
Concept explainers
a.
Draw the flow of the different models through the production process.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Production cost:
Production cost refers to the cost associated with the production process. Direct costs associated with the process and stages of completion are taken into consideration while computing the cost of the production of any product.
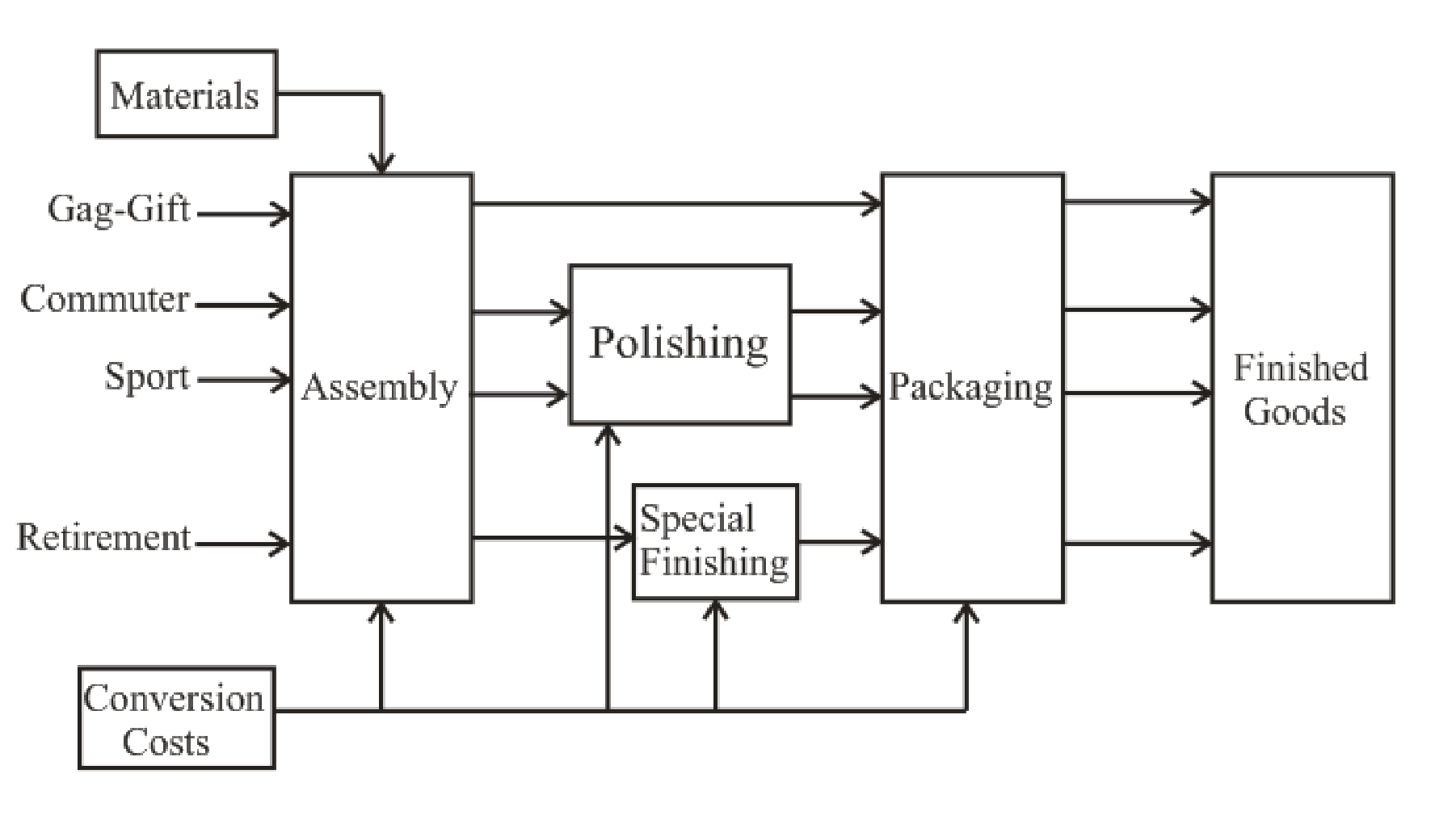
Description of the diagram:
The four products go through the process as drawn above. All the four products go through assembly line. Only the products commuter and sport go for polishing before going through packaging. Product retirement goes through special finishing process and not polishing. The only product that has been packaged straight away from assembly line is Gag-Gift. All the products are then converted into finished goods.
