
2.
To prepare: A table and to allocate the cost.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare table to show allocation of cost:
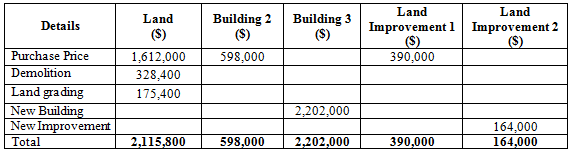
Table (1)
Working Notes:
Computation of total appraised value:
Total appraised value is $2,800,000.
Land
Computation of percentage of land of the total appraised value:
Percentage of land is 62%.
Apportioned cost
Computation of apportioned cost:
Apportioned cost of land is $1,612,000.
Building
Computation of percentage of building of the total appraised value:
Percentage of building is 23%.
Apportioned cost
Apportioned cost of building is $598,000.
Land Improvements 1
Computation of percentage of land improvements 1 of the total appraised value:
Percentage of land improvement 1 is 15%.
Apportioned cost
Computation of apportioned cost:
Apportioned cost of land improvement 1 is $390,000.
2.
To Prepare:
2.
Explanation of Solution
Record the entry for purchase of assets.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Jan1 | Land | 2,115,800 | ||
| Building 2 | 598,000 | |||
| Building 3 | 2,202,000 | |||
| Land improvements 1 | 390,000 | |||
| Land improvements 2 | 164,000 | |||
| Cash | 5,469,800 | |||
| (To record the purchase of assets) |
Table (2)
- Building is an asset account. Building account increases as the new building has been purchased; hence all the assets are debited as they increases in value.
- Land is an asset account. Land account increases as a new land is purchased and all the assets are debited as a new asset is purchased or if its value increases.
- Vehicle account is an asset account. Vehicles account increases as a new vehicle is purchased and all the assets are debited as a new asset is purchased or if its value increases.
- Land improvements are an asset account. Land improvement account increases as some improvements have been done on land to increase its useful life and all the assets are debited as their value increases.
- Cash account is an asset account. Cash account decreases as the amount paid for the purchase of all assets are made in cash and all the assets are credited as their values decreases.
3.
To Prepare:
3.
Explanation of Solution
Building 2
Record
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Depreciation | 26,900 | |||
| | 26,900 | |||
| (To record the depreciation) |
Table (3)
Working Notes:
Computation of depreciation:
Depreciation that will charge to building is $26,900.
Building 3
Record entry for depreciation on building 3
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Depreciation | 72,400 | |||
| Accumulated Depreciation | 72,400 | |||
| (To record the depreciation) |
Table (4)
Working Notes:
Computation of depreciation:
Depreciation that will charge to building 3 is $72,400.
Land improvement 1
To record entry for depreciation on Land improvement 1,
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Depreciation | 32,500 | |||
| Accumulated Depreciation | 32,500 | |||
| (To record the depreciation) |
Table (5)
Working Notes:
Computation of depreciation:
Depreciation charged to improvement 1 $32,500.
Land improvement 2
To record entry for depreciation on Land improvement 2,
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Depreciation | 8,200 | |||
| Accumulated Depreciation | 8,200 | |||
| (To record the depreciation) |
Table (6)
- Depreciation is an expense account. Depreciation account increases the balance of expense account and all the losses and expenses accounts are debited.
- Accumulated Depreciation account is a contra asset account. Accumulated depreciation has a credit balance and is increasing as the depreciation is transferred to this account. This is the reason it is credited.
Working Notes:
Computation of depreciation:
Depreciation that will charge to improvement 2 is $8200.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Loose-Leaf for Financial and Managerial Accounting
- Tragi Manufacturing produces a single product and has a JIT policy that ending inventory must equal 12% of the next month's sales. It estimates that May's ending inventory will consist of 25,000 units. June and July sales are estimated to be 250,000 and 270,000 units, respectively. Tragi assigns variable overhead at a rate of $3.00 per unit of production. Fixed overhead equals $500,000 per month. Compute the number of units to be produced and use this amount to compute the total budgeted overhead that would appear on the factory overhead budget for the month of June. Helparrow_forwardWhat is the per-unit manufacturing cost under variable costing?arrow_forwardWhat is The break-even point in bags?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





