
(a)
Interpretation:
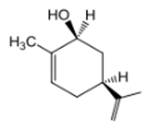
The missing C3H5 and OH substituents needs to be added to the template in order to get one possible chair conformation for each compound.
Concept Introduction:
Chair-like conformation for cyclohexane molecule is a three-dimensional way of representing the molecule. This is a non-planar conformation with all the angles approximately equal to 109.5o. This is stable conformation because it has lower strain energy than the flat hexagonal shape. All the carbon centers are equivalent in the chair conformation. In the flat hexagonal shape, the wedge and dashed bonds represent the group attached directed away and towards the plane of paper respectively. In the chair conformation, these wedge and dashed bonds are axial and equatorial respectively.
(b)
Interpretation:
The most appropriate method from MM2 or MOPAC to determine whether compound 1 or 2 is most stable product in each reaction needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Computational chemistry uses computer simulation to monitor solution of chemical problems. The theoretical chemistry is used in which efficient computer programs are incorporated to determine the structures and properties of molecules.
In the computational chemistry, the MM2 and MOPAC methods are defined as follows:
MM2:
This method is developed mainly for conformational analysis of small organic compounds such as hydrocarbons. This is designed to reproduce the equilibrium covalent geometry of molecules as close as possible.
MOPAC:
This is a computer program used in the computational chemistry for semi-empirical quantum chemistry algorithms. It runs on Mac, Windows and Linux.
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of chair-like conformation for the energy minimization needs to be determined. The alcohol and
Concept Introduction:
Chair-like conformation for cyclohexane molecule is a three-dimensional way of representing the molecule. This is a non-planar conformation with all the angles approximately equal to 109.5o. This is stable conformation because it has lower strain energy than the flat hexagonal shape. All the carbon centers are equivalent in the chair conformation. In the flat hexagonal shape, the wedge and dashed bonds represent the group attached directed away and towards the plane of paper respectively. In the chair conformation, these wedge and dashed bonds are axial and equatorial respectively.
(d)
Interpretation:
The input structure for compound 1 needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Computational chemistry uses computer simulation to monitor solution of chemical problems. The theoretical chemistry is used in which efficient computer programs are incorporated to determine the structures and properties of molecules.
MM2 method is developed mainly for conformational analysis of small organic compounds such as hydrocarbons. This is designed to reproduce the equilibrium covalent geometry of molecules as close as possible.
The compound 1 is given as follows:
The chair conformation is represented as follows:
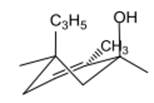
Here, both C3H5 and OH groups are at axial positions.
Thus, the input for compound 1 is represented as follows:
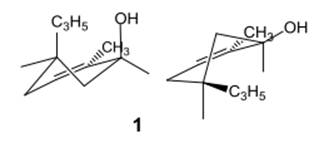
(e)
Interpretation:
The input structure for compound 2 needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Computational chemistry uses computer simulation to monitor solution of chemical problems. The theoretical chemistry is used in which efficient computer programs are incorporated to determine the structures and properties of molecules.
MM2 method is developed mainly for conformational analysis of small organic compounds such as hydrocarbons. This is designed to reproduce the equilibrium covalent geometry of molecules as close as possible.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
LABORATORY TECHNIQUES IN ORGANIC CHEMIS
- If a reaction occurs, what would be the major products? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing showing how the reaction occurs and what the final product is.arrow_forwardWould the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forward(a) Sketch the 'H NMR of the following chemical including the approximate chemical shifts, the multiplicity (splitting) of all signals and the integration (b) How many signals would you expect in the 13C NMR? CH3arrow_forward
- Draw the Show the major and minor product(s) for the following reaction mechanisms for both reactions and show all resonance structures for any Explain why the major product is favoured? intermediates H-Brarrow_forwardChoose the right answerarrow_forward8. What is the major product of the following reaction? KMnO4 b a TOH OH OH C d OH "OH HO OH OHarrow_forward
- Choose the right answerarrow_forward3. Draw ALL THE POSSBILE PRODUCTS AND THE MECHANISMS WITH ALL RESONANCE STRUCTURES. Explain using the resonance structures why the major product(s) are formed over the minor product(s). H₂SO4, HONO CHarrow_forward7. Provide the product(s), starting material(s) and/or condition(s) required for the No mechanisms required. below reaction HO + H-I CI FO Br2, FeBr3 O I-Oarrow_forward
- 6. Design the most efficient synthesis of the following product starting from phenot Provide the reaction conditions for each step (more than one step is required) and explain the selectivity of each reaction. NO MECHANISMS ARE REQUIRED. OH step(s) CIarrow_forwardWhat is the skeletal structure of the product of the following organic reaction?arrow_forwardIf a reaction occurs, what would be the major products? Please include a detailed explanation as well as a drawing showing how the reaction occurs and what the final product is.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

