
1.
Draw a graph of the data.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Draw a graph of the data.
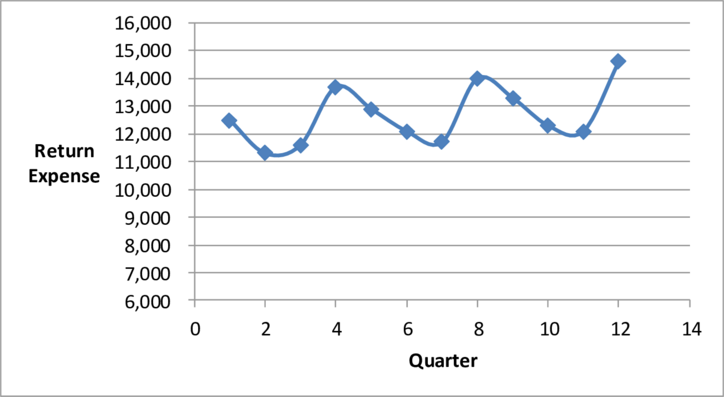
Figure (1)
2.
Compute quarterly
2.
Explanation of Solution
High-low method:
The graph in part (1) shows that high and low points are last and second data points, so these points develop the estimate of high-low.
Calculate the variable cost.
Calculate the fixed cost.
Compute quarterly prediction for the year 2019.
| 2019 Quarter | Return Expenses |
| 13 | $14,930 |
| 14 | $15,260 |
| 15 | $15,590 |
| 16 | $15,920 |
Table (1)
Note: Shown below is the formula to compute quarterly prediction.
These predictions do not take into account the seasonal variation as shown in the data, it is always useful to take into considerationthe results for a regression analysis as shown in part (3).
3.
Compute the quarterly forecast for 2019 using the results of a regression analysis. Calculate the result of regression analysis and necessary changes to improve the model.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Regression one:
| Regression Statistics | |
| Multiple R | 0.439734422 |
| R Square | 0.193366362 |
| Adjusted R Square | 0.112702998 |
| Standard Error | 974.8928577 |
| Observations | 12 |
Table (2)
| ANOVA | |||||
| df | SS | MS | F | Significance F | |
| Regression | 1 | 2278339.161 | 2278339 | 2.397202 | 0.152593037 |
| Residual | 10 | 9504160.839 | 950416.1 | ||
| Total | 11 | 11782500 | |||
Table (3)

Table (4)
| Regression Predictions | |
| Intercept | $11,855 |
| Coefficient | $126.22 |
Table (5)
| Quarterly Predictions | |
| 13 | $13,496 |
| 14 | $13,622 |
| 15 | $13,748 |
| 16 | $13,875 |
Table (6)
Note: Shown below is to compute rent expense.
Predicted expense for next four quarter using regression analysis:
| Quarter | Regression prediction | |
| 13 | | 13,495.45 |
| 14 | | 13,621.68 |
| 15 | | 13,747.90 |
| 16 | | 13,874.13 |
Table (7)
This shows how the regression model’s prediction differ from that of high-low method.
The above regression one has relatively low R-Squared (0.19) and low t-value for the independent variable, a revision of the regression model is considered. Since, there is visible seasonality in the data, by adding dummy variable it is possible to improve on the regression model with 1s in the periods 4,8, and 12, and 0s in the left-over periods. For the dummy variable the below given regression analysis indications a much higher R-Squared, improved SE and a substantial t-value.
Regression 2:
| Regression Statistics | |
| Multiple R | 0.873681599 |
| R Square | 0.763319537 |
| Adjusted R Square | 0.710723879 |
| Standard Error | 556.6454641 |
| Observations | 12 |
Table (8)
| ANOVA | |||||
| df | SS | MS | F | Significance F | |
| Regression | 2 | 8993812.445 | 4496906.223 | 14.51297616 | 0.00152662 |
| Residual | 9 | 2788687.555 | 309854.1728 | ||
| Total | 11 | 11782500 | |||
Table (9)
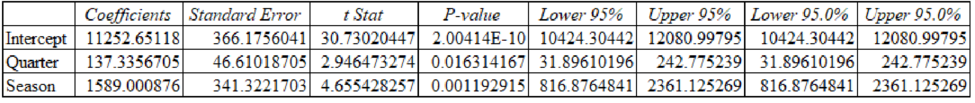
Table (10)
Equation for the above regression are:
| Regression Predictions | |
| Intercept | $11,252.65 |
| Coefficient Qtr. | $137.34 |
| Coefficient Season | $1,589 |
Table (11)
The regression prediction for the revised regression:
| Quarterly Predictions | |
| 13 | $14,627 |
| 14 | $13,175 |
| 15 | $13,313 |
| 16 | $15,039 |
Table (12)
The management accountant should depend on the above shown prediction because the second regression has better statistical measures.
4.
Explain how the analysis of costs change, if L Incorporation produces its products in multiple global production facilities to serve the global market.
4.
Explanation of Solution
If L Incorporation produces its products in multiple global production facilities, then the expenses incurred from returns has to be studied by the production facility. Due to various equipment used in manufacturing the DVD players, the cost incurred are likely to differ among the production facility.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
COST MANAGEMENT: (LL)W/ACCESS CUSTOM
- Summary information from the financial statements of two companies competing in the same industry follows. Barco Company Kyan Company Barco Kyan Company Company Data from the current year-end balance sheets Data from the current year's income statement Assets $ 810,000 $ 886,200 Cash $ 18,500 $ 32,000 Accounts receivable, net 36,400 84,340 590,100 7,600 644,500 Merchandise inventory Prepaid expenses Plant assets, net Total assets Liabilities and Equity Current liabilities Long-term notes payable Common stock, $5 par value Retained earnings Total liabilities and equity 6,100 330,000 52,400 132,500 7,600 305,400 $ 475,340 $ 529,900 Sales Cost of goods sold Interest expense Income tax expense Net income Basic earnings per share Cash dividends per share Beginning-of-year balance sheet data Accounts receivable, net Merchandise inventory Total assets $ 71,340 82,800 $ 98,300 117,000 170,000 151,200 226,000 88,600 Common stock, $5 par value $ 475,340 $ 529,900 Retained earnings 14,000 15,569…arrow_forwardQuestion: Record the purchase of equipment in a general journal format. • July 1, 2021- Signed a lease for an office and issued Check 101 for $15,600 to pay the rent in advance for six months. • July 1, 2021- Borrowed money from Bancorp West by issuing a four-month, 4.5 percent note for $40,000; received $39,400 because the bank deducted the interest in advance. • July 1, 2021- Signed an agreement with Johnson Ventures to provide financial services for one year at $6,000 per month; received the entire fee of $72,000 in advance. The $72,000 was credited to Unearned Financial Service Fees. • July 1, 2021- Purchased office equipment for $15,900 from Office Outfitters; issued a two-month, 6 percent note in payment. The equipment is estimated to have a useful life of five years and a $1,500 salvage value. The equipment will be depreciated using the straight-line method. • July 1, 2021- Purchased a one-year insurance policy and issued Check 102 for $1,860 to pay the entire…arrow_forwardQuestion: Record the fees received in advance in a general journal format. • July 1, 2021- Signed a lease for an office and issued Check 101 for $15,600 to pay the rent in advance for six months. • July 1, 2021- Borrowed money from Bancorp West by issuing a four-month, 4.5 percent note for $40,000; received $39,400 because the bank deducted the interest in advance. • July 1, 2021- Signed an agreement with Johnson Ventures to provide financial services for one year at $6,000 per month; received the entire fee of $72,000 in advance. The $72,000 was credited to Unearned Financial Service Fees. • July 1, 2021- Purchased office equipment for $15,900 from Office Outfitters; issued a two-month, 6 percent note in payment. The equipment is estimated to have a useful life of five years and a $1,500 salvage value. The equipment will be depreciated using the straight-line method. • July 1, 2021- Purchased a one-year insurance policy and issued Check 102 for $1,860 to pay the…arrow_forward
- Question: Record the payment of rent in a general journal format using the information below. July 1, 2021- Signed a lease for an office and issued Check 101 for $15,600 to pay the rent in advance for six months. • July 1, 2021- Borrowed money from Bancorp West by issuing a four-month, 4.5 percent note for $40,000; received $39,400 because the bank deducted the interest in advance. • July 1, 2021- Signed an agreement with Johnson Ventures to provide financial services for one year at $6,000 per month; received the entire fee of $72,000 in advance. The $72,000 was credited to Unearned Financial Service Fees. • July 1, 2021- Purchased office equipment for $15,900 from Office Outfitters; issued a two-month, 6 percent note in payment. The equipment is estimated to have a useful life of five years and a $1,500 salvage value. The equipment will be depreciated using the straight-line method. • July 1, 2021- Purchased a one-year insurance policy and issued Check 102 for $1,860…arrow_forwardQuestion: Record the borrowing in a general journal format. • July 1, 2021- Signed a lease for an office and issued Check 101 for $15,600 to pay the rent in advance for six months. • July 1, 2021- Borrowed money from Bancorp West by issuing a four-month, 4.5 percent note for $40,000; received $39,400 because the bank deducted the interest in advance. • July 1, 2021- Signed an agreement with Johnson Ventures to provide financial services for one year at $6,000 per month; received the entire fee of $72,000 in advance. The $72,000 was credited to Unearned Financial Service Fees. • July 1, 2021- Purchased office equipment for $15,900 from Office Outfitters; issued a two-month, 6 percent note in payment. The equipment is estimated to have a useful life of five years and a $1,500 salvage value. The equipment will be depreciated using the straight-line method. • July 1, 2021- Purchased a one-year insurance policy and issued Check 102 for $1,860 to pay the entire premium. •…arrow_forwardI need financial accounting question answerarrow_forward
- Can you help me solve this general accounting question using the correct accounting procedures?arrow_forwardI am looking for the most effective method for solving this financial accounting problem.arrow_forwardI need the correct answer to this general accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





