
Concept explainers
1.
Compute the cost of painting 3,300 square foot house with 14 external openings and 2,400 square foot house with 8 external openings.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Analysis based on square feet:
High point is Home 5 and low point is home 1.
Compute cost equation using square feet as the cost driver.
Variable cost:
Fixed cost:
Total cost is predicted for 3,300 square foot house with 14 openings using equation for square feet.
Calculate total cost.
Total cost is predicted for 2,400 square foot house with 8 openings:
Compute total cost.
2.
Compute the cost of painting 3,300 square foot house with independent variable and 2,400 square foot house with independent variable.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Analysis is based on external openings as the cost driver.
Compute cost equation using square feet as the cost driver.
Compute cost equation using square feet as the cost driver.
Compute total earnings for total cost.
Total cost is predicted for 3,300 square foot house with 14 external openings:
Using equation there should be no prediction until 8 external openings are outside the relevant rage, high-low equations were developed in the range.
3.
Identify the variable that is a better cost driver and give reason.
3.
Explanation of Solution
The graph shown below is the relationship between costs and square feet which is linear and has no significantly outlying points. The same circumstance exists between costs and number of openings. On the whole the home 8 equation is better suitable for the data than the home 9 equation that is removed from the data. As per this view point both variable are good cost drivers.
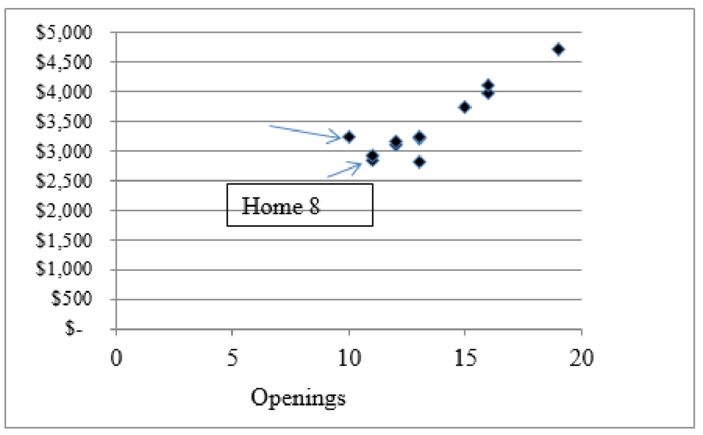
Figure (1)
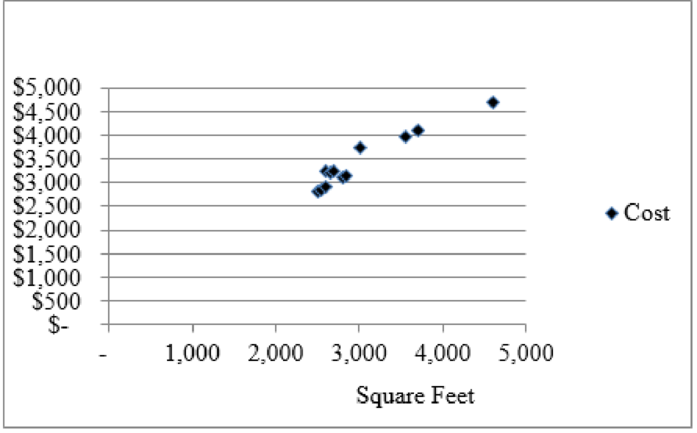
Figure (2)
4.
State the opinion on the statistical reliability and precision of this model.
4.
Explanation of Solution
The t-value and related p-value for independent variable, square feet, are important with p which is less than 0.05. The independent variable, opening is not important with a p-value of 0.3446. Using R-squared of 93% the overall regression is strong and the standard error of the estimate at 171 which is small percentage of the mean of $3,418 the dependent variable.
