
Depreciation is the amount of decrease in the value of an asset within a set time period due to wear and tear of that particular asset. It helps in readjusting the actual cost of the particular asset o which the depreciation is applied.
Straight Line Depreciation:
Straight line depreciation is one of the methods of depreciation in which fixed rate of depreciation is provided throughout the course of depreciation on a particular asset.
To prepare: A table and to allocate the cost.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare table to show allocation of cost:
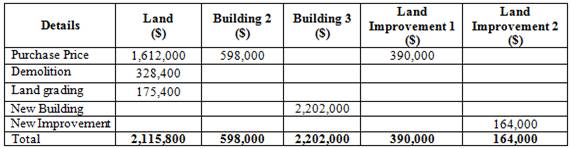
Table (1)
Working Notes:
Computation of total appraised value:
Total appraised value is $2,800,000.
Land
Computation of percentage of land of the total appraised value:
Percentage of land is 62%.
Apportioned cost
Computation of apportioned cost:
Apportioned cost of land is $1,612,000.
Building
Computation of percentage of building of the total appraised value:
Percentage of building is 23%.
Apportioned cost
Apportioned cost of building is $598,000.
Land Improvements 1
Computation of percentage of land improvements 1 of the total appraised value:
Percentage of land improvement 1 is 15%.
Apportioned cost
Computation of apportioned cost:
Apportioned cost of land improvement 1 is $390,000.
2.
To Prepare:
2.
Explanation of Solution
Record the entry for purchase of assets.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan1 | Land | 2,115,800 | ||
| Building 2 | 598,000 | |||
| Building 3 | 2,202,000 | |||
| Land improvements 1 | 390,000 | |||
| Land improvements 2 | 164,000 | |||
| Cash | 5,469,800 | |||
| (To record the purchase of assets) |
Table (2)
- Building is an asset account. Building account increases as the new building has been purchased; hence all the assets are debited as they increases in value.
- Land is an asset account. Land account increases as a new land is purchased and all the assets are debited as a new asset is purchased or if its value increases.
- Vehicle account is an asset account. Vehicles account increases as a new vehicle is purchased and all the assets are debited as a new asset is purchased or if its value increases.
- Land improvements are an asset account. Land improvement account increases as some improvements have been done on land to increase its useful life and all the assets are debited as their value increases.
- Cash account is an asset account. Cash account decreases as the amount paid for the purchase of all assets are made in cash and all the assets are credited as their values decreases.
3.
To Prepare:
3.
Explanation of Solution
Building 2
Record depreciation on building 2.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Depreciation | 26,900 | |||
| | 26,900 | |||
| (To record the depreciation) |
Table (3)
- Depreciation is an expense account. Depreciation account increases the balance of expense account and all the losses and expenses accounts are debited.
- Accumulated Depreciation account is a contra asset account. Accumulated depreciation has a credit balance and is increasing as the depreciation is transferred to this account. This is the reason it is credited.
Working Notes:
Computation of depreciation:
Depreciation that will charge to building is $26,900.
Building 3
Record entry for depreciation on building 3
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Depreciation | 72,400 | |||
| Accumulated Depreciation | 72,400 | |||
| (To record the depreciation) |
Table (4)
- Depreciation is an expense account. Depreciation account increases the balance of expense account and all the losses and expenses accounts are debited.
- Accumulated Depreciation account is a contra asset account. Accumulated depreciation has a credit balance and is increasing as the depreciation is transferred to this account. This is the reason it is credited.
Working Notes:
Computation of depreciation:
Depreciation that will charge to building 3 is $72,400.
Land improvement 1
To record entry for depreciation on Land improvement 1,
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Depreciation | 32,500 | |||
| Accumulated Depreciation | 32,500 | |||
| (To record the depreciation) |
Table (5)
- Depreciation is an expense account. Depreciation account increases the balance of expense account and all the losses and expenses accounts are debited.
- Accumulated Depreciation account is a contra asset account. Accumulated depreciation has a credit balance and is increasing as the depreciation is transferred to this account. This is the reason it is credited.
Working Notes:
Computation of depreciation:
Depreciation charged to improvement 1 $32,500.
Land improvement 2
To record entry for depreciation on Land improvement 2,
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Depreciation | 8,200 | |||
| Accumulated Depreciation | 8,200 | |||
| (To record the depreciation) |
Table (6)
- Depreciation is an expense account. Depreciation account increases the balance of expense account and all the losses and expenses accounts are debited.
- Accumulated Depreciation account is a contra asset account. Accumulated depreciation has a credit balance and is increasing as the depreciation is transferred to this account. This is the reason it is credited.
Working Notes:
Computation of depreciation:
Depreciation that will charge to improvement 2 is $8200.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Gen Combo Ll Financial Accounting Fundamentals; Connect Access Card
- The current sections of Kingbird Inc's balance sheets at December 31, 2024 and 2025, are presented here. Kingbird's net income for 2025 was $107,100. Depreciation expense was $18,900. 2025 2024 Current assets Cash $73,500 $69,300 Accounts receivable 56,000 62,300 Inventory 117,600 120,400 Prepaid expenses 18,900 15,400 Total current assets $266,000 $267,400 Current liabilities Accrued expenses payable $10,500 $3,500 Accounts payable 59,500 64,400 Total current liabilities $70,000 $67,900 Prepare the operating activities section of the company's statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2025, using the indirect method. (Show amounts that decrease cash flow with either a-sign eg.-15,000 or in parenthesis e.g. (15,000).) KINGBIRD INC. Statement of Cash Flows (Partial) - Indirect Method For the Year Ended December 31, 2025 Cash Flows from Operating Activities Net Income Adjustments to reconcile net income to Depreciation Expense 18900 6300 Decrease In Accounts Receivable…arrow_forwardWrong answer will get unhelpful ratearrow_forwardMetlock Lawn Service Company reported a net loss of $15300 for the year ended December 31, 2025. During the year, accounts receivable decreased $25000, inventory increased $20000, accounts payable increased by $30600, and depreciation expense of $26400 was recorded. During 2025, operating activities provided net cash of $77000 O provided net cash of $46700. O used net cash of $46700. ○ used net cash of $9200.arrow_forward
- A company purchased for cash a machine with a list price of $85,000. The machine was shipped FOB shipping point at a cost of $6,500. Installation and test runs of the machine cost $4,500. The recorded acquisition cost of the machine is which amount? Need helparrow_forwardJersey Manufacturing applies manufacturing overhead to its cost objects based on 80% of direct material cost. If Job 22B had $64,000 of manufacturing overhead applied to it during June, what was the amount for direct materials assigned to Job 22B? Answerarrow_forwardNet income is $145,000, accounts payable increased $12,000 during the year, inventory decreased $8,000, and accounts receivable increased $15,000 during the year. Under the indirect method, what is net cash provided by operations?arrow_forward
- Helparrow_forwardThe following data is available for Ivanhoe Corporation at December 31, 2025: Common stock, par $10 (authorized 32500 shares) $292500 Treasury stock (at cost $15 per share) $1110 Based on the data, how many shares of common stock are outstanding? 32500 32426 29250 ○ 29176arrow_forward???arrow_forward
 Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis...FinanceISBN:9781285190907Author:James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark BradshawPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT





