
- The accountant has recorded the check for office supplies of $3,456 as $3,465. So, the cash balance decreased by $9. Therefore, the balance should be added to books, to increase amount of the cash ledger account balance.
- Note receivable being collected by bank, is credited to bank account. But the company is not aware of it. So, while preparing bank reconciliation statement, company should add the amount to the cash balance per books.
- While reconciling bank statement and the cash ledger balance, the NSF check should be deducted from the cash balance per book. This is because the bank could not collect funds from the customer’s bank due to lack of funds. But being recorded as Accounts Receivable previously, the balance should be deducted from books, to increase the Accounts Receivable account.
- Banks deduct the service charge for the services rendered like lock box rental, or printed checks. But the company is not aware of such deductions. So, company deducts the cash balance per books while bank reconciliation preparation.
2.
Prepare
2.
Explanation of Solution
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in
stockholders’ equity accounts. - Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Prepare journal entry to record book error amount for Check Number: 1267.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2015 | ||||||
| December | 31 | Cash | 9 | |||
| Office Supplies | 9 | |||||
| (Record incorrectly recorded book error amount) | ||||||
Table (2)
Description:
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is increased because cash is received and an increase in asset is debited.
- Office Supplies is an asset account. The amount was erroneously recorded, and so cash balance decreased. Hence, office supplies is decreased by crediting.
Prepare journal entry to record note receivable collected by bank.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2015 | ||||||
| December | 31 | Cash | 18,980 | |||
| Collection Expense | 20 | |||||
| Note Receivable | 19,000 | |||||
| (Record note receivable collected by bank) | ||||||
Table (3)
Description:
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is increased because bank collected note receivable, and an increase in assets should be debited.
- Collection Expense is an expense account. Expenses decrease Equity account and decrease in Equity is debited.
- Note Receivable is an asset account. The amount has decreased because the amount to be received is collected by the bank, and, a decrease in assets should be credited.
Prepare journal entry to record NSF check.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2015 | ||||||
| December | 31 | Accounts Receivable | 762.50 | |||
| Cash | 762.50 | |||||
| (Record NSF as increase in accounts receivable) | ||||||
Table (4)
Description:
- Accounts Receivable is an asset account. The bank has not collected the amount from the customer due to insufficient funds, which was earlier recorded as a receipt. As the collection could not be made, amount to be received increased. Therefore, increase in asset would be debited.
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is decreased because bank could not collect amount due to insufficient funds in customer’s account, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Prepare journal entry to record bank printing charge.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2015 | ||||||
| December | 31 | Miscellaneous Expense | 99 | |||
| Cash | 99 | |||||
| (Record payment of printing charges) | ||||||
Table (5)
Description:
- Miscellaneous Expense is an expense account and the amount is increased because bank has charged service charges. Expenses decrease Equity account and decrease in Equity is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is decreased because printing charge is paid, and a decrease in asset is credited.
3.
a.
Explain the meaning of debit memorandum.
3.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Debit memorandum: This is the notification a bank sends to the depositor indicating that the bank has debited the depositor’s balance and that the amount of the depositor’s balance is reduced.
b.
Explain the meaning of credit memorandum.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Credit memorandum: This is the notification a bank sends to the depositor indicating that the bank has credited the depositor’s balance and that the amount of the depositor’s balance is increased.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Principles of Financial Accounting, Chapters 1-17 - With Access (Looseleaf)
- Bruno Manufacturing uses direct labor-hours in its predetermined overhead rate. At the beginning of the year, the total estimated manufacturing overhead was $680,000. At the end of the year, actual direct labor-hours for the year were 42,500 hours, manufacturing overhead for the year was underapplied by $25,500, and the actual manufacturing overhead was $695,000. The predetermined overhead rate for the year must have been closest to: A) $16.00 B) $15.75 C) $16.35 D) $16.94arrow_forwardWhat was manufactured overhead?arrow_forwardWhich of the following choices is the correct status of manufacturing overhead at year-end?arrow_forward
- Morris Corporation applies manufacturing overhead at the rate of $40 per machine hour. Budgeted machine hours for the current period were anticipated to be 200,000; however, higher than expected production resulted in actual machine hours worked of 225,000. Budgeted and actual manufacturing overhead figures for the year were $8,000,000 and $8,750,000, respectively. On the basis of this information, the company's year-end overhead was: A. overapplied by $250,000 B. underapplied by $250,000 C. overapplied by $750,000 D. underapplied by $750,000arrow_forwardAt the beginning of the year, manufacturing overhead for the year was estimated to be $560,000. At the end of the year, actual labor hours for the year were 35,000 hours, the actual manufacturing overhead for the year was $590,000, and the manufacturing overhead for the year was underapplied by $30,000. If the predetermined overhead rate is based on direct labor hours, then the estimated labor hours at the beginning of the year used in the predetermined overhead rate must have been ___ hours.arrow_forwardGive me Answerarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