Summary output:
| Regression Statistics | |
| Multiple R | 0.96439 |
| R square | 0.930048 |
| Adjusted R square | 0.914503 |
| Standard error | 171.1824 |
| Observation | 12 |
Table (1)
| ANOVA | |||||
| Particulars | df | SS | MS | F | Significance F |
| Regression | 2 | 3506442 | 1753221 | 59.8299 | 6.33284E-06 |
| Residual | 9 | 263730.8 | 29303.42 | ||
| Total | 11 | 3770173 | |||
Table (2)
| Particulars | Coefficients | Standard error | t-star | P-value | Lower 95% |
| Intercept | 641.7603 | 270.0336 | 2.376594 | 0.041458 | 30.90182229 |
| X Variable 1 | 0.706915 | 0.200038 | 3.533911 | 0.006375 | 0.254398405 |
| X Variable 2 | 48.34898 | 48.47343 | 0.997433 | 0.344614 | -61.30553286 |
Table (3)
5.
Identify the sustainability issues for this company and list the role of cost estimation in the regard.
5.
Explanation of Solution
There exists a high probability that MC Company may face multiple sustainability issues in future. Since the company activities involve renovation of older homes, they mostly deal with materials that are hazardous in nature. This may include asbestos that may be used decades ago in sliding and other construction materials.
The present construction codes mandate proper treatment of hazardous materials during renovation process. This implies hazardous materials are treated with special care and even if they are expensive.
The treatment and disposal of materials must be performed by adhering to the regulations mentioned under the local, state, and federal authority.
The sustainability issues tend to create delay in the operations of a project due to additional activities to treat the materials during renovation process.
Ensuring the safety and comfort of the homeowners is a primary concern since handling such toxic materials and environmental protection is a prime concern.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
COST MANAGMENT WITH CONNECT ACCESS
- I need help with this general accounting question using standard accounting techniques.arrow_forwardI need guidance in solving this financial accounting problem using standard procedures.arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with appropriate explanations.arrow_forward
- Can you help me solve this general accounting problem using the correct accounting process?arrow_forwardHow can I solve this financial accounting problem using the appropriate financial process?arrow_forwardPlease provide the accurate answer to this general accounting problem using valid techniquesarrow_forward
- I need help with this general accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forwardCan you explain the correct methodology to solve this general accounting problem?arrow_forwardDetermine the amount of the Earned Income Credit in each of the following cases. Assume that the person or persons are eligible to take the credit. Calculate the credit using the formulas. A single person with earned income of $ 7 , 8 5 4 and no qualifying children. A single person with earned income of $ 2 7 , 5 0 0 and two qualifying children. A married couple filing jointly with earned income of $ 3 4 , 1 9 0 and one qualifying child.arrow_forward
- Please help me solve this general accounting question using the right accounting principles.arrow_forwardAssets Martinez Company Comparative Balance Sheets December 31 2025 2024 Cash $91,000 $52,000 Accounts receivable 52,000 36,400 Inventory 72,800 52,000 Property, plant, and equipment 156,000 202,800 Accumulated depreciation Total (83,200) [62,400) $288,600 $290,800 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable $49,400 $ 39,000 Income taxes payable 18,200 20,800 Bonds payable 44,200 85,800 Common stock 46,900 36,400 Retained earnings 130,000 98,800 Total $288,600 $280,800 Martinez Company Income Statement For the Year Ended December 31, 2025 Sales revenue $629,200 Cost of goods sold 455,000 Gross profit 174,200 Selling expenses $46,800 Administrative expenses 15,600 62,400 Income from operations 111,800 Interest expense 7,800 Income before income taxes 104,000 Income tax expense 20,800 Net income $83,200 Additional data: 1. Depreciation expense was $45,500. 2. Dividends declared and paid were $52,000. 3. During the year, equipment was sold for $22,100 cash. This equipment…arrow_forwardagree or disagree with post The Stockholders' Equity section of a corporate balance sheet fundamentally differs from that of a single-owner business due to the inherent structure of a corporation versus a sole proprietorship. In a single-owner business, you'll usually see a single "Owner's Equity" account, which reflects the owner's investment, withdrawals, and accumulated profits or losses. Conversely, a corporation's Stockholders' Equity is more intricate, reflecting the contributions of multiple owners (stockholders) and the legal framework governing corporate capital. It's divided into contributed capital, which includes common and preferred stock, and retained earnings, which represents accumulated profits not yet distributed as dividends. Additionally, corporations may have accounts like "Additional Paid-in Capital" to capture amounts received above the par value of stock, and "Treasury Stock" to account for shares repurchased by the company. This detailed breakdown highlights…arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