The cost will be different for every product as well. Gag-Gift will include assembly and packaging. Commuter and sport will include assembly, polishing and packaging. Retirement includes cost of assembly, special finishing and packaging.
b.
Determine the cost per unit transferred to finished goods inventory for each of the four watches.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Cost per unit:
Total amount accounted for and total units accounted are considered computation of cost per equivalent unit.
Compute the cost per unit transferred to finished goods inventory for each of the four watches:
| Particulars | Total | Gag-Gift | Commuter | Sport | Retirement |
| Materials | $ 321,000 | $ 15,000 | $ 90,000 | $ 156,000 | $ 60,000 |
| Conversion costs: | |||||
| Assembly | $ 120,000 | $ 20,000(1) | $ 40,000(2) | $ 52,000(3) | $ 8,000(4) |
| Polishing | $ 69,000 | $ 0 | $ 30,000(5) | $ 39,000(6) | $ 0 |
| Special finishing | $ 20,000 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 0 | $ 20,000(7) |
| Packaging | $ 90,000 | $ 15,000(8) | $ 30,000(9) | $ 39,000(10) | $ 6,000(11) |
| Total conversion costs | $ 299,000 | $ 35,000 | $ 100,000 | $ 130,000 | $ 34,000 |
| Total product cost | $ 620,000 | $ 50,000 | $ 190,000 | $ 286,000 | $ 94,000 |
| Number of units | 5,000 | 10,000 | 13,000 | 2,000 | |
| Cost per unit | $ 10.00(12) | $ 19.00(13) | $ 22.00(14) | $ 47.00(15) |
Working note 1:
Compute the conversion costs of assembly for Gag-gift:
Working note 2:
Compute the conversion costs of assembly for Commuter:
Working note 3:
Compute the conversion costs of assembly for Sport:
Working note 4:
Compute the conversion costs of assembly for Retirement:
Working note 5:
Compute the conversion costs of polishing for Commuter:
Working note 6:
Compute the conversion costs of polishing for Sport:
Working note 7:
Compute the conversion costs of special packaging for Retirement:
Working note 8:
Compute the conversion costs of packaging for Gag-gift:
Working note 9:
Compute the conversion costs of packaging for Commuter:
Working note 10:
Compute the conversion costs of packaging for Sport:
Working note 11:
Compute the conversion costs of packaging for Retirement:
Working note 12:
Compute the cost per unit transferred to finished goods for Gag-gift:
Working note 13:
Compute the cost per unit transferred to finished goods for Commuter:
Working note 14:
Compute the cost per unit transferred to finished goods for Gag-gift:
Working note 15:
Compute the cost per unit transferred to finished goods for Gag-gift:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Fundamentals of Cost Accounting
- I need help with this general accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forwardCould you help me solve this financial accounting question using appropriate calculation techniques?arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with accurate accounting calculations?arrow_forward
- Halle Manufacturing has an overhead application rate of 125% and allocates overhead based on direct materials. During the current period, direct labor is $78,000, and direct materials used are $112,000. Determine the amount of overhead Halle Manufacturing should record in the current period. a. $78,000 b. $97,500 c. $112,000 d. $140,000 e. $190,000arrow_forwardPlease explain the correct approach for solving this general accounting question.arrow_forwardBentley industries applied manufacturing overhead on the basis of direct labor hours.arrow_forward
- Solve this question and accountingarrow_forwardDaley Industries wishes to develop a single predetermined overhead rate. The company's expected annual fixed overhead is $420,000, and its variable overhead cost per machine hour is $3.25. The company's relevant range is from 200,000 to 650,000 machine hours. Daley expects to operate at 520,000 machine hours for the coming year. The plant's theoretical capacity is 850,000 machine hours. The predetermined overhead rate per machine hour should be: a. $3.85 b. $4.06 c. $3.75 d. $4.25arrow_forwardAccounting question ?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,




